Q06413
Gene name |
MEF2C |
Protein name |
Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2C |
Names |
Myocyte enhancer factor 2C |
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:4208 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
SERUM RESPONSE FACTOR HOMOLOG (PTHR48019) |
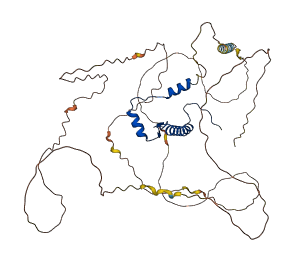
Descriptions
MEF2 factors regulate transcription during cardiac and skeletal myogenesis. Phosphorylation by p38 at Thr 293 and Thr 300 within a linker region, and Ser 387 within transcription repressor domain enhances MEF2C activity allosterically, which implicates potential mechanism of autoinhibition.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-61 (Transcription factor, MADS-box) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Mutagenesis experiment |
Target domain |
1-61 (Transcription factor, MADS-box) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Mutagenesis experiment |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q06413
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q06413-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
213 variants for Q06413
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
RCV000678390 rs1554150607 |
1 | M>I | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
RCV000254756 RCV000192846 rs545185248 |
1 | M>T | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
RCV000223956 CA10575830 rs876661308 |
3 | R>S | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
CA360425322 rs1554150584 RCV000551180 |
7 | Q>H | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
rs1202957297 RCV001592945 CA360425268 RCV000760219 |
15 | R>H | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV000627395 RCV001374908 rs1554150552 |
16 | N>* | Neurodevelopmental disorder [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs1554150543 RCV000509200 RCV000498824 |
17 | R>* | MEF2C-Related Disorder [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs1554139870 CA360425220 RCV000624618 |
20 | T>S | Inborn genetic diseases [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
RCV000191104 rs797045053 CA250375 |
23 | K>R | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
rs869312698 RCV000209864 CA358360 |
24 | R>K | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
RCV000033231 CA130789 rs397514656 |
27 | G>A | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
rs1799677960 RCV001262292 |
37 | V>A | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs397514655 CA360425096 RCV000622665 |
38 | L>P | Inborn genetic diseases [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
RCV000033229 CA130787 rs397514655 |
38 | L>Q | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
RCV000623153 rs1554139771 |
41 | C>* | Inborn genetic diseases [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
CA16043612 rs1057519001 RCV000415447 |
51 | T>I | Epilepsy [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
RCV001253221 rs1554139743 |
59 | S>R | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
RCV000791953 rs1580988138 |
65 | V>missing | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs1580988074 CA360424902 RCV001027718 |
65 | V>G | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
rs1554139723 RCV000718187 RCV000623417 |
72 | Y>missing | History of neurodevelopmental disorder Inborn genetic diseases [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
RCV001861501 RCV000419451 rs755436703 CA3337341 |
103 | A>V | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV000844907 rs1581753788 |
138 | P>missing | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs1581753587 RCV000844906 |
138 | P>missing | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
RCV000698332 rs1366038563 CA360423978 |
147 | I>S | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV000033232 rs730882192 |
153 | N>missing | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs1772953161 RCV001253802 |
178 | Q>* | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
RCV000693696 rs1250885583 CA360423751 |
182 | M>V | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar dbSNP gnomAD |
|
CA172586 COSM1439034 RCV000578993 COSM327913 rs587783747 COSM50878 RCV000146362 |
189 | R>* | large_intestine skin Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 breast [Cosmic, ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen cosmic curated ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
CA360423655 RCV001214620 rs1310323196 |
197 | G>R | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV000576280 rs1554110298 |
205 | T>missing | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
RCV000009503 rs267607233 CA120008 |
228 | S>* | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
COSM1071074 CA315931 rs796052733 COSM1595701 COSM1071073 RCV000754665 |
256 | R>* | endometrium Autism spectrum disorder [Cosmic, ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen cosmic curated ClinVar TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs1561697465 RCV000691890 |
261 | P>missing | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
CA360423169 RCV000719591 rs1561697163 |
267 | M>T | History of neurodevelopmental disorder [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
rs587783749 RCV000146367 RCV000255477 |
277 | L>* | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs777826971 RCV000656084 CA3337223 |
287 | S>L | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar ExAC dbSNP gnomAD |
|
RCV000820312 rs1581338441 |
303 | L>missing | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs796052726 RCV000576225 CA315910 RCV000767165 RCV000188143 |
327 | S>T | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
rs1759964009 RCV001059842 |
330 | L>missing | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs796052727 CA315913 RCV000188144 RCV001515418 |
343 | H>Q | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
CA208800 rs753002290 RCV000725072 RCV002056996 RCV000194560 |
