P63165
Gene name |
SUMO1 (SMT3C, SMT3H3, UBL1, OK/SW-cl.43) |
Protein name |
Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 |
Names |
SUMO-1, GAP-modifying protein 1, GMP1, SMT3 homolog 3, Sentrin, Ubiquitin-homology domain protein PIC1, Ubiquitin-like protein SMT3C, Smt3C, Ubiquitin-like protein UBL1 |
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:7341 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
SMALL UBIQUITIN-RELATED MODIFIER (PTHR10562) |
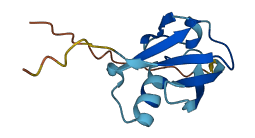
Descriptions
The N-terminal region of SUMO1 functions as an autoinhibition domain by blocking its binding to the phosphorylated SIMs of PML and Daxx. This autoinhibition is relieved by zinc, which stabilizes the complex between SUMO1 and a phospho-mimetic form of the SIM of PML, suggesting a paralog specific function of SUMO1 in regulating SUMO1-SIM interactions required for PML-NB formation and function.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
20-97 (Ubiquitin-like domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure
61 structures for P63165
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A5R | NMR | - | A | 1-101 | PDB |
| 1TGZ | X-ray | 280 A | B | 18-97 | PDB |
| 1WYW | X-ray | 210 A | B | 1-97 | PDB |
| 1Y8R | X-ray | 275 A | C/F | 1-97 | PDB |
| 1Z5S | X-ray | 301 A | B | 18-97 | PDB |
| 2ASQ | NMR | - | A | 1-97 | PDB |
| 2BF8 | X-ray | 230 A | B | 21-97 | PDB |
| 2G4D | X-ray | 280 A | B/D | 20-97 | PDB |
| 2IO2 | X-ray | 290 A | B | 18-97 | PDB |
| 2IY0 | X-ray | 277 A | B | 20-101 | PDB |
| 2IY1 | X-ray | 246 A | B/D | 20-101 | PDB |
| 2KQS | NMR | - | A | 1-97 | PDB |
| 2LAS | NMR | - | A | 1-101 | PDB |
| 2MW5 | NMR | - | A | 1-97 | PDB |
| 2N1A | NMR | - | A | 1-101 | PDB |
| 2N1V | NMR | - | A | 1-97 | PDB |
| 2PE6 | X-ray | 240 A | B | 1-97 | PDB |
| 2UYZ | X-ray | 140 A | B | 20-97 | PDB |
| 2VRR | X-ray | 222 A | B | 20-97 | PDB |
| 3KYC | X-ray | 245 A | D | 1-97 | PDB |
| 3KYD | X-ray | 261 A | D | 1-94 | PDB |
| 3RZW | X-ray | 215 A | C/D | 1-97 | PDB |
| 3UIP | X-ray | 229 A | B | 18-97 | PDB |
| 4WJN | X-ray | 150 A | A | 17-97 | PDB |
| 4WJO | X-ray | 146 A | A | 17-97 | PDB |
| 4WJP | X-ray | 170 A | A/C | 17-97 | PDB |
| 4WJQ | X-ray | 135 A | A/C | 17-97 | PDB |
| 5AEK | X-ray | 300 A | B/D/F/H/J/L/N/P/R/T/V/X | 20-97 | PDB |
| 5B7A | NMR | - | A | 1-97 | PDB |
| 5ELJ | X-ray | 198 A | B | 18-97 | PDB |
| 5GHD | NMR | - | A | 1-97 | PDB |
| 6EOP | X-ray | 240 A | D/E/F | 61-68 | PDB |
| 6EOT | X-ray | 350 A | C/E/F/H/J/L | 61-68 | PDB |
| 6J4I | NMR | - | A | 1-97 | PDB |
| 6JXU | NMR | - | A | 1-101 | PDB |
| 6JXV | NMR | - | A | 1-101 | PDB |
| 6K5T | NMR | - | A | 21-97 | PDB |
| 6TRW | X-ray | 300 A | D/E/F | 61-75 | PDB |
| 6UYO | X-ray | 164 A | A/C | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6UYP | X-ray | 142 A | A | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6UYQ | X-ray | 150 A | A | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6UYR | X-ray | 130 A | A | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6UYS | X-ray | 159 A | A/C | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6UYT | X-ray | 166 A | A | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6UYU | X-ray | 166 A | A/C | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6UYV | X-ray | 140 A | A | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6UYX | X-ray | 170 A | A/C | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6UYY | X-ray | 160 A | A | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6UYZ | X-ray | 140 A | A/C | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6V7P | X-ray | 140 A | A/C | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6V7Q | X-ray | 135 A | A/C | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6V7R | X-ray | 155 A | A/C | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6V7S | X-ray | 147 A | A/C | 17-97 | PDB |
| 6WW3 | X-ray | 210 A | A/B | 2-7 | PDB |
| 6XOG | X-ray | 198 A | C | 1-101 | PDB |
