Q03145
Gene name |
Epha2 (Eck, Myk2, Sek2) |
Protein name |
Ephrin type-A receptor 2 |
Names |
Epithelial cell kinase, Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor ECK, Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor MPK-5, Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor SEK-2 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:13836 |
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
(Annotation based on sequence homology with P29323)
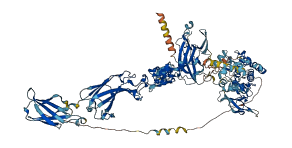
Ephrin type-B receptor 2 is a membrane-associated protein that mediates axon guidance, cell migration and morphogenesis. The Eph receptor tyrosine kinase family is regulated by autophosphorylation within the juxtamembrane region and the kinase activation segment. The structure, supported by mutagenesis data, reveals that the juxtamembrane segment adopts a helical conformation that distorts the small lobe of the kinase domain, and blocks the activation segment from attaining an activated conformation. Phosphorylation of the conserved juxtamembrane tyrosines would relieve this autoinhibition by disturbing the association of the juxtamembrane segment with the kinase domain, while liberating phosphotyrosine sites for binding SH2 domains of target proteins.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for Q03145
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5ZRX | X-ray | 150 A | A/B | 900-977 | PDB |
| AF-Q03145-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
39 variants for Q03145
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388715954 | 2 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388727869 | 44 | T>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388721397 | 47 | Y>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388725148 | 48 | G>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3388726177 | 49 | K>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388728487 | 81 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388729013 | 82 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388721389 | 87 | R>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3413100853 | 110 | G>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388704203 | 116 | E>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3388728508 | 124 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388724031 | 227 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388712451 | 232 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388728489 | 367 | C>R | No | EVA | |
| rs224200078 | 381 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388712452 | 398 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388733760 | 411 | F>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388733750 | 413 | V>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3388729026 | 415 | A>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3395035468 | 438 | T>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3395007458 | 467 | V>R* | No | EVA | |
| rs3395035473 | 503 | T>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388728978 | 540 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388725186 | 542 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388732267 | 554 | G>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388732320 | 572 | S>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388719710 | 640 | K>E | No | EVA | |
| rs225276299 | 643 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388732302 | 684 | S>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3388732283 | 687 | K>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388729001 | 762 | S>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388733692 | 822 | L>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388721411 | 826 | E>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3395061344 | 828 | M>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3395069476 | 853 | Q>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3388723975 | 874 | K>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388728989 | 878 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs13473305 | 901 | G>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388732318 | 938 | V>I | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q03145
13 regional properties for Q03145
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 614 - 876 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Ephrin receptor ligand binding domain | 27 - 205 | IPR001090 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 616 - 872 | IPR001245 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class V, conserved site | 181 - 201 | IPR001426-1 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class V, conserved site | 248 - 268 | IPR001426-2 |
| domain | Sterile alpha motif domain | 902 - 969 | IPR001660 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 329 - 433 | IPR003961-1 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 437 - 530 | IPR003961-2 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 736 - 748 | IPR008266 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 620 - 647 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 614 - 872 | IPR020635 |
| domain | Ephrin receptor, transmembrane domain | 539 - 611 | IPR027936 |
| domain | Ephrin type-A receptor 2, ligand binding domain | 27 - 200 | IPR034263 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
11 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| focal adhesion | A cell-substrate junction that anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix and that forms a point of termination of actin filaments. In insects focal adhesion has also been referred to as hemi-adherens junction (HAJ). |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| lamellipodium | A thin sheetlike process extended by the leading edge of a migrating cell or extending cell process; contains a dense meshwork of actin filaments. |
| lamellipodium membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a lamellipodium. |
| leading edge membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding the leading edge of a motile cell. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| ruffle membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a ruffle. |
| tight junction | A cell-cell junction that seals cells together in an epithelium in a way that prevents even small molecules from leaking from one side of the sheet to the other. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| growth factor binding | Binding to a growth factor, proteins or polypeptides that stimulate a cell or organism to grow or proliferate. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | Combining with a signal and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate. |
| transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity | Combining with a transmembrane ephrin to initiate a change in cell activity. |
49 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of GTPase activity | Any process that initiates the activity of an inactive GTPase through the replacement of GDP by GTP. |
| axial mesoderm formation | The process that gives rise to the axial mesoderm. This process pertains to the initial formation of the structure from unspecified parts. |
| axon guidance | The chemotaxis process that directs the migration of an axon growth cone to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| blood vessel development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a blood vessel over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood. |
| blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis | The multiplication or reproduction of blood vessel endothelial cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population contributing to sprouting angiogenesis. |
| blood vessel morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood. |