403 | T>A | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
CA360421905 rs1360994640 RCV001332879 |
440 | R>Q | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar dbSNP gnomAD |
|
CA360421876 RCV000535043 rs1554098567 |
444 | H>P | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
CA172583 rs607159 RCV000146361 |
468 | S>F | Intellectual disability, autosomal dominant 20 [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
RCV001257690 rs1227804681 |
474 | T>R | Intellectual disability [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
rs1554150590 RCV000762149 |
5 | K>missing | No |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
|
RCV000659017 rs1554150590 |
5 | K>missing | No |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
|
CA3337404 rs767074467 |
8 | I>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs528434394 CA122618652 |
11 | I>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs965091526 CA122618651 |
12 | M>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA315916 rs796052728 RCV000188145 |
15 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
rs774923789 CA3337402 |
16 | N>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA360425204 RCV001003588 rs1580990072 |
22 | T>R | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
rs1057518382 CA16042532 RCV000414651 |
31 | K>N | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
rs1057520584 RCV000418485 CA16604939 |
34 | E>* | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
COSM738977 rs765658557 COSM1150141 CA360425102 |
37 | V>L | lung [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC gnomAD |
|
CA3337377 rs765658557 |
37 | V>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA315919 VAR_078621 rs796052729 RCV000188146 |
39 | C>R | probable disease-associated variant found in a patient with infantile onset epileptic encephalopathy and autism spectrum disorder [UniProt] | No |
ClinGen ClinVar UniProt Ensembl dbSNP |
|
rs796052732 RCV000188149 |
40 | D>missing | No |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
|
rs1554139771 CA658772656 |
41 | C>* | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA243260 rs794727493 RCV000177153 |
41 | C>R | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
CA360425015 rs1156748158 |
50 | S>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA315922 rs1554139743 |
59 | S>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs199802258 CA122616691 |
64 | K>E | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
RCV001263271 rs1799641525 |
66 | L>V | No |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
|
rs768621677 CA360424844 |
73 | N>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA122616690 rs17852407 |
75 | P>Q | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs577764467 CA3337368 |
77 | E>K | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA360424804 RCV000658068 rs1554139693 |
79 | R>P | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
CA3337367 rs745588042 |
81 | N>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1284065269 CA360424765 |
85 | V>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337344 rs757991225 |
89 | R>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA360424700 rs1388407854 |
93 | L>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337343 rs752200616 |
96 | C>W | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337342 rs779532631 |
101 | P>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA360424604 rs750647048 |
107 | V>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs750647048 CA3337338 |
107 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1267170072 CA360424589 |
109 | H>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs191857330 CA122611832 |
111 | P>S | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
CA360424566 rs1340835191 |
112 | E>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA122611831 rs6898012 |
121 | N>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1039592903 CA122611830 |
129 | S>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA360424438 rs1267463351 |
130 | R>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1267052010 CA360424062 |
135 | A>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1222185162 CA360424057 |
136 | V>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA360424035 rs1206321054 |
139 | P>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA360423987 rs1581753302 |
146 | S>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1366038563 CA360423979 |
147 | I>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA360423967 rs1057349061 |
149 | V>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA122610890 rs1057349061 |
149 | V>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1581752987 CA360423964 |
150 | S>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs937519642 CA122610889 |
151 | S>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA360423950 rs1370166849 |
152 | H>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA122610887 rs927377195 |
155 | L>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA3337285 rs770331071 |
156 | V>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA360423856 rs1269917666 |
166 | N>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA360423845 rs1269161698 |
167 | P>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA360423846 rs1322552264 |
167 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA360423811 rs1266613767 |
173 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337282 rs747344450 |
174 | H>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1554112122 CA315904 |
175 | P>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1057521189 CA16604989 RCV000437126 |
176 | S>Y | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
rs1342956146 CA360423777 |
178 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1561821810 CA360423721 |
186 | V>A | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
