Q05030
Gene name |
Pdgfrb (Pdgfr, Pdgfr1) |
Protein name |
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta |
Names |
PDGF-R-beta , PDGFR-beta , EC 2.7.10.1 , Beta platelet-derived growth factor receptor , Beta-type platelet-derived growth factor receptor , CD140 antigen-like family member B , Platelet-derived growth factor receptor 1 , PDGFR-1 , CD antigen CD140b |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:24629 |
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
599-970 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
599-961 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
842-867 (Activation loop)
Target domain |
599-961 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Hubbard SR (2004) "Juxtamembrane autoinhibition in receptor tyrosine kinases", Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology, 5, 464-71
- Mol CD et al. (2004) "Structural basis for the autoinhibition and STI-571 inhibition of c-Kit tyrosine kinase", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 31655-63
- Chiara F et al. (2004) "Autoinhibition of the platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor tyrosine kinase by its C-terminal tail", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 19732-8
- Liang L et al. (2016) "Structural and biochemical studies of the PDGFRA kinase domain", Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 477, 667-672
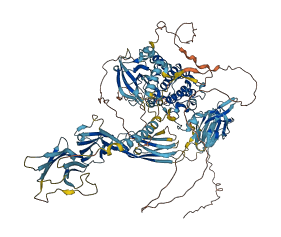
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q05030
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q05030-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q05030
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q05030 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q05030
16 regional properties for Q05030
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 599 - 961 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 600 - 954 | IPR001245 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class III, conserved site | 658 - 671 | IPR001824 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 44 - 106 | IPR003598-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 225 - 297 | IPR003598-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 330 - 402 | IPR003598-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 38 - 120 | IPR003599-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 219 - 310 | IPR003599-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 322 - 413 | IPR003599-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 26 - 110 | IPR007110-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 213 - 308 | IPR007110-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 415 - 523 | IPR007110-3 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 821 - 833 | IPR008266 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like beta-sandwich domain | 41 - 109 | IPR013151 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 605 - 633 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 599 - 957 | IPR020635 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
10 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| lysosomal lumen | The volume enclosed within the lysosomal membrane. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it and attached to it. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| ruffle | Projection at the leading edge of a crawling cell; the protrusions are supported by a microfilament meshwork. |
13 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| kinase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding | Binding to a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the addition of a phosphate group to an inositol lipid at the 3' position of the inositol ring. |
| platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor activity | Combining with platelet-derived growth factor isoform PDGF-BB or PDGF-AB to initiate a change in cell activity. |
| platelet-derived growth factor binding | Binding to platelet-derived growth factor. |
| platelet-derived growth factor receptor activity | Combining with platelet-derived growth factor receptor ligand and transmitting the signal across the plasma membrane to initiate a change in cell activity. |
| platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding | Binding to a platelet-derived growth factor receptor. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| vascular endothelial growth factor binding | Binding to a vascular endothelial growth factor. |
70 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adrenal gland development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the adrenal gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. This gland can either be a discrete structure located bilaterally above each kidney, or a cluster of cells in the head kidney that perform the functions of the adrenal gland. In either case, this organ consists of two cells types, aminergic chromaffin cells and steroidogenic cortical cells. |
| aorta morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of an aorta are generated and organized. An aorta is an artery that carries blood from the heart to other parts of the body. |
| blood vessel development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a blood vessel over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood. |
| cardiac myofibril assembly | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cardiac myofibril over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A cardiac myofibril is a myofibril specific to cardiac muscle cells. |
| cell chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). |
| cell migration involved in coronary angiogenesis | The orderly movement of a cell from one site to another that will contribute to the formation of new blood vessels in the heart from pre-existing blood vessels. |
| cell migration involved in vasculogenesis | The orderly movement of a cell from one site to another that will contribute to the differentiation of an endothelial cell that will form de novo blood vessels and tubes. |
| cellular response to hydrogen peroxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulus. |
| embryonic organ development | Development, taking place during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions. |
| glycosaminoglycan biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of glycosaminoglycans, any of a group of polysaccharides that contain amino sugars. |
| in utero embryonic development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the embryo in the uterus over time, from formation of the zygote in the oviduct, to birth. An example of this process is found in Mus musculus. |
| inner ear development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the inner ear over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| kidney development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the kidney over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The kidney is an organ that filters the blood and/or excretes the end products of body metabolism in the form of urine. |
| lung growth | The increase in size or mass of a lung. In all air-breathing vertebrates the lungs are developed from the ventral wall of the oesophagus as a pouch which divides into two sacs. In amphibians and many reptiles the lungs retain very nearly this primitive sac-like character, but in the higher forms the connection with the esophagus becomes elongated into the windpipe and the inner walls of the sacs become more and more divided, until, in the mammals, the air spaces become minutely divided into tubes ending in small air cells, in the walls of which the blood circulates in a fine network of capillaries. In mammals the lungs are more or less divided into lobes, and each lung occupies a separate cavity in the thorax. |