| bone remodeling | The continuous turnover of bone matrix and mineral that involves first, an increase in resorption (osteoclastic activity) and later, reactive bone formation (osteoblastic activity). The process of bone remodeling takes place in the adult skeleton at discrete foci. The process ensures the mechanical integrity of the skeleton throughout life and plays an important role in calcium homeostasis. An imbalance in the regulation of bone resorption and bone formation results in many of the metabolic bone diseases, such as osteoporosis. |
| branching involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis | The process in which the branching structure of the mammary gland duct is generated and organized. The mammary gland is a large compound sebaceous gland that in female mammals is modified to secrete milk. |
| cAMP metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate). |
| cell adhesion | The attachment of a cell, either to another cell or to an underlying substrate such as the extracellular matrix, via cell adhesion molecules. |
| cell chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| cell motility | Any process involved in the controlled self-propelled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another. |
| defense response to Gram-positive bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a Gram-positive bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| ephrin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by ephrin binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage | The series of molecular signals in which an intracellular signal is conveyed to trigger the apoptotic death of a cell. The pathway is induced by the detection of DNA damage, and ends when the execution phase of apoptosis is triggered. |
| keratinocyte differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a keratinocyte. |
| lens fiber cell morphogenesis | The process in which the structures of a lens fiber cell are generated and organized. This process occurs while the initially relatively unspecialized cell is acquiring the specialized features of a lens fiber cell. A lens fiber cell is any of the elongated, tightly packed cells that make up the bulk of the mature lens in a camera-type eye. |
| mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of mammary gland epithelial cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. Mammary gland epithelial cells make up the covering of surfaces of the mammary gland. The mammary gland is a large compound sebaceous gland that in female mammals is modified to secrete milk. |
| negative regulation of angiogenesis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of angiogenesis. |
| negative regulation of chemokine production | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of chemokine production. |
| negative regulation of cytokine production | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate of production of a cytokine. |
| negative regulation of lymphangiogenesis | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of lymphangiogenesis. |
| negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase B signaling, a series of reactions mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B. |
| neural tube development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the neural tube over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The mature structure of the neural tube exists when the tube has been segmented into the forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain and spinal cord regions. In addition neural crest has budded away from the epithelium. |
| neuron differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron. |
| notochord cell development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a notochord cell over time, from its formation to its mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate. |
| notochord formation | The formation of the notochord from the chordamesoderm. The notochord is composed of large cells packed within a firm connective tissue sheath and is found in all chordates at the ventral surface of the neural tube. In vertebrates, the notochord contributes to the vertebral column. |
| notochord morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the notochord are generated and organized. The notochord is a mesoderm-derived structure located ventral of the developing nerve cord. In vertebrates, the notochord serves as a core around which other mesodermal cells form the vertebrae. In the most primitive chordates, which lack vertebrae, the notochord persists as a substitute for a vertebral column. |
| osteoblast differentiation | The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an osteoblast, a mesodermal or neural crest cell that gives rise to bone. |
| osteoclast differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized monocyte acquires the specialized features of an osteoclast. An osteoclast is a specialized phagocytic cell associated with the absorption and removal of the mineralized matrix of bone tissue. |
| pericyte cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a pericyte cell. |
| positive regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of tight junction assembly. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to plasma membrane. |
| post-anal tail morphogenesis | The process in which a post-anal tail is generated and organized. A post-anal tail is a muscular region of the body that extends posterior to the anus. The post-anal tail may aid locomotion and balance. |
| protein kinase B signaling | A series of reactions, mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B (also called AKT), which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound. |
| protein localization to plasma membrane | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location in the plasma membrane. |
| regulation of angiogenesis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of angiogenesis. |
| regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the migration of the endothelial cells of blood vessels. |
| regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of cell adhesion mediated by integrin. |
| regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| regulation of lamellipodium assembly | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the formation of a lamellipodium, a thin sheetlike extension of the surface of a migrating cell. |
| response to growth factor | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a growth factor stimulus. |
| skeletal system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The skeleton is the bony framework of the body in vertebrates (endoskeleton) or the hard outer envelope of insects (exoskeleton or dermoskeleton). |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| vasculogenesis | The differentiation of endothelial cells from progenitor cells during blood vessel development, and the de novo formation of blood vessels and tubes. |
88 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P28693 | EPHB2 | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q07496 | EPHA4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07494 | EPHB1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07497 | EPHB5 | Ephrin type-B receptor 5 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P29318 | EPHA3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| O42422 | EPHA7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P54755 | EPHA5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07498 | EPHB3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P0C0K6 | EPHB6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | SS |
