P87378
Gene name |
crk |
Protein name |
Adapter molecule crk |
Names |
CRK2, SH2/SH3 adaptor crk |
Species |
Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) |
KEGG Pathway |
xla:398951 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
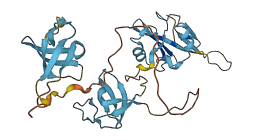
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
125-185 (N-terminal SH3 domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Kobashigawa Y et al. (2007) "Structural basis for the transforming activity of human cancer-related signaling adaptor protein CRK", Nature structural & molecular biology, 14, 503-10
- Ogawa S et al. (1994) "The C-terminal SH3 domain of the mouse c-Crk protein negatively regulates tyrosine-phosphorylation of Crk associated p130 in rat 3Y1 cells", Oncogene, 9, 1669-78
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P87378
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P87378-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P87378
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P87378 | |||||
No associated diseases with P87378
8 regional properties for P87378
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | FERM domain | 12 - 305 | IPR000299 |
| domain | Ezrin/radixin/moesin, C-terminal | 560 - 635 | IPR011259 |
| domain | FERM, N-terminal | 20 - 76 | IPR018979 |
| domain | FERM, C-terminal PH-like domain | 220 - 309 | IPR018980 |
| domain | FERM central domain | 101 - 216 | IPR019748 |
| domain | Band 4.1 domain | 8 - 216 | IPR019749 |
| domain | ERM family, FERM domain C-lobe | 210 - 306 | IPR041789 |
| domain | Ezrin/radixin/moesin, alpha-helical domain | 340 - 459 | IPR046810 |
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
No GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| No GO annotations for molecular function |
3 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ephrin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by ephrin binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of GTPase activity | Any process that modulates the rate of GTP hydrolysis by a GTPase. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAGNFDSEDR | ASWYWGKQNR | QEAVNLLQGQ | RHGVFLVRDS | TTIPGDYVLS | VSENSKVSHY |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| IINSVTNNRQ | SSTAGMVQSR | FRIGDQEFDS | LPTLLEFYKI | HYLDTTTLIE | PVSKSKQSGV |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| IQRQEEVEYL | RALFDFIGND | DEDLPFKKGD | ILRIREKPEE | QWWNAEDSDG | RRGMIPVPYV |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| EKYRPPSSPG | SALIGGNQEN | SHPQPLGGPE | PGPYAQPSVN | TPLPNLQNGP | IFARVIQKRV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | |
| PNAYDKTALA | LEVGDLVKVT | KINVSGQWEG | ECNGKYGHFP | FTHVRLLEQN | PEEDFS |