| male gonad development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the male gonad over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| metanephric comma-shaped body morphogenesis | The process in which the metanephric comma-shaped body is generated and organized. The metanephric comma-shaped body is the precursor structure to the metanephric S-shaped body that contributes to the morphogenesis of a nephron in the metanephros. |
| metanephric glomerular capillary formation | The process that gives rise to a metanephric glomerular capillary. This process pertains to the initial formation of a structure from unspecified parts. |
| metanephric glomerular mesangial cell proliferation involved in metanephros development | The multiplication or reproduction of glomerular mesangial cells in the metanephros, resulting in the expansion of the population. |
| metanephric glomerular mesangium development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the metanephric glomerular mesangium over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The metanephric glomerular mesangium is the thin membrane connective tissue composed of mesangial cells in the metanephros, which helps to support the capillary loops in a renal glomerulus. |
| metanephric glomerulus morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the metanephric glomerulus are generated and organized. The metanephric glomerulus is a capillary tuft surrounded by Bowman's capsule in nephrons of the vertebrate kidney, or metanephros. |
| metanephric mesenchymal cell migration | The orderly movement of undifferentiated metanephric mesenchymal cells (precursors to metanephric mesangial cells) from the mesenchyme into the cleft of the developing glomerulus, during development of the metanephros. |
| metanephric mesenchyme development | The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a metanephric mesenchyme from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of metanephric mesenchyme and ends with the mature structure. Metanephric mesenchyme is the tissue made up of loosely connected mesenchymal cells in the metanephros. |
| metanephric S-shaped body morphogenesis | The process in which the metanephric S-shaped body is generated and organized. The metanephric S-shaped body is the successor of the metanephric comma-shaped body that contributes to the morphogenesis of a nephron in the metanephros. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| phosphatidylinositol metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphatidylinositol, any glycophospholipid in which a sn-glycerol 3-phosphate residue is esterified to the 1-hydroxyl group of 1D-myo-inositol. |
| platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to a platelet-derived growth factor receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a ligand to a beta-type platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFbeta) on the surface of a signal-receiving cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of calcium ion import | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the directed movement of calcium ions into a cell or organelle. |
| positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of calcium-mediated signaling. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of cell proliferation by VEGF-activated platelet derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) binding to a platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) on the surface of a cell, which activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of chemotaxis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient. |
| positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals. |
| positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA biosynthetic process. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of multiplication or reproduction of fibroblast cells. |
| positive regulation of hepatic stellate cell activation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of hepatic stellate cell activation. |
| positive regulation of MAP kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of metanephric mesenchymal cell migration by platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of metanephric mesenchymal cell migration resulting from the platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of mitosis. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase B signaling, a series of reactions mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B. |
| positive regulation of phospholipase C activity | Any process that increases the rate of phospholipase C activity. |
| positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of reactive oxygen species metabolic process. |
| positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of Rho protein signal transduction. |
| positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the frequency, rate or extent of smooth muscle cell migration. |
| positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of smooth muscle cell proliferation. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| response to ceramide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a ceramide stimulus. |
| response to estradiol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of stimulus by estradiol, a C18 steroid hormone hydroxylated at C3 and C17 that acts as a potent estrogen. |
| response to estrogen | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of stimulus by an estrogen, C18 steroid hormones that can stimulate the development of female sexual characteristics. |
| response to fluid shear stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a fluid shear stress stimulus. Fluid shear stress is the force acting on an object in a system where the fluid is moving across a solid surface. |
| response to hydrogen peroxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulus. |
| response to hyperoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating increased oxygen tension. |
| response to lipid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipid stimulus. |
| response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| response to retinoic acid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a retinoic acid stimulus. |
| response to toxic substance | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a toxic stimulus. |
| retina vasculature development in camera-type eye | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the vasculature of the retina over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| ruffle assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a ruffle, a projection at the leading edge of a crawling cell; the protrusions are supported by a microfilament meshwork. The formation of ruffles (also called membrane ruffling) is thought to be controlled by a group of enzymes known as Rho GTPases, specifically RhoA, Rac1 and cdc42. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
| skeletal system morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized. |
| smooth muscle cell chemotaxis | The directed movement of a smooth muscle cell in response to an external stimulus. |
| smooth muscle tissue development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of smooth muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| tissue homeostasis | A homeostatic process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state within a defined tissue of an organism, including control of cellular proliferation and death and control of metabolic function. |
86 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P43481 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q06805 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q06807 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q28889 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| P13369 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| P18460 | FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P21804 | FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q9PUF6 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q08156 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8QHL3 | FLT1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P18461 | FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q6QNF3 | PDGFRB | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | SS |
