P68403
Gene name |
Prkcb (Pkcb, Prkcb1) |
Protein name |
Protein kinase C beta type |
Names |
PKC-B , PKC-beta , EC 2.7.11.13 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:25023 |
EC number |
2.7.11.13: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
344-586 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
344-586 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
483-506 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
341-664 (Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Classical Protein Kinase C beta) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
483-506 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
341-664 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Steinberg SF (2008) "Structural basis of protein kinase C isoform function", Physiological reviews, 88, 1341-78
- Sommese RF et al. (2017) "The Role of Regulatory Domains in Maintaining Autoinhibition in the Multidomain Kinase PKCα", The Journal of biological chemistry, 292, 2873-2880
- Pears CJ et al. (1990) "Mutagenesis of the pseudosubstrate site of protein kinase C leads to activation", European journal of biochemistry, 194, 89-94
- Smith MK et al. (1990) "Specificities of autoinhibitory domain peptides for four protein kinases. Implications for intact cell studies of protein kinase function", The Journal of biological chemistry, 265, 1837-40
- Slater SJ et al. (2002) "Regulation of PKC alpha activity by C1-C2 domain interactions", The Journal of biological chemistry, 277, 15277-85
- Jones AC et al. (2020) "Hypothesis: Unifying model of domain architecture for conventional and novel protein kinase C isozymes", IUBMB life, 72, 2584-2590
- Kirwan AF et al. (2003) "Inhibition of protein kinase C catalytic activity by additional regions within the human protein kinase Calpha-regulatory domain lying outside of the pseudosubstrate sequence", The Biochemical journal, 373, 571-81
- Huang X et al. (2003) "Crystal structure of an inactive Akt2 kinase domain", Structure (London, England : 1993), 11, 21-30
- Truebestein L et al. (2021) "Structure of autoinhibited Akt1 reveals mechanism of PIP(3)-mediated activation", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 118,
- Lučić I et al. (2018) "Conformational sampling of membranes by Akt controls its activation and inactivation", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115, E3940-E3949
- Wagner J et al. (2009) "Discovery of 3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-4-[2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)quinazolin-4-yl]pyrrole-2,5-dione (AEB071), a potent and selective inhibitor of protein kinase C isotypes", Journal of medicinal chemistry, 52, 6193-6
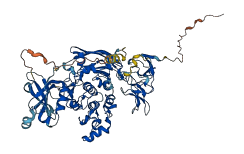
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

3 structures for P68403
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A25 | X-ray | 270 A | A/B | 154-289 | PDB |
| 3PFQ | X-ray | 400 A | A | 1-661 | PDB |
| AF-P68403-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P68403
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P68403 | |||||
No associated diseases with P68403
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.13 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
11 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| brush border membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding the brush border. |
| calyx of Held | The terminal specialization of a calyciferous axon which forms large synapses in the mammalian auditory central nervous system. |
| centrosome | A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it and attached to it. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| presynapse | The part of a synapse that is part of the presynaptic cell. |
| presynaptic cytosol | The region of the cytosol consisting of all cytosol that is part of the presynapse. |
| spectrin | Membrane associated dimeric protein (240 and 220 kDa) of erythrocytes. Forms a complex with ankyrin, actin and probably other components of the membrane cytoskeleton, so that there is a mesh of proteins underlying the plasma membrane, potentially restricting the lateral mobility of integral proteins. |
12 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| calcium channel regulator activity | Modulates the activity of a calcium channel. |
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| diacylglycerol-dependent serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| histone binding | Binding to a histone, any of a group of water-soluble proteins found in association with the DNA of eukaryotic or archaeal chromosomes. They are involved in the condensation and coiling of chromosomes during cell division and have also been implicated in gene regulation and DNA replication. They may be chemically modified (methylated, acetlyated and others) to regulate gene transcription. |
| histone H3T6 kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| nuclear androgen receptor binding | Binding to a nuclear androgen receptor. |
| nuclear receptor coactivator activity | A transcription coactivator activity that activates or increases the transcription of specific gene sets via binding to a DNA-bound nuclear receptor, either on its own or as part of a complex. Coactivators often act by altering chromatin structure and modifications. For example, one class of transcription coregulators modifies chromatin structure through covalent modification of histones. A second class remodels the conformation of chromatin in an ATP-dependent fashion. A third class modulates interactions of DNA-bound DNA-binding transcription factors with other transcription coregulators. A fourth class of coactivator activity is the bridging of a DNA-binding transcription factor to the general (basal) transcription machinery. The Mediator complex, which bridges sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factors and RNA polymerase, is also a transcription coactivator. |
| protein kinase C binding | Binding to protein kinase C. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
| zinc ion binding | Binding to a zinc ion (Zn). |
30 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adaptive immune response | An immune response mediated by cells expressing specific receptors for antigens produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for an enhanced secondary response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). |
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| B cell activation | The change in morphology and behavior of a mature or immature B cell resulting from exposure to a mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or an antigen for which it is specific. |
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a B cell. |
| calcium ion transport | The directed movement of calcium (Ca) ions into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| cellular response to carbohydrate stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a carbohydrate stimulus. |
