P63329
Gene name |
Ppp3ca (Calna) |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit alpha isoform |
Names |
CAM-PRP catalytic subunit, Calmodulin-dependent calcineurin A subunit alpha isoform |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:24674 |
EC number |
3.1.3.16: Phosphoric monoester hydrolases |
Protein Class |
|
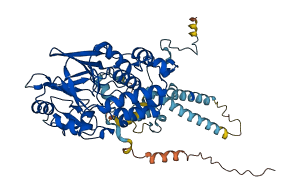
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
84-284 (Calcineurin-like phosphoesterase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
84-284 (Calcineurin-like phosphoesterase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Tokoyoda K et al. (2000) "Synergism between the calmodulin-binding and autoinhibitory domains on calcineurin is essential for the induction of their phosphatase activity", The Journal of biological chemistry, 275, 11728-34
- Li SJ et al. (2016) "Cooperative autoinhibition and multi-level activation mechanisms of calcineurin", Cell research, 26, 336-49
- Rumi-Masante J et al. (2012) "Structural basis for activation of calcineurin by calmodulin", Journal of molecular biology, 415, 307-17
- Kissinger CR et al. (1995) "Crystal structures of human calcineurin and the human FKBP12-FK506-calcineurin complex", Nature, 378, 641-4
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for P63329
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4IL1 | X-ray | 300 A | A/B/C/D | 1-492 | PDB |
| AF-P63329-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
2 variants for P63329
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs197342160 | 274 | L>M | No | Ensembl | |
| rs197342160 | 274 | L>V | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with P63329
5 regional properties for P63329
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 67 - 328 | IPR000719 |
| domain | AGC-kinase, C-terminal | 329 - 399 | IPR000961 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 190 - 202 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 73 - 99 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Protein kinase, C-terminal | 349 - 389 | IPR017892 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.1.3.16 | Phosphoric monoester hydrolases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
14 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| calcineurin complex | A heterodimeric calcium ion and calmodulin dependent protein phosphatase composed of catalytic and regulatory subunits; the regulatory subunit is very similar in sequence to calmodulin. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The leaflet the plasma membrane that faces the cytoplasm and any proteins embedded or anchored in it or attached to its surface. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendritic spine | A small, membranous protrusion from a dendrite that forms a postsynaptic compartment, typically receiving input from a single presynapse. They function as partially isolated biochemical and an electrical compartments. Spine morphology is variable:they can be thin, stubby, mushroom, or branched, with a continuum of intermediate morphologies. They typically terminate in a bulb shape, linked to the dendritic shaft by a restriction. Spine remodeling is though to be involved in synaptic plasticity. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| sarcolemma | The outer membrane of a muscle cell, consisting of the plasma membrane, a covering basement membrane (about 100 nm thick and sometimes common to more than one fiber), and the associated loose network of collagen fibers. |
| Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse | A synapse between the Schaffer collateral axon of a CA3 pyramidal cell and a CA1 pyramidal cell. |
| synapse | The junction between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron, a muscle fiber or a glial cell. As the axon approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic terminal bouton, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the terminal bouton is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic terminal bouton secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
| Z disc | Platelike region of a muscle sarcomere to which the plus ends of actin filaments are attached. |
11 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATPase binding | Binding to an ATPase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP. |
| calcium-dependent protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: protein serine phosphate + H2O = protein serine + phosphate; and protein threonine phosphate + H2O = protein threonine + phosphate. These reactions require the presence of calcium ions. |
| calmodulin binding | Binding to calmodulin, a calcium-binding protein with many roles, both in the calcium-bound and calcium-free states. |
| calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: protein serine/threonine phosphate + H2O = protein serine/threonine + phosphate, dependent on the presence of calcium-bound calmodulin. |
| cyclosporin A binding | Binding to cyclosporin A, a cyclic undecapeptide that contains several N-methylated and unusual amino acids. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| phosphoprotein phosphatase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: a phosphoprotein + H2O = a protein + phosphate. Together with protein kinases, these enzymes control the state of phosphorylation of cellular proteins and thereby provide an important mechanism for regulating cellular activity. |
| protein dimerization activity | The formation of a protein dimer, a macromolecular structure consists of two noncovalently associated identical or nonidentical subunits. |
| protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: protein serine phosphate + H2O = protein serine + phosphate, and protein threonine phosphate + H2O = protein threonine + phosphate. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
36 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| aging | A developmental process that is a deterioration and loss of function over time. Aging includes loss of functions such as resistance to disease, homeostasis, and fertility, as well as wear and tear. Aging includes cellular senescence, but is more inclusive. May precede death and may succeed developmental maturation (GO:0021700). |
| brain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.). |
| calcineurin-mediated signaling | Any intracellular signal transduction in which the signal is passed on within the cell by activation of a transcription factor as a consequence of dephosphorylation by Ca(2+)-activated calcineurin. The process begins with calcium-dependent activation of the phosphatase calcineurin. Calcineurin is a calcium- and calmodulin-dependent serine/threonine protein phosphatase with a conserved function in eukaryotic species from yeast to humans. In yeast and fungi, calcineurin regulates stress signaling and cell cycle, and sporulation and virulence in pathogenic fungi. In metazoans, calcineurin is involved in cell commitment, organogenesis and organ development and immune function of T-lymphocytes. By a conserved mechanism, calcineurin phosphatase activates fungal Crz1 and mammalian NFATc by dephosphorylation and translocation of these transcription factors to the nucleus to regulate gene expression. |
| calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade | Any intracellular signal transduction in which the signal is passed on within the cell by activation of a member of the NFAT protein family as a consequence of NFAT dephosphorylation by Ca(2+)-activated calcineurin. The cascade begins with calcium-dependent activation of the phosphatase calcineurin. Calcineurin dephosphorylates multiple phosphoserine residues on NFAT, resulting in the translocation of NFAT to the nucleus. The cascade ends with regulation of transcription by NFAT. The calcineurin-NFAT cascade lies downstream of many cell surface receptors, including G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) that signal to mobilize calcium ions (Ca2+). |