| P29322 | EPHA8 | Ephrin type-A receptor 8 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P21709 | EPHA1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54764 | EPHA4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54753 | EPHB3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29320 | EPHA3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P54760 | EPHB4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q15375 | EPHA7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q5JZY3 | EPHA10 | Ephrin type-A receptor 10 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29323 | EPHB2 | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9UF33 | EPHA6 | Ephrin type-A receptor 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54762 | EPHB1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54756 | EPHA5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O15197 | EPHB6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29317 | EPHA2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54754 | Ephb3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03137 | Epha4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61772 | Epha7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O09127 | Epha8 | Ephrin type-A receptor 8 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8CBF3 | Ephb1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P29319 | Epha3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62413 | Epha6 | Ephrin type-A receptor 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54763 | Ephb2 | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O08644 | Ephb6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P54761 | Ephb4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60629 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60750 | Epha1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00993 | Axl | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60805 | Mertk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z138 | Ror2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9WTL4 | Insrr | Insulin receptor-related protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3UFB7 | Ntrk1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z139 | Ror1 | Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P97793 | Alk | ALK tyrosine kinase receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15208 | Insr | Insulin receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35546 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61006 | Musk | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62371 | Ddr2 | Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03146 | Ddr1 | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15209 | Ntrk2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6VNS1 | Ntrk3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35917 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35969 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35918 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60751 | Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16092 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P21803 | Fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03142 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62190 | Mst1r | Macrophage-stimulating protein receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P55144 | Tyro3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TYRO3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70424 | Erbb2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61527 | Erbb4 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61526 | Erbb3 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q01279 | Egfr | Epidermal growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q01887 | Ryk | Tyrosine-protein kinase RYK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q02858 | Tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q06806 | Tie1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05532 | Kit | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P05622 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P09581 | Csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26618 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00342 | Flt3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16056 | Met | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61851 | Fgfr3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P54757 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P54759 | Epha7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09759 | Ephb1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P0C0K7 | Ephb6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08680 | Epha3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O61460 | vab-1 | Ephrin receptor 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| C0LGG3 | At1g51820 | Probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g51820 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9ZQR3 | At2g14510 | Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At2g14510 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LIG2 | At3g21340 | Receptor-like protein kinase At3g21340 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SNA3 | At3g46340 | Putative receptor-like protein kinase At3g46340 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| C0LGW2 | PAM74 | Probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase PAM74 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FN94 | At5g59670 | Receptor-like protein kinase At5g59670 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FN93 | At5g59680 | Probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At5g59680 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O13147 | ephb3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O73878 | ephb4b | Ephrin type-B receptor 4b | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O13146 | epha3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MELRAVGFCL | ALLWGCALAA | AAAQGKEVVL | LDFAAMKGEL | GWLTHPYGKG | WDLMQNIMDD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| MPIYMYSVCN | VVSGDQDNWL | RTNWVYREEA | ERIFIELKFT | VRDCNSFPGG | ASSCKETFNL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| YYAESDVDYG | TNFQKRQFTK | IDTIAPDEIT | VSSDFEARNV | KLNVEERMVG | PLTRKGFYLA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| FQDIGACVAL | LSVRVYYKKC | PEMLQSLARF | PETIAVAVSD | TQPLATVAGT | CVDHAVVPYG |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| GEGPLMHCTV | DGEWLVPIGQ | CLCQEGYEKV | EDACRACSPG | FFKSEASESP | CLECPEHTLP |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| STEGATSCQC | EEGYFRAPED | PLSMSCTRPP | SAPNYLTAIG | MGAKVELRWT | APKDTGGRQD |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| IVYSVTCEQC | WPESGECGPC | EASVRYSEPP | HALTRTSVTV | SDLEPHMNYT | FAVEARNGVS |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| GLVTSRSFRT | ASVSINQTEP | PKVRLEDRST | TSLSVTWSIP | VSQQSRVWKY | EVTYRKKGDA |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| NSYNVRRTEG | FSVTLDDLAP | DTTYLVQVQA | LTQEGQGAGS | KVHEFQTLST | EGSANMAVIG |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| GVAVGVVLLL | VLAGVGLFIH | RRRRNLRARQ | SSEDVRFSKS | EQLKPLKTYV | DPHTYEDPNQ |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| AVLKFTTEIH | PSCVARQKVI | GAGEFGEVYK | GTLKASSGKK | EIPVAIKTLK | AGYTEKQRVD |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| FLSEASIMGQ | FSHHNIIRLE | GVVSKYKPMM | IITEYMENGA | LDKFLREKDG | EFSVLQLVGM |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| LRGIASGMKY | LANMNYVHRD | LAARNILVNS | NLVCKVSDFG | LSRVLEDDPE | ATYTTSGGKI |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| PIRWTAPEAI | SYRKFTSASD | VWSYGIVMWE | VMTYGERPYW | ELSNHEVMKA | INDGFRLPTP |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| MDCPSAIYQL | MMQCWQQERS | RRPKFADIVS | ILDKLIRAPD | SLKTLADFDP | RVSIRLPSTS |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| GSEGVPFRTV | SEWLESIKMQ | QYTEHFMVAG | YTAIEKVVQM | SNEDIKRIGV | RLPGHQKRIA |
| 970 | |||||
| YSLLGLKDQV | NTVGIPI |