COSM282757 COSM282756 rs777918857 CA3337281 |
189 | R>Q | large_intestine [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC gnomAD |
|
RCV000481751 rs1554112069 |
190 | P>missing | No |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
|
rs1302283751 CA360423701 |
190 | P>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1426913388 CA360423636 |
198 | G>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA122610584 rs1029856807 |
198 | G>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA360423632 rs1472815211 |
199 | L>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA360423620 rs1179591536 |
200 | M>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1363110487 CA360423626 |
200 | M>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1425567374 CA360423616 |
201 | G>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1425567374 CA360423614 |
201 | G>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA360423575 rs1460180013 |
208 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs866114394 CA122610582 |
208 | A>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA360423548 rs1404349468 |
212 | A>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA360423547 rs1404349468 |
212 | A>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1039513477 CA122610581 |
212 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1162864526 CA360423432 |
229 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1561698356 CA360423372 RCV000760934 |
237 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
RCV001008970 rs1581392920 |
243 | P>missing | No |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
|
CA3337255 rs763969325 |
243 | P>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs752349182 CA315907 RCV000188142 |
244 | M>V | No |
ClinGen ClinVar ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
|
CA360423317 rs1240688412 |
245 | N>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA360423312 rs1175233907 |
246 | L>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs796052723 CA315895 |
248 | M>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA360423237 rs1399640142 |
257 | V>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA360423227 rs1268731100 |
258 | L>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA360423223 rs1347746132 |
259 | I>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs759108180 CA3337253 |
259 | I>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed |
|
|
rs1278522595 CA360423213 |
261 | P>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs766839744 CA3337251 |
266 | T>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1761753278 RCV001172160 |
267 | M>V | No |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
|
CA360423133 rs1337373823 |
271 | S>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1382265841 CA360423016 |
285 | S>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337224 rs745875924 |
286 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA16618220 RCV000481686 rs777826971 |
287 | S>* | No |
ClinGen ClinVar ExAC dbSNP gnomAD |
|
|
CA360423004 rs1158997480 |
288 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337220 rs778660968 |
293 | T>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337218 rs753559873 |
295 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
CA3337217 rs765881880 |
296 | V>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA360422951 rs765881880 |
296 | V>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1581339047 CA360422945 |
297 | S>F | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA3337215 COSM1159214 rs749895889 COSM218856 COSM218857 |
298 | V>I | pancreas [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC gnomAD |
|
rs749895889 CA360422944 |
298 | V>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs768178049 CA3337214 |
300 | T>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337213 rs762386648 |
302 | T>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1315101427 CA360422901 |
305 | G>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs786200981 RCV000153485 |
310 | G>missing | No |
ClinVar dbSNP |
|
|
rs775791215 CA3337209 |
313 | S>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
RCV000486123 rs1064796969 CA16618219 |
314 | A>G | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
CA3337203 rs748106924 |
330 | L>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA122608613 rs200887424 |
332 | S>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs778783316 CA3337202 |
339 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs797045703 RCV000193723 CA207404 |
341 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ClinVar dbSNP gnomAD |
|
|
rs980341351 CA122608611 |
344 | L>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs748980354 CA3337200 |
346 | S>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1431233073 CA360422612 |
349 | G>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1490177097 CA360422563 |
355 | L>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1197579572 CA360422539 |
358 | M>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs17852408 CA122608609 |
359 | P>Q | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1355343472 CA360422536 |
359 | P>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1481007836 CA360422517 |
362 | A>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA360422493 rs1581321362 COSM3393700 RCV001002553 COSM3393702 COSM3393701 COSM3393699 |
365 | Q>H | pancreas [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
CA360422424 rs1487982052 |
374 | L>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA360422398 rs1194276851 |
377 | S>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1462857323 CA360422395 |
378 | S>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337193 rs764636524 |
379 | N>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1321876412 CA360422346 |
