Q06180
Gene name |
Ptpn2 (Ptpt) |
Protein name |
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 2 |
Names |
Protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTP-2 , EC 3.1.3.48 , MPTP |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:19255 |
EC number |
3.1.3.48: Phosphoric monoester hydrolases |
Protein Class |
|
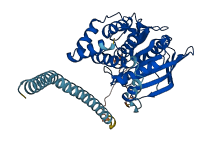
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-288 (Catalytic domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Cleavage |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Hao L et al. (1997) "The noncatalytic C-terminal segment of the T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase regulates activity via an intramolecular mechanism", The Journal of biological chemistry, 272, 29322-9
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q06180
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q06180-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
14 variants for Q06180
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3389509572 | 64 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3408675149 | 98 | W>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3408874915 | 99 | L>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3389502198 | 118 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389524424 | 128 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389506018 | 184 | G>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3389509061 | 184 | G>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3389518027 | 195 | F>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389475884 | 249 | L>M | No | EVA | |
| rs257328356 | 310 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs241484278 | 326 | T>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3408675150 | 328 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3389512640 | 330 | S>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3402645598 | 371 | E>D | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q06180
5 regional properties for Q06180
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | CRIB domain | 202 - 260 | IPR000095 |
| domain | WH1/EVH1 domain | 32 - 141 | IPR000697 |
| domain | WH2 domain | 402 - 427 | IPR003124-1 |
| domain | WH2 domain | 431 - 454 | IPR003124-2 |
| domain | WASP family, EVH1 domain | 40 - 138 | IPR033927 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.1.3.48 | Phosphoric monoester hydrolases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment | A complex system of membrane-bounded compartments located between endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the Golgi complex, with a distinctive membrane protein composition; involved in ER-to-Golgi and Golgi-to-ER transport. |
| endosome lumen | The volume enclosed by the membrane of an endosome. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| integrin binding | Binding to an integrin. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine phosphatase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein tyrosine phosphatase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| receptor tyrosine kinase binding | Binding to a receptor that possesses protein tyrosine kinase activity. |
| STAT family protein binding | Binding to a member of the signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) protein family. STATs are, as the name indicates, both signal transducers and transcription factors. STATs are activated by cytokines and some growth factors and thus control important biological processes including cell growth, cell differentiation, apoptosis and immune responses. |
| syntaxin binding | Binding to a syntaxin, a SNAP receptor involved in the docking of synaptic vesicles at the presynaptic zone of a synapse. |
33 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| B cell differentiation | The process in which a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a B cell. A B cell is a lymphocyte of B lineage with the phenotype CD19-positive and capable of B cell mediated immunity. |
| erythrocyte differentiation | The process in which a myeloid precursor cell acquires specializes features of an erythrocyte. |
| glucose homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of glucose within an organism or cell. |
| insulin receptor recycling | The process that results in the return of an insulin receptor to an active state at the plasma membrane. An active state is when the receptor is ready to receive an insulin signal. Internalized insulin receptors can be recycled to the plasma membrane or sorted to lysosomes for protein degradation. |
| insulin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of the insulin receptor binding to insulin. |
| negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of chemotaxis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient. |
| negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway activity. |
| negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| negative regulation of inflammatory response | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response. |
| negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of insulin receptor signaling. |
| negative regulation of interleukin-2-mediated signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of interleukin-2-mediated signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of interleukin-4-mediated signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of interleukin-4-mediated signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of interleukin-6-mediated signaling pathway | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of an interleukin-6-mediated signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of lipid storage | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of lipid storage. Lipid storage is the accumulation and maintenance in cells or tissues of lipids, compounds soluble in organic solvents but insoluble or sparingly soluble in aqueous solvents. Lipid reserves can be accumulated during early developmental stages for mobilization and utilization at later stages of development. |
| negative regulation of macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of macrophage differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage differentiation. |
| negative regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of positive thymic T cell selection | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of positive thymic T cell selection. |
| negative regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of protein tyrosine kinase activity. |
| negative regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT. |
| negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of signaling pathways initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a T cell. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway | Any process that decreases the rate or extent of the tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway. The tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway is the series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of tumor necrosis factor binding to a cell surface receptor. |
| negative regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of a type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of an interferon-gamma-mediated signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the introduction of a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue of a STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) protein. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation | The removal of phosphoric residues from peptidyl-O-phospho-tyrosine to form peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of gluconeogenesis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of gluconeogenesis. |
| positive regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the PERK-mediated unfolded protein response. |
| regulation of hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway. |
| T cell differentiation | The process in which a precursor cell type acquires characteristics of a more mature T-cell. A T cell is a type of lymphocyte whose definin characteristic is the expression of a T cell receptor complex. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P18031 | PTPN1 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P17706 | PTPN2 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35821 | Ptpn1 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P20417 | Ptpn1 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| A1L1L3 | Ptpn20 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 20 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P35233 | Ptpn2 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSATIEREFE | ELDAQCRWQP | LYLEIRNESH | DYPHRVAKFP | ENRNRNRYRD | VSPYDHSRVK |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LQSTENDYIN | ASLVDIEEAQ | RSYILTQGPL | PNTCCHFWLM | VWQQKTKAVV | MLNRTVEKES |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VKCAQYWPTD | DREMVFKETG | FSVKLLSEDV | KSYYTVHLLQ | LENINTGETR | TISHFHYTTW |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| PDFGVPESPA | SFLNFLFKVR | ESGCLTPDHG | PAVIHCSAGI | GRSGTFSLVD | TCLVLMEKGE |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| DVNVKQLLLN | MRKYRMGLIQ | TPDQLRFSYM | AIIEGAKYTK | GDSNIQKRWK | ELSKEDLSPI |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| CDHSQNRVMV | EKYNGKRIGS | EDEKLTGLPS | KVQDTVEESS | ESILRKRIRE | DRKATTAQKV |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | ||
| QQMKQRLNET | ERKRKRWLYW | QPILTKMGFV | SVILVGALVG | WTLLFH |