| calcium ion transport | The directed movement of calcium (Ca) ions into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| calcium-mediated signaling | Any intracellular signal transduction in which the signal is passed on within the cell via calcium ions. |
| cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress | The physiological enlargement or overgrowth of all or part of the heart muscle due to an increase in size (not length) of individual cardiac muscle fibers, without cell division, as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis. |
| cellular response to glucose stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucose stimulus. |
| dephosphorylation | The process of removing one or more phosphoric (ester or anhydride) residues from a molecule. |
| excitatory postsynaptic potential | A process that leads to a temporary increase in postsynaptic potential due to the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell. The flow of ions that causes an EPSP is an excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) and makes it easier for the neuron to fire an action potential. |
| G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle | The mitotic cell cycle transition by which a cell in G1 commits to S phase. The process begins with the build up of G1 cyclin-dependent kinase (G1 CDK), resulting in the activation of transcription of G1 cyclins. The process ends with the positive feedback of the G1 cyclins on the G1 CDK which commits the cell to S phase, in which DNA replication is initiated. |
| modulation of chemical synaptic transmission | Any process that modulates the frequency or amplitude of synaptic transmission, the process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse. Amplitude, in this case, refers to the change in postsynaptic membrane potential due to a single instance of synaptic transmission. |
| multicellular organismal response to stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a multicellular organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation). |
| negative regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis. |
| negative regulation of chromatin binding | Any process that stops or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of chromatin binding. Chromatin binding is the selective interaction with chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| negative regulation of dendrite morphogenesis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of dendrite morphogenesis. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| negative regulation of insulin secretion | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of insulin. |
| negative regulation of production of miRNAs involved in gene silencing by miRNA | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of maturation of miRNAs. |
| peptidyl-serine dephosphorylation | The removal of phosphoric residues from peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine to form peptidyl-serine. |
| positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the enlargement or overgrowth of all or part of the heart due to an increase in size (not length) of individual cardiac muscle fibers, without cell division. |
| positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress. |
| positive regulation of cell adhesion | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell adhesion. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of connective tissue replacement | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of connective tissue replacement. |
| positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activity of a transcription factor, any factor involved in the initiation or regulation of transcription. |
| positive regulation of endocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of endocytosis. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission | Any process, acting in the postsynapse that results in modulation of chemical synaptic transmission. |
| protein dephosphorylation | The process of removing one or more phosphoric residues from a protein. |
| protein import into nucleus | The directed movement of a protein from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. |
| response to amphetamine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an amphetamine stimulus. Amphetamines consist of a group of compounds related to alpha-methylphenethylamine. |
| response to calcium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a calcium ion stimulus. |
| skeletal muscle fiber development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeletal muscle fiber over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Muscle fibers are formed by the maturation of myotubes. They can be classed as slow, intermediate/fast or fast. |
| transition between fast and slow fiber | The process of conversion of fast-contracting muscle fibers to a slower character. This may involve slowing of contractile rate, slow myosin gene induction, increase in oxidative metabolic properties, altered electrophysiology and altered innervation. This process also regulates skeletal muscle adapatation. |
13 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P23287 | CNA1 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit A1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| P48452 | PPP3CA | Protein phosphatase 3 catalytic subunit alpha | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q27889 | Pp2B-14D | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit 2 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P48456 | CanA1 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9VXF1 | CanA-14F | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit 3 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P16298 | PPP3CB | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit beta isoform | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P48454 | PPP3CC | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit gamma isoform | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q08209 | PPP3CA | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit alpha isoform | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P48455 | Ppp3cc | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit gamma isoform | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P48453 | Ppp3cb | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit beta isoform | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P63328 | Ppp3ca | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit alpha isoform | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P20651 | Ppp3cb | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit beta isoform | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q0G819 | tax-6 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B catalytic subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSEPKAIDPK | LSTTDRVVKA | VPFPPSHRLT | AKEVFDNDGK | PRVDILKAHL | MKEGRLEESV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ALRIITEGAS | ILRQEKNLLD | IDAPVTVCGD | IHGQFFDLMK | LFEVGGSPAN | TRYLFLGDYV |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DRGYFSIECV | LYLWALKILY | PKTLFLLRGN | HECRHLTEYF | TFKQECKIKY | SERVYDACMD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| AFDCLPLAAL | MNQQFLCVHG | GLSPEINTLD | DIRKLDRFKE | PPAYGPMCDI | LWSDPLEDFG |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NEKTQEHFTH | NTVRGCSYFY | SYPAVCDFLQ | HNNLLSILRA | HEAQDAGYRM | YRKSQTTGFP |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| SLITIFSAPN | YLDVYNNKAA | VLKYENNVMN | IRQFNCSPHP | YWLPNFMDVF | TWSLPFVGEK |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VTEMLVNVLN | ICSDDELGSE | EDGFDGATAA | ARKEVIRNKI | RAIGKMARVF | SVLREESESV |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LTLKGLTPTG | MLPSGVLSGG | KQTLQSATVE | AIEADEAIKG | FSPQHKITSF | EEAKGLDRIN |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | ||
| ERMPPRRDAM | PSDANLNSIN | KALASETNGT | DSNGSNSSNI | Q |