| dibenzo-p-dioxin metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving dibenzo-p-dioxin, a substance composed of two benzene rings linked by two ether bonds. Dibenzo-p-dioxins are generated as by-products in the manufacturing of herbicides, insecticides, fungicides, paper pulp bleaching, and in incineration, and can accumulate in milk and throughout the food chain, creating significant health concern. |
| intracellular calcium ion homeostasis | A homeostatic process involved in the maintenance of a steady state level of calcium ions within a cell. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| negative regulation of glucose transmembrane transport | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of glucose transport across a membrane. Glucose transport is the directed movement of the hexose monosaccharide glucose into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of insulin receptor signaling. |
| phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway | A phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway initiated by acetylcholine binding to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| positive regulation of angiogenesis | Any process that activates or increases angiogenesis. |
| positive regulation of B cell receptor signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signaling pathways initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a B cell. |
| positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| positive regulation of insulin secretion | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of insulin. |
| positive regulation of odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the formation and development of teeth, the hard, bony appendages that are borne on the jaws, or on other bones in the walls of the mouth or pharynx of most vertebrates. |
| positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway activity. |
| post-translational protein modification | The process of covalently altering one or more amino acids in a protein after the protein has been completely translated and released from the ribosome. |
| presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission | Any process, acting in the presynapse that results in modulation of chemical synaptic transmission. |
| regulation of dopamine secretion | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of dopamine. |
| regulation of glucose transmembrane transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of glucose transport across a membrane. Glucose transport is the directed movement of the hexose monosaccharide glucose into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| regulation of growth | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the growth of all or part of an organism so that it occurs at its proper speed, either globally or in a specific part of the organism's development. |
| regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| response to ethanol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ethanol stimulus. |
| response to glucose | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucose stimulus. |
| response to vitamin D | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a vitamin D stimulus. |
| response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
28 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P24583 | PKC1 | Protein kinase C-like 1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | SS |
| P04409 | PRKCA | Protein kinase C alpha type | Bos taurus (Bovine) | EV SS |
| P05128 | PRKCG | Protein kinase C gamma type | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P05126 | PRKCB | Protein kinase C beta type | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P13677 | inaC | Protein kinase C, eye isozyme | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P05130 | Pkc53E | Protein kinase C, brain isozyme | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P05129 | PRKCG | Protein kinase C gamma type | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P17252 | PRKCA | Protein kinase C alpha type | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P05771 | PRKCB | Protein kinase C beta type | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P20444 | Prkca | Protein kinase C alpha type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P63318 | Prkcg | Protein kinase C gamma type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P68404 | Prkcb | Protein kinase C beta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05696 | Prkca | Protein kinase C alpha type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P63319 | Prkcg | Protein kinase C gamma type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O55173 | Pdpk1 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09217 | Prkcz | Protein kinase C zeta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1M7Y5 | Prkci | Protein kinase C iota type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63433 | Pkn1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08874 | Pkn2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q64617 | Prkch | Protein kinase C eta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P09216 | Prkce | Protein kinase C epsilon type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P09215 | Prkcd | Protein kinase C delta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P47197 | Akt2 | RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P47196 | Akt1 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q63484 | Akt3 | RAC-gamma serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P90980 | pkc-2 | Protein kinase C-like 2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| A8KBH6 | prkcb | Protein kinase C beta type | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| Q7SY24 | prkcbb | Protein kinase C beta type | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MADPAAGPPP | SEGEESTVRF | ARKGALRQKN | VHEVKNHKFT | ARFFKQPTFC | SHCTDFIWGF |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GKQGFQCQVC | CFVVHKRCHE | FVTFSCPGAD | KGPASDDPRS | KHKFKIHTYS | SPTFCDHCGS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LLYGLIHQGM | KCDTCMMNVH | KRCVMNVPSL | CGTDHTERRG | RIYIQAHIDR | EVLIVVVRDA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| KNLVPMDPNG | LSDPYVKLKL | IPDPKSESKQ | KTKTIKCSLN | PEWNETFRFQ | LKESDKDRRL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SVEIWDWDLT | SRNDFMGSLS | FGISELQKAG | VDGWFKLLSQ | EEGEYFNVPV | PPEGSEGNEE |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LRQKFERAKI | GQGTKAPEEK | TANTISKFDN | NGNRDRMKLT | DFNFLMVLGK | GSFGKVMLSE |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| RKGTDELYAV | KILKKDVVIQ | DDDVECTMVE | KRVLALPGKP | PFLTQLHSCF | QTMDRLYFVM |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| EYVNGGDLMY | HIQQVGRFKE | PHAVFYAAEI | AIGLFFLQSK | GIIYRDLKLD | NVMLDSEGHI |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| KIADFGMCKE | NIWDGVTTKT | FCGTPDYIAP | EIIAYQPYGK | SVDWWAFGVL | LYEMLAGQAP |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| FEGEDEDELF | QSIMEHNVAY | PKSMSKEAVA | ICKGLMTKHP | GKRLGCGPEG | ERDIKEHAFF |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| RYIDWEKLER | KEIQPPYKPK | ARDKRDTSNF | DKEFTRQPVE | LTPTDKLFIM | NLDQNEFAGF |
| 670 | |||||
| SYTNPEFVIN | V |