386 | Q>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1191561734 CA360422336 |
387 | S>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1064797057 RCV000479668 CA16618217 |
401 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ClinVar dbSNP gnomAD |
|
|
rs1064797057 CA360422221 |
401 | R>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1305718026 CA360422185 |
405 | P>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337191 rs765537349 |
406 | S>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs776785470 CA3337189 |
410 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337188 rs771034207 COSM240642 |
412 | T>M | prostate [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
CA360422104 rs1403721275 |
414 | H>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1172286190 CA360422109 |
414 | H>Y | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs545693893 CA3337187 |
415 | E>K | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337185 rs768570497 |
416 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs749145830 CA3337184 |
417 | G>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs779688828 CA3337183 |
424 | L>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs780925017 CA3337180 |
431 | Y>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA360421949 rs1345666452 |
434 | S>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs778488653 CA122608079 |
436 | R>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1259504949 CA360421917 |
438 | D>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1237249484 CA360421913 |
439 | H>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337175 rs753156153 |
447 | I>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1320099771 CA360421850 |
448 | G>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1351393780 CA360421845 |
449 | L>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA3337174 rs765543733 |
451 | R>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
CA360421828 rs1382590951 |
452 | P>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337173 rs201684050 |
454 | P>A | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337172 rs186353882 |
455 | D>E | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA360421811 rs1581204990 |
455 | D>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA315935 rs796052734 |
455 | D>H | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA122608076 rs796052734 |
455 | D>N | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1385998887 CA360421801 |
456 | E>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1163142825 CA360421795 |
457 | R>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
RCV000600963 CA360421783 rs1554098520 |
459 | S>G | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
rs1581204463 CA360421771 |
460 | P>L | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA360421760 rs1194300256 |
462 | V>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337170 rs760804914 |
465 | M>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA3337171 rs766533792 |
465 | M>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs766533792 CA360421744 |
465 | M>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1490696028 CA360421728 |
467 | L>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1244759936 CA360421725 |
468 | S>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1244759936 CA360421726 |
468 | S>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs17856763 CA122608074 |
470 | G>* | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1561641773 RCV000762148 CA360421696 |
472 | A>E | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
|
rs1271598402 CA360421691 |
473 | T>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1227804681 CA360421686 |
474 | T>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
3 associated diseases with Q06413
[MIM: 604187]: Spastic paraplegia 10, autosomal dominant (SPG10)
A form of spastic paraplegia, a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs. Rate of progression and the severity of symptoms are quite variable. Initial symptoms may include difficulty with balance, weakness and stiffness in the legs, muscle spasms, and dragging the toes when walking. In some forms of the disorder, bladder symptoms (such as incontinence) may appear, or the weakness and stiffness may spread to other parts of the body. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 617235]: Myoclonus, intractable, neonatal (NEIMY)
An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder characterized by severe, infantile-onset myoclonic seizures, hypotonia, optic nerve abnormalities, dysphagia, apnea, and early developmental arrest. Brain imaging shows a progressive leukoencephalopathy. Some patients may die in infancy. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 617921]: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 25 (ALS25)
A form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a neurodegenerative disorder affecting upper motor neurons in the brain and lower motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord, resulting in fatal paralysis. Sensory abnormalities are absent. The pathologic hallmarks of the disease include pallor of the corticospinal tract due to loss of motor neurons, presence of ubiquitin-positive inclusions within surviving motor neurons, and deposition of pathologic aggregates. The etiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is likely to be multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. The disease is inherited in 5-10% of the cases. ALS25 is an autosomal dominant form with variable adult onset and incomplete penetrance. . Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. The mutation NM_004984.2:c.33019A>G encoding the predicted missence variant p.Arg1007Gly, may also affect splicing and induce the skipping of exon 27, resulting in a frameshift and a premature stop codon producing a truncated protein p.Asn999Valfs*39. .
