Q05688
Gene name |
IGF1R |
Protein name |
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor |
Names |
EC 2.7.10.1 , Insulin-like growth factor I receptor , IGF-I receptor , CD antigen CD221 [Cleaved into: Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor alpha chain; Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor beta chain] |
Species |
Bos taurus (Bovine) |
KEGG Pathway |
bta:281848 |
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
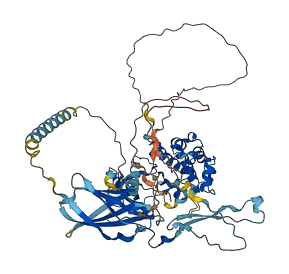
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
272-547 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
425-450 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
272-547 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
425-450 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
272-547 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Craddock BP et al. (2007) "Autoinhibition of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor by the juxtamembrane region", FEBS letters, 581, 3235-40
- Uchikawa E et al. (2019) "Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex", eLife, 8,
- Nielsen J et al. (2022) "Structural Investigations of Full-Length Insulin Receptor Dynamics and Signalling", Journal of molecular biology, 434, 167458
- Chen YS et al. (2021) "Insertion of a synthetic switch into insulin provides metabolite-dependent regulation of hormone-receptor activation", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 118,
- Huang X et al. (2009) "Structural insights into the inhibited states of the Mer receptor tyrosine kinase", Journal of structural biology, 165, 88-96
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q05688
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q05688-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q05688
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q05688 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q05688
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| insulin receptor complex | A disulfide-bonded, heterotetrameric receptor complex. The alpha chains are entirely extracellular, while each beta chain has one transmembrane domain. The ligand binds to the alpha subunit extracellular domain and the kinase is associated with the beta subunit intracellular domain. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| insulin receptor activity | Combining with insulin receptor ligand and transmitting the signal across the plasma membrane to initiate a change in cell activity. |
| insulin receptor substrate binding | Binding to an insulin receptor substrate (IRS) protein, an adaptor protein that bind to the transphosphorylated insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors, are themselves phosphorylated and in turn recruit SH2 domain-containing signaling molecules to form a productive signaling complex. |
| insulin-like growth factor binding | Binding to an insulin-like growth factor, any member of a group of polypeptides that are structurally homologous to insulin and share many of its biological activities, but are immunologically distinct from it. |
| insulin-like growth factor receptor activity | Combining with insulin-like growth factor receptor ligand and transmitting the signal across the plasma membrane to initiate a change in cell activity. |
| phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding | Binding to a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the addition of a phosphate group to an inositol lipid at the 3' position of the inositol ring. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| structural molecule activity | The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a complex. |
8 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to glucose stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucose stimulus. |
| insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to an insulin-like growth factor receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPKKK cascade. |
| positive regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPK cascade. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase B signaling, a series of reactions mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| regulation of JNK cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the JNK cascade. |
17 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q769I5 | MET | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q06807 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q06805 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P43481 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P09208 | InR | Insulin-like receptor | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P06213 | INSR | Insulin receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P14616 | INSRR | Insulin receptor-related protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P08069 | IGF1R | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9WTL4 | Insrr | Insulin receptor-related protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15208 | Insr | Insulin receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60751 | Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q64716 | Insrr | Insulin receptor-related protein | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P15127 | Insr | Insulin receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P24062 | Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q94C25 | At5g20050 | Probable receptor-like protein kinase At5g20050 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FG33 | LECRKS5 | Probable L-type lectin-domain containing receptor kinase S.5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9STF0 | LECRKS3 | Receptor like protein kinase S.3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| NAIFVPRPER | KRREVMQIAN | TTMSSRSRNT | TVLDTYNITD | PEELETEYPF | FESRVDNKER |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| TVISNLRPFT | LYRIDIHSCN | HEAEKLGCSA | SNFVFARTMP | AEGADDIPGP | VTWEPRPENS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| IFLKWPEPEN | PNGLILMYEI | KYGSQVEDQR | ECVSRQEYRK | YGGAKLNRLN | PGNYTARIQA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TSLSGNGSWT | DPVFFYVQAK | TTYENFIHLM | IALPIAVLLI | VGGLVIMLYV | FHRKRNSSRL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| GNGVLYASVN | PEYFSAADVY | VPDEWEVARE | KITMSRELGQ | GSFGMVYEGV | AKGVVKDEPE |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TRVAIKTVNE | AASMRERIEF | LNEASVMKEF | NCHHVVRLLG | VVSQGQPTLV | IMELMTRGDL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KSYLRSLRPE | MENNPVLAPP | SLSKMIQMAG | EIADGMAYLN | ANKFVHRDLA | ARNCMVAEDF |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| TVKIGDFGMT | RDIYETDYYR | KGGKGLLPVR | WMSPESLKDG | VFTTHSDVWS | FGVVLWEIAT |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| LAEQPYQGLS | NEQVLRFVME | GGLLDKPDNC | PDMLFELMRM | CWQYNPKMRP | SFLEIISSVK |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| DEMEAGFREV | SFYYSEENKP | PEPEELDLEP | ENMESVPLDP | SASSASLPLP | DRHSGHKAEN |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | |||
| GPGPGVLVLR | ASFDERQPYA | HMNGGRKNER | ALPLPQSSTC |