Q02858
Gene name |
Tek (Hyk, Tie-2, Tie2) |
Protein name |
Angiopoietin-1 receptor |
Names |
|
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:21687 |
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
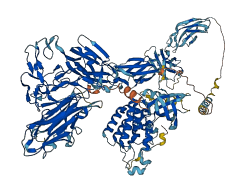
Descriptions
TEK is an endothelial cell receptor tyrosine kinase that induces signal transduction pathways involved in cell migration upon angiopoietin-1 (Ang1) stimulation.
The juxtamembrane region (769-805) inhibits the kinase domain like other receptor tyrosine kinases. Deletion of the C-terminal tail increases the kinase activity of TEK. The end of the C-terminal tail could block access to the substrate binding site.
Unlike other RTKs, in which the activation loop (A-loop, 982-1008) obstructs substrate or ATP binding in the inactive state, the A-loop of TEK assumes an active-like conformation, which would appear to facilitate substrate binding. However, the nucleotide binding loop adopts an apparent inhibitory conformation, with the side chains of several residues in this loop occupying the ATP binding site.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
822-1094 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Target domain |
822-1094 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Target domain |
822-1094 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
979-1001 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
822-1094 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Niu XL et al. (2002) "Deletion of the carboxyl terminus of Tie2 enhances kinase activity, signaling, and function. Evidence for an autoinhibitory mechanism", The Journal of biological chemistry, 277, 31768-73
- Shewchuk LM et al. (2000) "Structure of the Tie2 RTK domain: self-inhibition by the nucleotide binding loop, activation loop, and C-terminal tail", Structure (London, England : 1993), 8, 1105-13
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q02858
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q02858-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
2 variants for Q02858
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs28120604 | 325 | R>Q | No | Ensembl | |
| rs28120509 | 744 | K>E | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q02858
13 regional properties for Q02858
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 822 - 1094 | IPR000719 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 216 - 252 | IPR000742-1 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 267 - 299 | IPR000742-2 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 822 - 1089 | IPR001245 |
| domain | Laminin-type EGF domain | 230 - 275 | IPR002049 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 444 - 539 | IPR003961-1 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 541 - 635 | IPR003961-2 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 638 - 733 | IPR003961-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 350 - 440 | IPR007110 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 958 - 970 | IPR008266 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 828 - 853 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor Tie-2, Ig-like domain 1, N-terminal | 24 - 118 | IPR018941 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 822 - 1090 | IPR020635 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
15 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| basal plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the basal end of the cell. Often used in reference to animal polarized epithelial membranes, where the basal membrane is the part attached to the extracellular matrix, or in plant cells, where the basal membrane is defined with respect to the zygotic axis. |
| basolateral plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane that includes the basal end and sides of the cell. Often used in reference to animal polarized epithelial membranes, where the basal membrane is the part attached to the extracellular matrix, or in plant cells, where the basal membrane is defined with respect to the zygotic axis. |
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| cell-cell junction | A cell junction that forms a connection between two or more cells of an organism; excludes direct cytoplasmic intercellular bridges, such as ring canals in insects. |
| centriolar satellite | A small (70-100 nm) cytoplasmic granule that contains a number of centrosomal proteins; centriolar satellites traffic toward microtubule minus ends and are enriched near the centrosome. |
| extracellular region | The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite. |
| focal adhesion | A cell-substrate junction that anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix and that forms a point of termination of actin filaments. In insects focal adhesion has also been referred to as hemi-adherens junction (HAJ). |
| integral component of membrane | The component of a membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| membrane raft | Any of the small (10-200 nm), heterogeneous, highly dynamic, sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that compartmentalize cellular processes. Small rafts can sometimes be stabilized to form larger platforms through protein-protein and protein-lipid interactions. |
| microvillus | Thin cylindrical membrane-covered projections on the surface of an animal cell containing a core bundle of actin filaments. Present in especially large numbers on the absorptive surface of intestinal cells. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| growth factor binding | Binding to a growth factor, proteins or polypeptides that stimulate a cell or organism to grow or proliferate. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| signaling receptor activity | Receiving a signal and transmitting it in the cell to initiate a change in cell activity. A signal is a physical entity or change in state that is used to transfer information in order to trigger a response. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | Combining with a signal and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate. |
44 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| angiogenesis | Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels. |
| branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis | The process of coordinated growth and sprouting of blood vessels giving rise to the organized vascular system. |
| cell-cell adhesion | The attachment of one cell to another cell via adhesion molecules. |
| cell-matrix adhesion | The binding of a cell to the extracellular matrix via adhesion molecules. |
| endothelial cell proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of endothelial cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. Endothelial cells are thin flattened cells which line the inside surfaces of body cavities, blood vessels, and lymph vessels, making up the endothelium. |
| glomerulus vasculature development | The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a glomerulus vasculature from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the glomerulus vasculature and ends with the mature structure. The glomerulus vasculature is composed of the tubule structures that carry blood or lymph in the glomerulus. |
| heart development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. |
| heart trabecula formation | The process of creating a trabecula in the heart. A trabecula is a tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod. |
| hemopoiesis | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the myeloid and lymphoid derived organ/tissue systems of the blood and other parts of the body over time, from formation to the mature structure. The site of hemopoiesis is variable during development, but occurs primarily in bone marrow or kidney in many adult vertebrates. |
