P97814
Gene name |
Pstpip1 |
Protein name |
Proline-serine-threonine phosphatase-interacting protein 1 |
Names |
PEST phosphatase-interacting protein 1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:19200 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
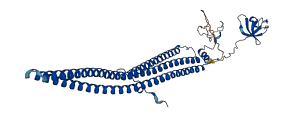
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P97814
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P97814-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P97814
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P97814 | |||||
No associated diseases with P97814
Functions
10 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament | A filamentous structure formed of a two-stranded helical polymer of the protein actin and associated proteins. Actin filaments are a major component of the contractile apparatus of skeletal muscle and the microfilaments of the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. The filaments, comprising polymerized globular actin molecules, appear as flexible structures with a diameter of 5-9 nm. They are organized into a variety of linear bundles, two-dimensional networks, and three dimensional gels. In the cytoskeleton they are most highly concentrated in the cortex of the cell just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| actomyosin contractile ring | A cytoskeletal structure composed of actin filaments and myosin that forms beneath the plasma membrane of many cells, including animal cells and yeast cells, in a plane perpendicular to the axis of the spindle, i.e. the cell division plane. In animal cells, the contractile ring is located at the cleavage furrow. In budding fungal cells, e.g. mitotic S. cerevisiae cells, the contractile ring forms at the mother-bud neck before mitosis. |
| cleavage furrow | The cleavage furrow is a plasma membrane invagination at the cell division site. The cleavage furrow begins as a shallow groove and eventually deepens to divide the cytoplasm. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| lamellipodium | A thin sheetlike process extended by the leading edge of a migrating cell or extending cell process; contains a dense meshwork of actin filaments. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| stress fiber | A contractile actin filament bundle that consists of short actin filaments with alternating polarity, cross-linked by alpha-actinin and possibly other actin bundling proteins, and with myosin present in a periodic distribution along the fiber. |
| uropod | A membrane projection with related cytoskeletal components at the trailing edge of a cell in the process of migrating or being activated, found on the opposite side of the cell from the leading edge or immunological synapse, respectively. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin binding | Binding to monomeric or multimeric forms of actin, including actin filaments. |
| actin filament binding | Binding to an actin filament, also known as F-actin, a helical filamentous polymer of globular G-actin subunits. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| protein phosphatase binding | Binding to a protein phosphatase. |
5 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament polymerization | Assembly of actin filaments by the addition of actin monomers to a filament. |
| cell adhesion | The attachment of a cell, either to another cell or to an underlying substrate such as the extracellular matrix, via cell adhesion molecules. |
| endocytosis | A vesicle-mediated transport process in which cells take up external materials or membrane constituents by the invagination of a small region of the plasma membrane to form a new membrane-bounded vesicle. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
10 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q05080 | HOF1 | Cytokinesis protein 2 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q9BQI5 | SGIP1 | SH3-containing GRB2-like protein 3-interacting protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9H939 | PSTPIP2 | Proline-serine-threonine phosphatase-interacting protein 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O60861 | GAS7 | Growth arrest-specific protein 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8VD37 | Sgip1 | SH3-containing GRB2-like protein 3-interacting protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q99JB8 | Pacsin3 | Protein kinase C and casein kinase II substrate protein 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61644 | Pacsin1 | Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q9WVE8 | Pacsin2 | Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q99M15 | Pstpip2 | Proline-serine-threonine phosphatase-interacting protein 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60780 | Gas7 | Growth arrest-specific protein 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MMAQLQFRDA | FWCRDFTAHT | GYEVLLQRLL | DGRKMCKDVE | ELLRQRAQAE | ERYGKELVQI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ARKAGGQTEM | NSLRTSFDSL | KQQTENVGSA | HIQLALALRE | ELRSLEEFRE | RQKEQRKKYE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| AIMDRVQKSK | LSLYKKTMES | KKAYDQKCRD | ADDAEQAFER | VSANGHQKQV | EKSQNKAKQC |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| KESATEAERV | YRQNIEQLER | ARTEWEQEHR | TTCEAFQLQE | FDRLTILRNA | LWVHCNQLSM |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| QCVKDDELYE | EVRLTLEGCD | VEGDINGFIQ | SKSTGREPPA | PVPYQNYYDR | EVTPLIGSPS |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| IQPSCGVIKR | FSGLLHGSPK | TTPSAPAAST | ETLTPTPERN | ELVYASIEVQ | ATQGNLNSSA |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | |
| QDYRALYDYT | AQNSDELDIS | AGDILAVILE | GEDGWWTVER | NGQRGFVPGS | YLEKL |