| 6XOH | X-ray | 223 A | C | 1-101 | PDB |
| 6XOI | X-ray | 200 A | C | 1-101 | PDB |
| 8DJH | X-ray | 177 A | A | 2-97 | PDB |
| 8DJI | X-ray | 197 A | A | 2-97 | PDB |
| 8ODR | X-ray | 285 A | B | 18-97 | PDB |
| AF-P63165-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
46 variants for P63165
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs142025459 | 2 | S>C | No |
ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| rs1360385299 | 3 | D>A | No | gnomAD | |
| rs1183133930 | 3 | D>E | No | TOPMed | |
| rs1246545175 | 4 | Q>H | No | TOPMed | |
| TCGA novel | 5 | E>R | Variant assessed as Somatic; HIGH impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| rs865944351 | 6 | A>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs1466085744 | 6 | A>V | No | gnomAD | |
| TCGA novel | 7 | K>E | Variant assessed as Somatic; MODERATE impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| rs762396174 | 7 | K>Q | No |
ExAC gnomAD |
|
| rs1258744066 | 8 | P>L | No | gnomAD | |
| COSM4833179 | 9 | S>* | Variant assessed as Somatic; HIGH impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA Cosmic |
| TCGA novel | 15 | D>I | Variant assessed as Somatic; HIGH impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| COSM1134537 | 16 | K>N | Variant assessed as Somatic; MODERATE impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA Cosmic |
| rs769332103 | 19 | G>D | No |
ExAC gnomAD |
|
| rs769332103 | 19 | G>V | No |
ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1279066314 COSM4583094 |
20 | E>D | Variant assessed as Somatic; MODERATE impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
gnomAD NCI-TCGA Cosmic |
| rs952329386 | 23 | K>T | No | TOPMed | |
| TCGA novel | 26 | V>A | Variant assessed as Somatic; MODERATE impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| rs998380889 | 27 | I>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs1286710471 | 28 | G>R | No | gnomAD | |
| COSM1134536 | 30 | D>H | Variant assessed as Somatic; MODERATE impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA Cosmic |
| rs139098088 | 41 | T>I | No |
ESP TOPMed |
|
| rs1235297281 | 45 | K>E | No | gnomAD | |
| TCGA novel | 49 | E>* | Variant assessed as Somatic; HIGH impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| COSM1482659 | 50 | S>* | Variant assessed as Somatic; HIGH impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA Cosmic |
| rs759040827 | 55 | Q>E | No |
ExAC gnomAD |
|
| COSM5917805 | 56 | G>S | Variant assessed as Somatic; MODERATE impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA Cosmic |
| rs1293611839 | 57 | V>I | No | gnomAD | |
| COSM3576399 | 58 | P>L | Variant assessed as Somatic; MODERATE impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA Cosmic |
| rs757518063 | 59 | M>L | No |
ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| rs757518063 | 59 | M>V | No |
ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| rs751409542 | 62 | L>F | No |
ExAC gnomAD |
|
| rs1559240018 | 62 | L>P | No | Ensembl | |
| TCGA novel | 70 | R>I | Variant assessed as Somatic; MODERATE impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| rs758112346 | 75 | H>R | No |
ExAC gnomAD |
|
| COSM1591707 | 79 | E>* | Variant assessed as Somatic; HIGH impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA Cosmic |
| TCGA novel | 81 | G>E | Variant assessed as Somatic; HIGH impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| rs753349557 | 82 | M>V | No |
ExAC gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 84 | E>* | Variant assessed as Somatic; HIGH impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| rs1384477352 | 85 | E>D | No | gnomAD | |
| rs765931862 | 92 | Q>P | No |
ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| rs1320311472 | 95 | T>M | No | gnomAD | |
| rs1163101525 | 97 | G>D | No | gnomAD | |
| rs767056612 | 100 | T>A | No |
ExAC gnomAD |
|
| rs1373778471 | 100 | T>I | No | gnomAD | |
| rs763400377 | 102 | V>Q | No |
ExAC gnomAD |
