Q00495
Gene name |
Csf1r (Csfmr, Fms) |
Protein name |
Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor |
Names |
|
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
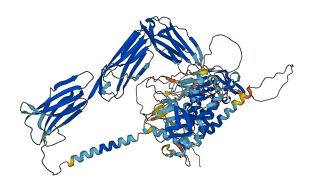
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
793-818 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
580-914 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q00495
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q00495-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q00495
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q00495 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q00495
18 regional properties for Q00495
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 580 - 914 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 580 - 905 | IPR001245 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class III, conserved site | 639 - 652 | IPR001824 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 33 - 91 | IPR003598-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 215 - 285 | IPR003598-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 27 - 102 | IPR003599-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 112 - 196 | IPR003599-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 209 - 296 | IPR003599-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 308 - 397 | IPR003599-4 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 402 - 504 | IPR003599-5 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 21 - 85 | IPR007110-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 104 - 188 | IPR007110-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 203 - 294 | IPR007110-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 400 - 500 | IPR007110-4 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 772 - 784 | IPR008266 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin | 210 - 292 | IPR013151 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 586 - 614 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 580 - 908 | IPR020635 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell body | The portion of a cell bearing surface projections such as axons, dendrites, cilia, or flagella that includes the nucleus, but excludes all cell projections. |
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| CSF1-CSF1R complex | A protein complex consisting of a macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF1, also called M-CSF) dimer bound to a dimerized receptor (CSF1R, also called FMS). Receptor dimerization requires the presence of the ligand. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| perikaryon | The portion of the cell soma (neuronal cell body) that excludes the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| cytokine binding | Binding to a cytokine, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity. |
| macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor activity | Combining with macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) receptor ligand and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein homodimerization activity | Binding to an identical protein to form a homodimer. |
| protein phosphatase binding | Binding to a protein phosphatase. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | Combining with a signal and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate. |
77 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| axon guidance | The chemotaxis process that directs the migration of an axon growth cone to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| cardiac muscle cell proliferation | The expansion of a cardiac muscle cell population by cell division. |
| cell population proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. |
| cell-cell junction maintenance | The maintenance of junctions between cells. |
| cellular response to cytokine stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cytokine stimulus. |
| cellular response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a transforming growth factor beta stimulus. |
| cellular response to tumor necrosis factor | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a tumor necrosis factor stimulus. |
| cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a cytokine to a receptor on the surface of a cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| dentate gyrus development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dentate gyrus over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The dentate gyrus is one of two interlocking gyri of the hippocampus. It contains granule cells, which project to the pyramidal cells and interneurons of the CA3 region of the ammon gyrus. |
| forebrain neuron differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron that will reside in the forebrain. |
| hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation | The process in which precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a hematopoietic progenitor cell, a class of cell types including myeloid progenitor cells and lymphoid progenitor cells. |
| hemopoiesis | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the myeloid and lymphoid derived organ/tissue systems of the blood and other parts of the body over time, from formation to the mature structure. The site of hemopoiesis is variable during development, but occurs primarily in bone marrow or kidney in many adult vertebrates. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of the cytokine macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| microglia development | The process aimed at the progression of a microglial cell over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell. |
| microglial cell activation | The change in morphology and behavior of a microglial cell resulting from exposure to a cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor. |
| microglial cell proliferation | The expansion of a microglial cell population by cell division. |
| monocyte homeostasis | The process of regulating the proliferation and elimination of monocytes such that the total number of monocytes within a whole or part of an organism is stable over time in the absence of an outside stimulus. |
| mononuclear cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a mononuclear cell. |
| myoblast proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of myoblasts, resulting in the expansion of a myoblast cell population. A myoblast is a mononucleate cell type that, by fusion with other myoblasts, gives rise to the myotubes that eventually develop into skeletal muscle fibers. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of cell death | Any process that decreases the rate or frequency of cell death. Cell death is the specific activation or halting of processes within a cell so that its vital functions markedly cease, rather than simply deteriorating gradually over time, which culminates in cell death. |
| negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of epithelial cell differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of epithelial cell differentiation. |
| negative regulation of myotube differentiation | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of myotube differentiation. Myotube differentiation is the process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a myotube cell. Myotubes are multinucleated cells that are formed when proliferating myoblasts exit the cell cycle, differentiate and fuse. |
| negative regulation of platelet formation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of platelet formation. |
| neuron projection extension | Long distance growth of a single neuron projection involved in cellular development. A neuron projection is a prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| neutrophil homeostasis | The process of regulating the proliferation and elimination of neutrophils such that the total number of neutrophils within a whole or part of an organism is stable over time in the absence of an outside stimulus. |
| olfactory bulb development | The progression of the olfactory bulb over time from its initial formation until its mature state. The olfactory bulb coordinates neuronal signaling involved in the perception of smell. It receives input from the sensory neurons and outputs to the olfactory cortex. |
| osteoclast differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized monocyte acquires the specialized features of an osteoclast. An osteoclast is a specialized phagocytic cell associated with the absorption and removal of the mineralized matrix of bone tissue. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| phosphatidylinositol metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphatidylinositol, any glycophospholipid in which a sn-glycerol 3-phosphate residue is esterified to the 1-hydroxyl group of 1D-myo-inositol. |
| phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling | The series of molecular signals in which a cell uses a phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling to convert a signal into a response. Phosphatidylinositols include phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) and its phosphorylated derivatives. |
| positive regulation by host of viral process | A process in which a host organism activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the release of a process being mediated by a virus with which it is infected. |
| positive regulation of astrocyte activation | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of astrocyte activation. |
| positive regulation of bone mineralization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of bone mineralization. |
| positive regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition | Any signalling pathway that activates or increases the activity of a cell cycle cyclin-dependent protein kinase to modulate the switch from G1 phase to S phase of the cell cycle. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of cell motility | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell motility. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of chemokine production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of chemokine production. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| positive regulation of leukocyte proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte proliferation. |
| positive regulation of lymphocyte proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of lymphocyte proliferation. |
| positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of macrophage chemotaxis. Macrophage chemotaxis is the movement of a macrophage in response to an external stimulus. |
| positive regulation of macrophage migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage migration. |
| positive regulation of macrophage proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage proliferation. |
| positive regulation of myoblast proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of myoblast proliferation. |
| positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of osteoclast differentiation. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of protein serine/threonine kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of protein tyrosine kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of tumor necrosis factor production. |
| positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the introduction of a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue of a STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) protein. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of actin cytoskeleton reorganization. |
| regulation of bone resorption | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone tissue loss (resorption). |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| regulation of gene expression | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| regulation of inflammatory response | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response, the immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. |
| regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of mononuclear cell proliferation. |
| response to axon injury | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an axon injury stimulus. |
| response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
| response to ischemia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a inadequate blood supply. |
| response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| response to mechanical stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a mechanical stimulus. |
| response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| response to organonitrogen compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organonitrogen stimulus. An organonitrogen compound is formally a compound containing at least one carbon-nitrogen bond. |
| ruffle organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a ruffle, a projection at the leading edge of a crawling cell. |
| skeletal muscle cell proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of skeletal muscle cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. |
| skeletal muscle tissue development | The developmental sequence of events leading to the formation of adult skeletal muscle tissue. The main events are: the fusion of myoblasts to form myotubes that increase in size by further fusion to them of myoblasts, the formation of myofibrils within their cytoplasm and the establishment of functional neuromuscular junctions with motor neurons. At this stage they can be regarded as mature muscle fibers. |
| tooth eruption | The tooth development process in which the teeth enter the mouth and become visible. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
27 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P13369 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| P07333 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P09581 | Csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| G3V9H8 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62838 | Musk | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63474 | Ddr1 | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63604 | Ntrk2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P35739 | Ntrk1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q03351 | Ntrk3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q91ZT1 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P53767 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O08775 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q64716 | Insrr | Insulin receptor-related protein | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P24062 | Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P15127 | Insr | Insulin receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q04589 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q498D6 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P57097 | Mertk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P97523 | Met | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P06494 | Erbb2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62956 | Erbb4 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62799 | Erbb3 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q05030 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P20786 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9S9M2 | WAKL4 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q7X8C5 | WAKL2 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9I8N6 | csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MELGPPLVLL | LATVWHGQGA | PVIEPSGPEL | VVEPGETVTL | RCVSNGSVEW | DGPISPYWTL |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| DPESPGSTLT | TRNATFKNTG | TYRCTELEDP | MAGSTTIHLY | VKDPAHSWNL | LAQEVTVVEG |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QEAVLPCLIT | DPALKDSVSL | MREGGRQVLR | KTVYFFSAWR | GFIIRKAKVL | DSNTYVCKTM |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| VNGRESTSTG | IWLKVNRVHP | EPPQIKLEPS | KLVRIRGEAA | QIVCSATNAE | VGFNVILKRG |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| DTKLEIPLNS | DFQDNYYKKV | RALSLNAVDF | QDAGIYSCVA | SNDVGTRTAT | MNFQVVESAY |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LNLTSEQSLL | QEVSVGDSLI | LTVHADAYPS | IQHYNWTYLG | PFFEDQRKLE | FITQRAIYRY |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| TFKLFLNRVK | ASEAGQYFLM | AQNKAGWNNL | TFELTLRYPP | EVSVTWMPVN | GSDVLFCDVS |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| GYPQPSVTWM | ECRGHTDRCD | EAQALQVWND | THPEVLSQKP | FDKVIIQSQL | PIGTLKHNMT |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| YFCKTHNSVG | NSSQYFRAVS | LGQSKQLPDE | SLFTPVVVAC | MSVMSLLVLL | LLLLLYKYKQ |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| KPKYQVRWKI | IERYEGNSYT | FIDPTQLPYN | EKWEFPRNNL | QFGKTLGAGA | FGKVVEATAF |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| GLGKEDAVLK | VAVKMLKSTA | HADEKEALMS | ELKIMSHLGQ | HENIVNLLGA | CTHGGPVLVI |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| TEYCCYGDLL | NFLRRKAEAM | LGPSLSPGQD | SEGDSSYKNI | HLEKKYVRRD | SGFSSQGVDT |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| YVEMRPVSTS | SSDSFFKQDL | DKEPSRPLEL | WDLLHFSSQV | AQGMAFLASK | NCIHRDVAAR |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| NVLLTSGHVA | KIGDFGLARD | IMNDSNYVVK | GNARLPVKWM | APESILYCVY | TVQSDVWSYG |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| ILLWEIFSLG | LNPYPGILVN | NKFYKLVKDG | YQMAQPVFAP | KNIYSIMQSC | WDLEPTRRPT |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| FQQICFLLQE | QARLERRDQD | YANLPSSGGS | SGSDSGGGSS | GGSSSEPEEE | SSSEHLACCE |
| 970 | |||||
| PGDIAQPLLQ | PNNYQFAC |