Q00655
Gene name |
SYK |
Protein name |
Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK |
Names |
Spleen tyrosine kinase |
Species |
Sus scrofa (Pig) |
KEGG Pathway |
ssc:100125540 |
EC number |
2.7.10.2: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
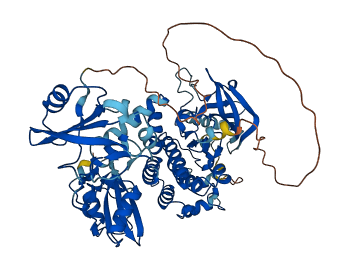
Descriptions
Syk is non-receptor tyrosine kinase which mediates signal transduction downstream of a variety of transmembrane receptors including classical immunoreceptors like the B-cell receptor (BCR). Upon BCR crosslinking, Syk is recruited via its tandem SH2 domain to tyrosine-phosphorylated Ig-α/Ig-β constituting components of BCR, and intimately cooperates with the signaling subunits of the BCR and plays a central role in the amplification and diversification of BCR signals.
Syk has two linkers called interdomains that regulate conformations of SYK: interdomain A (SH2-SH2), interdomain B (SH2-kinase domain). The interdomain interaction of A and B maintains the kinase domain inactive.
Binding of its SH2 domain to activated ITAM opens the kinase domain.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
364-624 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding, PTM |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
364-624 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding, PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
504-530 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
364-624 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Adachi T et al. (2007) "Interdomain A is crucial for ITAM-dependent and -independent regulation of Syk", Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 364, 111-7
- Kulathu Y et al. (2009) "Autoinhibition and adapter function of Syk", Immunological reviews, 232, 286-99
- Grädler U et al. (2013) "Structural and biophysical characterization of the Syk activation switch", Journal of molecular biology, 425, 309-33
- Bond PJ et al. (2011) "Molecular mechanism of selective recruitment of Syk kinases by the membrane antigen-receptor complex", The Journal of biological chemistry, 286, 25872-81
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q00655
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q00655-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q00655
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q00655 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q00655
5 regional properties for Q00655
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| conserved_site | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DEAD-box, conserved site | 345 - 353 | IPR000629 |
| domain | Helicase, C-terminal | 414 - 575 | IPR001650 |
| domain | DEAD/DEAH box helicase domain | 204 - 391 | IPR011545 |
| domain | Helicase superfamily 1/2, ATP-binding domain | 199 - 418 | IPR014001 |
| domain | RNA helicase, DEAD-box type, Q motif | 180 - 208 | IPR014014 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.2 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| early phagosome | A membrane-bounded intracellular vesicle as initially formed upon the ingestion of particulate material by phagocytosis. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + protein L-tyrosine = ADP + protein L-tyrosine phosphate by a non-membrane spanning protein. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
30 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adaptive immune response | An immune response mediated by cells expressing specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for an enhanced secondary response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). |
| angiogenesis | Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels. |
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a B cell. |
| blood vessel morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood. |
| cellular response to low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus. |
| cellular response to molecule of fungal origin | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus by molecules of fungal origin such as chito-octamer oligosaccharide. |
| defense response to bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| integrin-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to an integrin on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| interleukin-3-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by interleukin-3 binding to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| leukocyte activation involved in immune response | A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response. |
| leukocyte cell-cell adhesion | The attachment of a leukocyte to another cell via adhesion molecules. |
| lymph vessel development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a lymph vessel over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| macrophage activation involved in immune response | A change in morphology and behavior of a macrophage resulting from exposure to a cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response. |
| neutrophil activation involved in immune response | The change in morphology and behavior of a neutrophil resulting from exposure to a cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response. |
| neutrophil chemotaxis | The directed movement of a neutrophil cell, the most numerous polymorphonuclear leukocyte found in the blood, in response to an external stimulus, usually an infection or wounding. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of bone resorption | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of bone resorption. |
| positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of cell adhesion mediated by integrin. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-4 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-4 production. |
| receptor internalization | A receptor-mediated endocytosis process that results in the movement of receptors from the plasma membrane to the inside of the cell. The process begins when cell surface receptors are monoubiquitinated following ligand-induced activation. Receptors are subsequently taken up into endocytic vesicles from where they are either targeted to the lysosome or vacuole for degradation or recycled back to the plasma membrane. |
| regulation of arachidonic acid secretion | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of arachidonic acid secretion, the controlled release of arachidonic acid from a cell or a tissue. |
| regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| regulation of neutrophil degranulation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of neutrophil degranulation. |
| regulation of phagocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of phagocytosis, the process in which phagocytes engulf external particulate material. |
| regulation of platelet activation | Any process that modulates the rate or frequency of platelet activation. Platelet activation is a series of progressive, overlapping events triggered by exposure of the platelets to subendothelial tissue. |
| regulation of platelet aggregation | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of platelet aggregation. Platelet aggregation is the adhesion of one platelet to one or more other platelets via adhesion molecules. |
| regulation of superoxide anion generation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of enzymatic generation of superoxide by a cell. |
| serotonin secretion by platelet | The regulated release of serotonin by a platelet or group of platelets. |
13 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1N9Y5 | SYK | Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P43403 | ZAP70 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ZAP-70 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P43405 | SYK | Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P43404 | Zap70 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ZAP-70 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P48025 | Syk | Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| A1Y2K1 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q64725 | Syk | Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9SYA0 | At1g61500 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61500 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9FG33 | LECRKS5 | Probable L-type lectin-domain containing receptor kinase S.5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| F4JTP5 | STY46 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY46 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O22558 | STY8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q2MHE4 | HT1 | Serine/threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase HT1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWL6 | STY17 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY17 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MADSANHLPF | FFGQITREEA | EDYLVQGGMS | DGLYLLRQSR | NYLGGFALSV | AYDRKAHHYT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| IERELNGTYA | ISGGRTHGSP | AELCHYHSQE | LDGLVCLLKN | PFNRPPGVQP | KTGPFEDLKE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| NLIREYVKQT | WNLQGQALEQ | AIISQKPQLE | KLIATTAHEK | MPWFHGKISR | DESEQIVLIG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SKTNGKFLIR | ARDNGSYALG | LLHEGKVLHY | RIDKDKTGKL | SIPGGKNFDT | LWQLVEHYSY |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| KSDGLLRVLT | VPCQKIGGQT | GNDSFRPQLP | SAHPATWSAG | GIISRIKSYS | FPKPGHRKAS |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| SPQGNRPESL | VSYNPYESDR | GPWANEREAQ | REALPMDTEV | YESPYADPEE | IRPKEVYLDR |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KLLTLEDKEL | GSGNFGTVKK | GYYQMKKVVK | TVAVKILKNE | ANDPALKDEL | LAEANVMQQL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| DNPYIVRMIG | ICEAESWMLV | MEMAELGPLN | KYLQQNRHVK | DKNIIELVHQ | VSMGMKYLEE |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| CNFVHRDLAA | RNVLLVTQHY | AKISDFGLSK | ALRADENYYK | AQTHGKWPVK | WYAPECINYY |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| KFSSKSDVWS | FGVLMWEAFS | YGQKPYRGMK | GSEVSAMLEK | GERMGCPPGC | PREMYELMTL |
| 610 | 620 | ||||
| CWTYDVENRP | GFVAVELRLR | NYYYDVVN |