Without disease ID
- A form of spastic paraplegia, a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs. Rate of progression and the severity of symptoms are quite variable. Initial symptoms may include difficulty with balance, weakness and stiffness in the legs, muscle spasms, and dragging the toes when walking. In some forms of the disorder, bladder symptoms (such as incontinence) may appear, or the weakness and stiffness may spread to other parts of the body. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder characterized by severe, infantile-onset myoclonic seizures, hypotonia, optic nerve abnormalities, dysphagia, apnea, and early developmental arrest. Brain imaging shows a progressive leukoencephalopathy. Some patients may die in infancy. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- A form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a neurodegenerative disorder affecting upper motor neurons in the brain and lower motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord, resulting in fatal paralysis. Sensory abnormalities are absent. The pathologic hallmarks of the disease include pallor of the corticospinal tract due to loss of motor neurons, presence of ubiquitin-positive inclusions within surviving motor neurons, and deposition of pathologic aggregates. The etiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is likely to be multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. The disease is inherited in 5-10% of the cases. ALS25 is an autosomal dominant form with variable adult onset and incomplete penetrance. . Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. The mutation NM_004984.2:c.33019A>G encoding the predicted missence variant p.Arg1007Gly, may also affect splicing and induce the skipping of exon 27, resulting in a frameshift and a premature stop codon producing a truncated protein p.Asn999Valfs*39. .
No regional properties for Q06413
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for Q06413 | |||
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR48019 | SERUM RESPONSE FACTOR HOMOLOG |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR48019:SF109 | MYOCYTE-SPECIFIC ENHANCER FACTOR 2A |
| PANTHER Protein Class | MADS box transcription factor | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category |
p38 MAPK pathway MEF Oxidative stress response MEF-2 |
|
10 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromatin | The ordered and organized complex of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that forms the chromosome. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| intracellular membrane-bounded organelle | Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane. |
| nuclear speck | A discrete extra-nucleolar subnuclear domain, 20-50 in number, in which splicing factors are seen to be localized by immunofluorescence microscopy. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| postsynapse | The part of a synapse that is part of the post-synaptic cell. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
| sarcoplasm | The cytoplasm of a muscle cell; includes the sarcoplasmic reticulum. |
13 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that activates or increases transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity | A transcription regulator activity that modulates transcription of gene sets via selective and non-covalent binding to a specific double-stranded genomic DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within a cis-regulatory region. Regulatory regions include promoters (proximal and distal) and enhancers. Genes are transcriptional units, and include bacterial operons. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a DNA-binding transcription factor, a protein that interacts with a specific DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within the regulatory region of a gene to modulate transcription. |
| histone deacetylase binding | Binding to histone deacetylase. |
| minor groove of adenine-thymine-rich DNA binding | Binding to a DNA structure formed by the minor groove of adenine-thymine-rich DNA regions. Examples of proteins having this function are AT-rich interaction domain (ARID)-containing proteins. |
| protein heterodimerization activity | Binding to a nonidentical protein to form a heterodimer. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific sequence of DNA that is part of a regulatory region that controls the transcription of a gene or cistron by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a sequence-specific DNA binding RNA polymerase II transcription factor, any of the factors that interact selectively and non-covalently with a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. |
| sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA, e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
| transcription cis-regulatory region binding | Binding to a specific sequence of DNA that is part of a regulatory region that controls transcription of that section of the DNA. The transcribed region might be described as a gene, cistron, or operon. |
85 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| B cell homeostasis | The process of regulating the proliferation and elimination of B cells such that the total number of B cells within a whole or part of an organism is stable over time in the absence of an outside stimulus. |
| B cell proliferation | The expansion of a B cell population by cell division. Follows B cell activation. |
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a B cell. |
| blood vessel development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a blood vessel over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood. |
| blood vessel remodeling | The reorganization or renovation of existing blood vessels. |
| cardiac ventricle formation | The developmental process pertaining to the initial formation of a cardiac ventricle from unspecified parts. A cardiac ventricle receives blood from a cardiac atrium and pumps it out of the heart. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation | The process in which the structures of a neuron are generated and organized. This process occurs while the initially relatively unspecialized cell is acquiring the specialized features of a neuron. |
| cellular response to calcium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a calcium ion stimulus. |
| cellular response to fluid shear stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a fluid shear stress stimulus. Fluid shear stress is the force acting on an object in a system where the fluid is moving across a solid surface. |
| cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| cellular response to parathyroid hormone stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a parathyroid hormone stimulus. |
| cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a transforming growth factor beta stimulus. |
| cellular response to trichostatin A | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a trichostatin A stimulus. |
| cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organism exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| chondrocyte differentiation | The process in which a chondroblast acquires specialized structural and/or functional features of a chondrocyte. A chondrocyte is a polymorphic cell that forms cartilage. |
| endochondral ossification | Replacement ossification wherein bone tissue replaces cartilage. |
| epithelial cell proliferation involved in renal tubule morphogenesis | Any epithelial cell proliferation that is involved in renal tubule morphogenesis. |
| excitatory postsynaptic potential | A process that leads to a temporary increase in postsynaptic potential due to the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell. The flow of ions that causes an EPSP is an excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) and makes it easier for the neuron to fire an action potential. |
| germinal center formation | The process in which germinal centers form. A germinal center is a specialized microenvironment formed when activated B cells enter lymphoid follicles. Germinal centers are the foci for B cell proliferation and somatic hypermutation. |
| glomerulus morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the glomerulus are generated and organized. The glomerulus is a capillary tuft surrounded by Bowman's capsule in nephrons of the vertebrate kidney. |
| heart development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. |
| heart looping | The tube morphogenesis process in which the primitive heart tube loops asymmetrically. This looping brings the primitive heart chambers into alignment preceding their future integration. Heart looping begins with dextral-looping and ends when the main regional divisions of the mature heart and primordium of the great arterial trunks become established preceeding septation. |
| humoral immune response | An immune response mediated through a body fluid. |
| learning or memory | The acquisition and processing of information and/or the storage and retrieval of this information over time. |
| MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tiers: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| melanocyte differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a melanocyte. |
| muscle cell fate determination | The cell fate determination process in which a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into a muscle cell regardless of its environment; upon determination, the cell fate cannot be reversed. |
| muscle organ development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The muscle is an organ consisting of a tissue made up of various elongated cells that are specialized to contract and thus to produce movement and mechanical work. |
| myotube differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a myotube cell. Myotube differentiation starts with myoblast fusion and the appearance of specific cell markers (this is the cell development step). Then individual myotubes can fuse to form bigger myotubes and start to contract. Myotubes are multinucleated cells that are formed when proliferating myoblasts exit the cell cycle, differentiate and fuse. |
| negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the migration of the endothelial cells of blood vessels. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process in neurons. |
| negative regulation of ossification | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of ossification, the formation of bone or of a bony substance or the conversion of fibrous tissue or of cartilage into bone or a bony substance. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration. |
| negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of vascular endothelial cell proliferation. |
| nephron tubule epithelial cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells of the nephron tubule as it progresses from its formation to the mature state. |
| nervous system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state. |
| neural crest cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neural crest cell. |
| neuron development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell. |
| neuron differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron. |
| neuron migration | The characteristic movement of an immature neuron from germinal zones to specific positions where they will reside as they mature. |
| osteoblast differentiation | The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an osteoblast, a mesodermal or neural crest cell that gives rise to bone. |
| outflow tract morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the outflow tract are generated and organized. The outflow tract is the portion of the heart through which blood flows into the arteries. |
| platelet formation | The process in which platelets bud from long processes extended by megakaryocytes. |
| positive regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of alkaline phosphatase activity, the catalysis of the reaction: an orthophosphoric monoester + H2O = an alcohol + phosphate, with an alkaline pH optimum. |
| positive regulation of B cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of B cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of behavioral fear response | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of behavioral fear response. |
| positive regulation of bone mineralization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of bone mineralization. |
| positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cardiac muscle cell differentiation. |
| positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cardiac muscle cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of macrophage apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of MAP kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of myoblast differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of myoblast differentiation. A myoblast is a mononucleate cell type that, by fusion with other myoblasts, gives rise to the myotubes that eventually develop into skeletal muscle fibers. |
| positive regulation of neuron differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation. |
| positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast differentiation. |
| positive regulation of skeletal muscle cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of skeletal muscle cell differentiation. |
| positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of skeletal muscle tissue development. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| primary heart field specification | The process that results in the delineation of a specific region of the lateral mesoderm into the area which will form the primary beating heart tube. In mammals the primary heart field gives rise to the left ventricle. |
| regulation of AMPA receptor activity | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of AMPA selective glutamate receptor activity. |
| regulation of dendritic spine development | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of dendritic spine development, the process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendritic spine over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| regulation of germinal center formation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of germinal center formation. |
| regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of megakaryocyte differentiation. |
| regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that modulates the occurrence or rate of cell death by apoptotic process in neurons. |
| regulation of neurotransmitter secretion | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a neurotransmitter from a cell. |
| regulation of NMDA receptor activity | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of N-methyl-D-aspartate selective glutamate receptor activity. |
| regulation of synapse assembly | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of synapse assembly, the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a synapse. |
| regulation of synaptic activity | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of synaptic activity, the controlled release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft and their subsequent detection by a postsynaptic cell. |
| regulation of synaptic plasticity | A process that modulates synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to change as circumstances require. They may alter function, such as increasing or decreasing their sensitivity, or they may increase or decrease in actual numbers. |
| regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of glutamatergic synaptic transmission, the process of communication from a neuron to another neuron across a synapse using the neurotransmitter glutamate. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| renal tubule morphogenesis | The process in which the renal tubule is generated by specification of cell fate, through the maintenance of cell polarity, regulated cell proliferation and morphogenetic cell rearrangements, shape changes and growth. A renal tubule is a tube that filters, re-absorbs and secretes substances to rid an organism of waste and to play a role in fluid homeostasis. |
| response to ischemia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a inadequate blood supply. |
| secondary heart field specification | The process that results in the delineation of a specific region of the lateral mesoderm into the area which will form the majority of the mesodermal component of the right ventricle, arterial pole (outflow tract) and venous pole (inflow tract). |
| sinoatrial valve morphogenesis | The process in which the structure of the sinoatrial valve is generated and organized. |
| skeletal muscle tissue development | The developmental sequence of events leading to the formation of adult skeletal muscle tissue. The main events are: the fusion of myoblasts to form myotubes that increase in size by further fusion to them of myoblasts, the formation of myofibrils within their cytoplasm and the establishment of functional neuromuscular junctions with motor neurons. At this stage they can be regarded as mature muscle fibers. |
| smooth muscle cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a smooth muscle cell; smooth muscle lacks transverse striations in its constituent fibers and are almost always involuntary. |
| ventricular cardiac muscle cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a ventricular cardiac muscle cell. Cardiac muscle cells are striated muscle cells that are responsible for heart contraction. The ventricle is the part of the heart that pumps blood out of the organ. |
17 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A2VDZ3 | MEF2A | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q9W6U8 | MEF2A | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q02078 | MEF2A | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q60929 | Mef2a | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8CFN5 | Mef2c | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| A2ICN5 | MEF2A | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| A4UTP7 | MEF2C | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2C | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q2MJT0 | Mef2a | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| A0A096MJY4 | Mef2c | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2C | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q40702 | MADS2 | MADS-box transcription factor 2 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q5K4R0 | MADS47 | MADS-box transcription factor 47 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q655V4 | MADS30 | MADS-box transcription factor 30 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| P35632 | AP3 | Floral homeotic protein APETALA 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P29383 | AGL3 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q683D7 | MAF5 | Protein MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q1PFA4 | AGL30 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL30 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FUY6 | J | MADS-box protein JOINTLESS | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGRKKIQITR | IMDERNRQVT | FTKRKFGLMK | KAYELSVLCD | CEIALIIFNS | TNKLFQYAST |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| DMDKVLLKYT | EYNEPHESRT | NSDIVETLRK | KGLNGCDSPD | PDADDSVGHS | PESEDKYRKI |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| NEDIDLMISR | QRLCAVPPPN | FEMPVSIPVS | SHNSLVYSNP | VSSLGNPNLL | PLAHPSLQRN |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SMSPGVTHRP | PSAGNTGGLM | GGDLTSGAGT | SAGNGYGNPR | NSPGLLVSPG | NLNKNMQAKS |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| PPPMNLGMNN | RKPDLRVLIP | PGSKNTMPSV | SEDVDLLLNQ | RINNSQSAQS | LATPVVSVAT |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| PTLPGQGMGG | YPSAISTTYG | TEYSLSSADL | SSLSGFNTAS | ALHLGSVTGW | QQQHLHNMPP |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| SALSQLGACT | STHLSQSSNL | SLPSTQSLNI | KSEPVSPPRD | RTTTPSRYPQ | HTRHEAGRSP |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | |
| VDSLSSCSSS | YDGSDREDHR | NEFHSPIGLT | RPSPDERESP | SVKRMRLSEG | WAT |