P97367
Gene name |
Meis2 (Mrg1, Stra10) |
Protein name |
Homeobox protein Meis2 |
Names |
Meis1-related protein 1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:17536 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
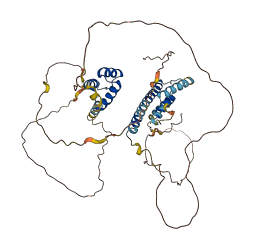
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
340-470 (C-terminal transcriptional activation domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P97367
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P97367-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P97367
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P97367 | |||||
No associated diseases with P97367
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that activates or increases transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
| sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA, e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
| transcription factor binding | Binding to a transcription factor, a protein required to initiate or regulate transcription. |
14 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| animal organ morphogenesis | Morphogenesis of an animal organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process in which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions. |
| brain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.). |
| embryonic pattern specification | The process that results in the patterns of cell differentiation that will arise in an embryo. |
| eye development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the eye over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The eye is the organ of sight. |
| negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of myeloid cell differentiation. |
| pancreas development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the pancreas over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The pancreas is an endoderm derived structure that produces precursors of digestive enzymes and blood glucose regulating enzymes. |
| positive regulation of cardiac muscle myoblast proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cardiac muscle myoblast proliferation. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of progression through the mitotic cell cycle. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| response to growth factor | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a growth factor stimulus. |
| response to mechanical stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a mechanical stimulus. |
| visual learning | Any process in an organism in which a change in behavior of an individual occurs in response to repeated exposure to a visual cue. |
10 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8MIB7 | TGIF2LX | Homeobox protein TGIF2LX | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | PR |
| O00470 | MEIS1 | Homeobox protein Meis1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q8IUE1 | TGIF2LX | Homeobox protein TGIF2LX | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O14770 | MEIS2 | Homeobox protein Meis2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O35984 | Pbx2 | Pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P97368 | Meis3 | Homeobox protein Meis3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q75LX9 | Os03g0673500 | Putative homeobox protein knotted-1-like 5 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q75LX7 | OSH10 | Homeobox protein knotted-1-like 4 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q1PFD1 | BLH11 | BEL1-like homeodomain protein 11 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SIW1 | BLH7 | BEL1-like homeodomain protein 7 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAQRYDELPH | YGGMDGVGVP | ASMYGDPHAP | RPIPPVHHLN | HGPPLHATQH | YGAHAPHPNV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| MPASMGSAVN | DALKRDKDAI | YGHPLFPLLA | LVFEKCELAT | CTPREPGVAG | GDVCSSDSFN |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| EDIAVFAKQV | RAEKPLFSSN | PELDNLMIQA | IQVLRFHLLE | LEKVHELCDN | FCHRYISCLK |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GKMPIDLVID | ERDGSSKSDH | EELSGSSTNL | ADHNPSSWRD | HDDATSTHSA | GTPGPSSGGH |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| ASQSGDNSSE | QGDGLDNSVA | SPGTGDDDDP | DKDKKRQKKR | GIFPKVATNI | MRAWLFQHLT |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| HPYPSEEQKK | QLAQDTGLTI | LQVNNWFINA | RRRIVQPMID | QSNRAGFLLD | PSVSQGAAYS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| PEGQPMGSFV | LDGQQHMGIR | PAGLQSMPGD | YVSQGGPMGM | GMAQPSYTPP | QMTPHPTQLR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | |
| HGPPMHSYLP | SHPHHPAMVM | HGGPPTHPGM | TMSAQSPTML | NSVDPNVGGQ | VMDIHAQ |