Q05512
Gene name |
Mark2 (Emk) |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase MARK2 |
Names |
EC 2.7.11.1 , EC 2.7.11.26 , ELKL motif kinase 1 , EMK-1 , MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 2 , PAR1 homolog , PAR1 homolog b , Par-1b , mPar-1b |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:13728 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
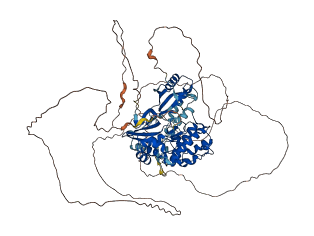
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
53-304 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Others |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
192-214 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
53-304 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
192-214 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
53-304 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q05512
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q05512-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q05512
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q05512 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q05512
6 regional properties for Q05512
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 53 - 304 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Kinase associated domain 1 (KA1) | 727 - 776 | IPR001772 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 171 - 183 | IPR008271 |
| domain | Ubiquitin-associated domain | 323 - 362 | IPR015940 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 59 - 82 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Serine/threonine-protein kinase MARK 1-4, catalytic domain | 52 - 304 | IPR049508 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
11 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament | A filamentous structure formed of a two-stranded helical polymer of the protein actin and associated proteins. Actin filaments are a major component of the contractile apparatus of skeletal muscle and the microfilaments of the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. The filaments, comprising polymerized globular actin molecules, appear as flexible structures with a diameter of 5-9 nm. They are organized into a variety of linear bundles, two-dimensional networks, and three dimensional gels. In the cytoskeleton they are most highly concentrated in the cortex of the cell just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| basal cortex | The region that lies just beneath the plasma membrane on the basal edge of a cell. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| lateral plasma membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane at the lateral side of the cell. In epithelial cells, lateral plasma membranes are on the sides of cells which lie at the interface of adjacent cells. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it and attached to it. |
| microtubule bundle | An arrangement of closely apposed microtubules running parallel to each other. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynapse | The part of a synapse that is part of the post-synaptic cell. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| lipid binding | Binding to a lipid. |
| magnesium ion binding | Binding to a magnesium (Mg) ion. |
| molecular function activator activity | A molecular function regulator that activates or increases the activity of its target via non-covalent binding that does not result in covalent modification to the target. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
| tau protein binding | Binding to tau protein. tau is a microtubule-associated protein, implicated in Alzheimer's disease, Down Syndrome and ALS. |
| tau-protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
15 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon development | The progression of an axon over time. Covers axonogenesis (de novo generation of an axon) and axon regeneration (regrowth), as well as processes pertaining to the progression of the axon over time (fasciculation and defasciculation). |
| establishment of cell polarity | The specification and formation of anisotropic intracellular organization or cell growth patterns. |
| establishment or maintenance of cell polarity regulating cell shape | Any cellular process that results in the specification, formation or maintenance of a polarized intracellular organization or cell growth patterns that regulate the shape of a cell. |
| establishment or maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity | Any cellular process that results in the specification, formation or maintenance of the apicobasal polarity of an epithelial cell. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| microtubule cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins. |
| neuron migration | The characteristic movement of an immature neuron from germinal zones to specific positions where they will reside as they mature. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of axonogenesis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis, the generation of an axon, the long process of a neuron. |
| regulation of cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures. |
| regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of postsynapse organization | Any process that modulates the physical form of a postsynapse. |
| Wnt signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell and ending with a change in cell state. |
20 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q96L34 | MARK4 | MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P57059 | SIK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SIK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P27448 | MARK3 | MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9P0L2 | MARK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase MARK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q7KZI7 | MARK2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase MARK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q8C0N0 | Gm4922 | Sperm motility kinase Z | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8C0X8 | Sperm motility kinase X | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR | |
| A0AUV4 | Gm7168 | Sperm motility kinase Y | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VBY2 | Camkk1 | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8CIP4 | Mark4 | MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8VHJ5 | Mark1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase MARK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8CEE6 | Pask | PAS domain-containing serine/threonine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03141 | Mark3 | MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O08678 | Mark1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase MARK1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q8VHF0 | Mark3 | MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08679 | Mark2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase MARK2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q852Q1 | OSK4 | Serine/threonine protein kinase OSK4 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q852Q2 | OSK1 | Serine/threonine protein kinase OSK1 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q852Q0 | OSK3 | Serine/threonine protein kinase OSK3 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q9TW45 | par-1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase par-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSSARTPLPT | LNERDTEQPT | LGHLDSKPSS | KSNMLRGRNS | ATSADEQPHI | GNYRLLKTIG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| KGNFAKVKLA | RHILTGKEVA | VKIIDKTQLN | SSSLQKLFRE | VRIMKVLNHP | NIVKLFEVIE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| TEKTLYLVME | YASGGEVFDY | LVAHGRMKEK | EARAKFRQIV | SAVQYCHQKF | IVHRDLKAEN |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LLLDADMNIK | IADFGFSNEF | TFGNKLDTFC | GSPPYAAPEL | FQGKKIDGPE | VDVWSLGVIL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| YTLVSGSLPF | DGQNLKELRE | RVLRGKYRIP | FYMSTDCENL | LKKFLILNPS | KRGTLEQIMK |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DRWMNVGHED | DELKPYVEPL | PDYKDPRRTE | LMVSMGYTRE | EIQDSLVGQR | YNEVMATYLL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| LGYKSSELEG | DTITLKPRPS | ADLTNSSAPS | PSHKVQRSVS | ANPKQRRSSD | QAVPAIPTSN |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| SYSKKTQSNN | AENKRPEEET | GRKASSTAKV | PASPLPGLDR | KKTTPAPSTN | SVLSTSTNRS |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| RNSPLLDRAS | LGQASIQNGK | DSLTMPGSRA | STASASAAVS | AARPRQHQKS | MSASVHPNKA |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| SGLPPTESNC | EVPRPSTAPQ | RVPVASPSAH | NISSSSGAPD | RTNFPRGVSS | RSTFHAGQLR |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| QVRDQQNLPY | GVTPASPSGH | SQGRRGASGS | IFSKFTSKFV | RRNLNEPESK | DRVETLRPHV |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| VGSGGTDKDK | EEFREAKPRS | LRFTWSMKTT | SSMEPNEMMR | EIRKVLDANS | CQSELHERYM |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | |
| LLCVHGTPGH | ENFVQWEMEV | CKLPRLSLNG | VRFKRISGTS | MAFKNIASKI | ANELKL |