| negative regulation of angiogenesis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of angiogenesis. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of endothelial cell apoptotic process. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of actin cytoskeleton reorganization. |
| positive regulation of angiogenesis | Any process that activates or increases angiogenesis. |
| positive regulation of cell adhesion | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell adhesion. |
| positive regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of cytokine production that contributes to an immune response. |
| positive regulation of endothelial cell migration | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the orderly movement of an endothelial cell into the extracellular matrix to form an endothelium. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of focal adhesion assembly, the establishment and maturation of focal adhesions. |
| positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of intracellular signal transduction. |
| positive regulation of kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| positive regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPK cascade. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase cascade. |
| positive regulation of protein import into nucleus | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of movement of proteins from the cytoplasm into the nucleus. |
| positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase B signaling, a series of reactions mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway activity. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| regulation of angiogenesis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of angiogenesis. |
| regulation of cell migration | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| regulation of endothelial cell proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of endothelial cell proliferation. |
| regulation of establishment or maintenance of cell polarity | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the specification, formation or maintenance of anisotropic intracellular organization or cell growth patterns. |
| regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| response to estrogen | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of stimulus by an estrogen, C18 steroid hormones that can stimulate the development of female sexual characteristics. |
| response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
| response to retinoic acid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a retinoic acid stimulus. |
| sprouting angiogenesis | The extension of new blood vessels from existing vessels into avascular tissues, this process includes the specialization of endothelial cells into leading tip and stalk cells, proliferation and migration of the endothelial cells and cell adhesion resulting in angiogenic sprout fusion or lumen formation. |
| substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading | The morphogenetic process that results in flattening of a cell as a consequence of its adhesion to a substrate. |
| Tie signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an angiopoietin binding to the Tie receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| vasculogenesis | The differentiation of endothelial cells from progenitor cells during blood vessel development, and the de novo formation of blood vessels and tubes. |
122 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P43481 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q06805 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q06807 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q28889 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| P13369 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| P18460 | FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P21804 | FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q9PUF6 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q08156 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8QHL3 | FLT1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P18461 | FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07407 | htl | Fibroblast growth factor receptor homolog 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q6J9G0 | STYK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P36888 | FLT3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P16234 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09619 | PDGFRB | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35916 | FLT4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P35968 | KDR | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P17948 | FLT1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P07333 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P10721 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P22455 | FGFR4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P22607 | FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07949 | RET | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35590 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P11362 | FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P21802 | FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q02763 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q91V87 | Fgfrl1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q6J9G1 | Styk1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P09581 | Csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35917 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35918 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q06806 | Tie1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35546 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61006 | Musk | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z138 | Ror2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z139 | Ror1 | Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62371 | Ddr2 | Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03146 | Ddr1 | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15209 | Ntrk2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3UFB7 | Ntrk1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6VNS1 | Ntrk3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35969 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03145 | Epha2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60750 | Epha1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54761 | Ephb4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60629 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P97793 | Alk | ALK tyrosine kinase receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9WTL4 | Insrr | Insulin receptor-related protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60751 | Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15208 | Insr | Insulin receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16092 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P21803 | Fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03142 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60805 | Mertk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62190 | Mst1r | Macrophage-stimulating protein receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00993 | Axl | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P55144 | Tyro3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TYRO3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70424 | Erbb2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61527 | Erbb4 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61526 | Erbb3 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q01279 | Egfr | Epidermal growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q01887 | Ryk | Tyrosine-protein kinase RYK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P05532 | Kit | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P05622 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26618 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00342 | Flt3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61851 | Fgfr3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P16056 | Met | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q2HWD6 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q7TQM3 | Fgfrl1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P53767 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P20786 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q91ZT1 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q04589 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G3V9H8 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q498D6 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q05030 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08775 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q17833 | old-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor old-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q19238 | F09A5.2 | Putative tyrosine-protein kinase F09A5.2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q10656 | egl-15 | Myoblast growth factor receptor egl-15 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| P34892 | kin-16 | Receptor-like tyrosine-protein kinase kin-16 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| G5ED65 | ver-1 | Protein ver-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| O64782 | SD129 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-29 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64770 | At1g61490 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61490 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9LW83 | CES101 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase CES101 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64774 | At1g61460 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61460 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64778 | At1g61420 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61420 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64783 | At1g61370 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61370 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O81833 | SD11 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64780 | At1g61400 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61400 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64477 | At2g19130 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At2g19130 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9SXB4 | At1g11300 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g11300 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SY95 | At1g61550 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61550 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9SYA0 | At1g61500 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61500 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9SXB5 | At1g11303 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g11303 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LPZ9 | SD113 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-13 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64776 | At1g61440 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61440 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9M345 | LECRK42 | L-type lectin-domain containing receptor kinase IV.2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9M2S4 | LECRKS4 | L-type lectin-domain containing receptor kinase S.4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O80939 | LECRK41 | L-type lectin-domain containing receptor kinase IV.1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O81291 | LECRK44 | L-type lectin-domain containing receptor kinase IV.4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O81292 | LECRK43 | L-type lectin-domain containing receptor kinase IV.3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q96285 | LECRK55 | L-type lectin-domain containing receptor kinase V.5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9M1G4 | LECRK15 | Probable L-type lectin-domain containing receptor kinase I.5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FG33 | LECRKS5 | Probable L-type lectin-domain containing receptor kinase S.5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64784 | At1g61360 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61360 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64793 | At1g67520 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g67520 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q39203 | SD22 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD2-2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9LSR8 | LECRK19 | L-type lectin-domain containing receptor kinase I.9 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8AXB3 | kdrl | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor kdr-like | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5GIT4 | kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q90Z00 | fgfr1a | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1-A | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q8JG38 | fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9I8N6 | csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q90413 | fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9DE49 | pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q8JFR5 | kita | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor kita | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5MD89 | flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O73791 | tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MDSLAGLVLC | GVSLLLYGVV | EGAMDLILIN | SLPLVSDAET | SLTCIASGWH | PHEPITIGRD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| FEALMNQHQD | PLEVTQDVTR | EWAKKVVWKR | EKASKINGAY | FCEGRVRGQA | IRIRTMKMRQ |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QASFLPATLT | MTVDRGDNVN | ISFKKVLIKE | EDAVIYKNGS | FIHSVPRHEV | PDILEVHLPH |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| AQPQDAGVYS | ARYIGGNLFT | SAFTRLIVRR | CEAQKWGPDC | SRPCTTCKNN | GVCHEDTGEC |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| ICPPGFMGRT | CEKACEPHTF | GRTCKERCSG | PEGCKSYVFC | LPDPYGCSCA | TGWRGLQCNE |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| ACPSGYYGPD | CKLRCHCTNE | EICDRFQGCL | CSQGWQGLQC | EKEGRPRMTP | QIEDLPDHIE |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VNSGKFNPIC | KASGWPLPTS | EEMTLVKPDG | TVLQPNDFNY | TDRFSVAIFT | VNRVLPPDSG |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| VWVCSVNTVA | GMVEKPFNIS | VKVLPEPLHA | PNVIDTGHNF | AIINISSEPY | FGDGPIKSKK |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| LFYKPVNQAW | KYIEVTNEIF | TLNYLEPRTD | YELCVQLARP | GEGGEGHPGP | VRRFTTASIG |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LPPPRGLSLL | PKSQTALNLT | WQPIFTNSED | EFYVEVERRS | LQTTSDQQNI | KVPGNLTSVL |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| LSNLVPREQY | TVRARVNTKA | QGEWSEELRA | WTLSDILPPQ | PENIKISNIT | DSTAMVSWTI |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| VDGYSISSII | IRYKVQGKNE | DQHIDVKIKN | ATVTQYQLKG | LEPETTYHVD | IFAENNIGSS |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| NPAFSHELRT | LPHSPASADL | GGGKMLLIAI | LGSAGMTCIT | VLLAFLIMLQ | LKRANVQRRM |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| AQAFQNREEP | AVQFNSGTLA | LNRKAKNNPD | PTIYPVLDWN | DIKFQDVIGE | GNFGQVLKAR |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| IKKDGLRMDA | AIKRMKEYAS | KDDHRDFAGE | LEVLCKLGHH | PNIINLLGAC | EHRGYLYLAI |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| EYAPHGNLLD | FLRKSRVLET | DPAFAIANST | ASTLSSQQLL | HFAADVARGM | DYLSQKQFIH |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| RDLAARNILV | GENYIAKIAD | FGLSRGQEVY | VKKTMGRLPV | RWMAIESLNY | SVYTTNSDVW |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| SYGVLLWEIV | SLGGTPYCGM | TCAELYEKLP | QGYRLEKPLN | CDDEVYDLMR | QCWREKPYER |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | ||
| PSFAQILVSL | NRMLEERKTY | VNTTLYEKFT | YAGIDCSAEE | AA |