| Q07407 | htl | Fibroblast growth factor receptor homolog 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q6J9G0 | STYK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P36888 | FLT3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P16234 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35916 | FLT4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P35968 | KDR | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P17948 | FLT1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P07333 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P10721 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P22455 | FGFR4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P22607 | FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07949 | RET | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35590 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q02763 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P11362 | FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P21802 | FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09619 | PDGFRB | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q03142 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P05532 | Kit | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91V87 | Fgfrl1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35917 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P09581 | Csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35969 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35546 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q06806 | Tie1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00342 | Flt3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6J9G1 | Styk1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P16092 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61851 | Fgfr3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q02858 | Tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35918 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P21803 | Fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26618 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05622 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q2HWD6 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q7TQM3 | Fgfrl1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q498D6 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| G3V9H8 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62838 | Musk | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63604 | Ntrk2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P35739 | Ntrk1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q03351 | Ntrk3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q91ZT1 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08775 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q64716 | Insrr | Insulin receptor-related protein | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P24062 | Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P57097 | Mertk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P97523 | Met | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q62956 | Erbb4 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62799 | Erbb3 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P20786 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P53767 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q04589 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63474 | Ddr1 | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P15127 | Insr | Insulin receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P06494 | Erbb2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q00495 | Csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q17833 | old-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor old-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q19238 | F09A5.2 | Putative tyrosine-protein kinase F09A5.2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q10656 | egl-15 | Myoblast growth factor receptor egl-15 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| P34892 | kin-16 | Receptor-like tyrosine-protein kinase kin-16 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| G5ED65 | ver-1 | Protein ver-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9S9M2 | WAKL4 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q7X8C5 | WAKL2 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8AXB3 | kdrl | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor kdr-like | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5GIT4 | kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O73791 | tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q90Z00 | fgfr1a | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1-A | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q8JG38 | fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9I8N6 | csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q90413 | fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9DE49 | pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q8JFR5 | kita | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor kita | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5MD89 | flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGLPEVMPAS | VLRGQLLLFV | LLLLGPQISQ | GLVITPPGPE | FVLNISSTFV | LTCSSSAPVM |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| WEQMSQVPWQ | EAAMNQDGTF | SSVLTLTNVT | GGDTGEYFCV | YNNSLGPELS | ERKRIYIFVP |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DPTMGFLPMD | SEDLFIFVTD | VTETTIPCRV | TDPQLEVTLH | EKKVDIPLHV | PYDHQRGFIG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TFEDKTYICK | TTIGDREVDS | DTYYVYSLQV | SSINVSVNAV | QTVVRQGESI | TIRCIVMGND |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| VVNFQWTYPR | MKSGRLVEPV | TDYLFGVPSR | IGSILHIPTA | ELSDSGTYTC | NVSVSVNDHG |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DEKAINVTVI | ENGYVRLLET | LEDVQIAELH | RSRTLQVVFE | AYPTPSVLWF | KDNRTLGDSS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| AGELVLSTRN | VSETRYVSEL | TLVRVKVSEA | GYYTMRAFHA | DDQVQLSFKL | QVNVPVRVLE |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LSESHPANGE | QILRCRGRGM | PQPNVTWSTC | RDLKRCPRKL | SPTPLGNSSK | EESQLETNVT |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| FWEEDQEYEV | VSTLRLRHVD | QPLSVRCMLQ | NSMGRDSQEV | TVVPHSLPFK | VVVISAILAL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| VVLTVISLII | LIMLWQRKPR | YEIRWKVIES | VSSDGHEYIY | VDPVQLPYDS | TWELPRDQLV |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| LGRTLGSGAF | GQVVEATAHG | LSHSQATMKV | AVKMLKSTAR | SSEKQALMSE | LKIMSHLGPH |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| LNVVNLLGAC | TKGGPIYIIT | EYCRYGDLVD | YLHRNKHTFL | QRHSNKHCPP | STELYSNALP |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| VGLSLPSHLN | LTGESDGGYM | DMSKDESVDY | VPMLDMKGHI | KYADIESSSY | MAPYDNYVPS |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| APERTYRATL | INDSPVLSYT | DLVGFSYQVA | NGMEFLASKN | CVHRDLAARN | VLICEGKLVK |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| ICDFGLARDI | MRDSNYISKG | STFLPLKWMA | PESIFNSLYT | TLSDVWSFGI | LLWEIFTLGG |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| TPYPELPMND | QFYNAIKRGY | RMAQPAHASD | EIYEIMQKCW | EEKFETRPPF | SQLVLLLERL |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| LGEGYKKKYQ | QVDEEFLRSD | HPAILRSQAR | LPGLHSLRSP | LDTSSVLYTA | VQPNETDNDY |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| IIPLPDPKPD | AADEGLLEGS | PSLASSTLNE | VNTSSTISCD | SPLELQEEPQ | AEPEAQLEQP |
| 1090 | |||||
| QDSGCPGPLA | EAEDSFL |