Q03957
Gene name |
CTK1 (YKL139W) |
Protein name |
CTD kinase subunit alpha |
Names |
CTDK-I subunit alpha, CTD kinase 58 kDa subunit, CTD kinase subunit 1 |
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YKL139W |
EC number |
2.7.11.23: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
323-345 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
183-469 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
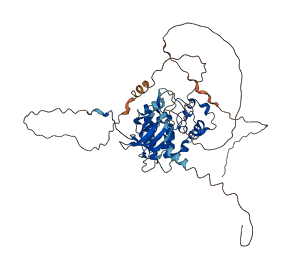
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for Q03957
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7JV7 | X-ray | 185 A | A | 159-508 | PDB |
| AF-Q03957-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
6 variants for Q03957
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s11-183173 | 71 | R>C | No | SGRP | |
| s11-183221 | 87 | S>G | No | SGRP | |
| s11-183256 | 98 | N>K | No | SGRP | |
| s11-183614 | 218 | G>R | No | SGRP | |
| s11-183963 | 334 | R>P | No | SGRP | |
| s11-184145 | 395 | K>Q | No | SGRP |
No associated diseases with Q03957
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.23 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| carboxy-terminal domain protein kinase complex | A protein complex that phosphorylates amino acid residues of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain repeats; phosphorylation occurs mainly on Ser2 and Ser5. |
| CTDK-1 complex | A positive transcription elongation factor complex that comprises the CDK kinase CTK1 (in budding yeast), Lsk1 (in fission yeast) (corresponding to the Panther PTHR24056:SF39 family), a cyclin and an additional gamma subunit (corresponding to the InterPRO entry IPR024638). |
| cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex | Cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs) are enzyme complexes that contain a kinase catalytic subunit associated with a regulatory cyclin partner. |
| cyclin/CDK positive transcription elongation factor complex | A transcription elongation factor complex that facilitates the transition from abortive to productive elongation by phosphorylating the CTD domain of the large subunit of DNA-directed RNA polymerase II, holoenzyme. Contains a cyclin and a cyclin-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleolus | A small, dense body one or more of which are present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is rich in RNA and protein, is not bounded by a limiting membrane, and is not seen during mitosis. Its prime function is the transcription of the nucleolar DNA into 45S ribosomal-precursor RNA, the processing of this RNA into 5.8S, 18S, and 28S components of ribosomal RNA, and the association of these components with 5S RNA and proteins synthesized outside the nucleolus. This association results in the formation of ribonucleoprotein precursors; these pass into the cytoplasm and mature into the 40S and 60S subunits of the ribosome. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| cyclin binding | Binding to cyclins, proteins whose levels in a cell varies markedly during the cell cycle, rising steadily until mitosis, then falling abruptly to zero. As cyclins reach a threshold level, they are thought to drive cells into G2 phase and thus to mitosis. |
| cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Cyclin-dependent catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| RNA polymerase II CTD heptapeptide repeat kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + RNA polymerase II large subunit CTD heptapeptide repeat (YSPTSPS) = ADP + H+ + phosphorylated RNA polymerase II. |
11 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to DNA damage stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism. |
| mRNA 3'-end processing | Any process involved in forming the mature 3' end of an mRNA molecule. |
| phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to an amino acid residue in the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Typically, this occurs during the transcription cycle and results in production of an RNA polymerase II enzyme where the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit is extensively phosphorylated, often referred to as hyperphosphorylated or the II(0) form. Specific types of phosphorylation within the CTD are usually associated with specific regions of genes, though there are exceptions. The phosphorylation state regulates the association of specific complexes such as the capping enzyme or 3'-RNA processing machinery to the elongating RNA polymerase complex. |
| positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription elongation, the extension of an RNA molecule after transcription initiation and promoter clearance by the addition of ribonucleotides catalyzed by a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase I. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription elongation, the extension of an RNA molecule after transcription initiation and promoter clearance by the addition of ribonucleotides, catalyzed by RNA polymerase II. |
| positive regulation of translational fidelity | Any process that increases the ability of the translational apparatus to interpret the genetic code. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II promoter | The extension of an RNA molecule after transcription initiation and promoter clearance at an RNA polymerase II promoter by the addition of ribonucleotides catalyzed by RNA polymerase II. |
| translational initiation | The process preceding formation of the peptide bond between the first two amino acids of a protein. This includes the formation of a complex of the ribosome, mRNA or circRNA, and an initiation complex that contains the first aminoacyl-tRNA. |
3 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P39073 | SSN3 | Meiotic mRNA stability protein kinase SSN3 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| F4I114 | At1g09600 | Probable serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g09600 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9ZVM9 | At1g54610 | Probable serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g54610 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSYNNGNTYS | KSYSRNNKRP | LFGKRSPNPQ | SLARPPPPKR | IRTDSGYQSN | MDNISSHRVN |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| SNDQPGHTKS | RGNNNLSRYN | DTSFQTSSRY | QGSRYNNNNT | SYENRPKSIK | RDETKAEFLS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| HLPKGPKSVE | KSRYNNSSNT | SNDIKNGYHA | SKYYNHKGQE | GRSVIAKKVP | VSVLTQQRST |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SVYLRIMQVG | EGTYGKVYKA | KNTNTEKLVA | LKKLRLQGER | EGFPITSIRE | IKLLQSFDHP |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NVSTIKEIMV | ESQKTVYMIF | EYADNDLSGL | LLNKEVQISH | SQCKHLFKQL | LLGMEYLHDN |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| KILHRDVKGS | NILIDNQGNL | KITDFGLARK | MNSRADYTNR | VITLWYRPPE | LLLGTTNYGT |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| EVDMWGCGCL | LVELFNKTAI | FQGSNELEQI | ESIFKIMGTP | TINSWPTLYD | MPWFFMIMPQ |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| QTTKYVNNFS | EKFKSVLPSS | KCLQLAINLL | CYDQTKRFSA | TEALQSDYFK | EEPKPEPLVL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | ||
| DGLVSCHEYE | VKLARKQKRP | NILSTNTNNK | GNGNSNNNNN | NNNDDDDK |