1 associated diseases with P63165
[MIM: 613705]: Non-syndromic orofacial cleft 10 (OFC10)
A birth defect consisting of cleft lips with or without cleft palate. Cleft lips are associated with cleft palate in two-third of cases. A cleft lip can occur on one or both sides and range in severity from a simple notch in the upper lip to a complete opening in the lip extending into the floor of the nostril and involving the upper gum. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. A chromosomal aberration involving SUMO1 is the cause of OFC10. Translocation t(2;8)(q33.1;q24.3). The breakpoint occurred in the SUMO1 gene and resulted in haploinsufficiency confirmed by protein assays.
Without disease ID
- A birth defect consisting of cleft lips with or without cleft palate. Cleft lips are associated with cleft palate in two-third of cases. A cleft lip can occur on one or both sides and range in severity from a simple notch in the upper lip to a complete opening in the lip extending into the floor of the nostril and involving the upper gum. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. A chromosomal aberration involving SUMO1 is the cause of OFC10. Translocation t(2;8)(q33.1;q24.3). The breakpoint occurred in the SUMO1 gene and resulted in haploinsufficiency confirmed by protein assays.
No regional properties for P63165
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for P63165 | |||
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR10562 | SMALL UBIQUITIN-RELATED MODIFIER |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR10562:SF14 | SMALL UBIQUITIN-RELATED MODIFIER 1 |
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category |
p53 pathway Sumo-1 ligase |
|
11 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| nuclear body | Extra-nucleolar nuclear domains usually visualized by confocal microscopy and fluorescent antibodies to specific proteins. |
| nuclear membrane | Either of the lipid bilayers that surround the nucleus and form the nuclear envelope; excludes the intermembrane space. |
| nuclear pore | A protein complex providing a discrete opening in the nuclear envelope of a eukaryotic cell, where the inner and outer nuclear membranes are joined. |
| nuclear speck | A discrete extra-nucleolar subnuclear domain, 20-50 in number, in which splicing factors are seen to be localized by immunofluorescence microscopy. |
| nuclear stress granule | A dense aggregation in the nucleus composed of proteins and RNAs that appear when the cell is under stress. |
| nucleolus | A small, dense body one or more of which are present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is rich in RNA and protein, is not bounded by a limiting membrane, and is not seen during mitosis. Its prime function is the transcription of the nucleolar DNA into 45S ribosomal-precursor RNA, the processing of this RNA into 5.8S, 18S, and 28S components of ribosomal RNA, and the association of these components with 5S RNA and proteins synthesized outside the nucleolus. This association results in the formation of ribonucleoprotein precursors; these pass into the cytoplasm and mature into the 40S and 60S subunits of the ribosome. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| PML body | A class of nuclear body; they react against SP100 auto-antibodies (PML, promyelocytic leukemia); cells typically contain 10-30 PML bodies per nucleus; alterations in the localization of PML bodies occurs after viral infection. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| potassium channel regulator activity | Binds to and modulates the activity of a potassium channel. |
| protein tag activity | A molecular function exhibited by a protein that is covalently attached (AKA tagged or conjugated) to another protein where it acts as a marker, recognized by the cellular apparatus to target the tagged protein for some cellular process such as modification, sequestration, transport or degradation. |
| RNA binding | Binding to an RNA molecule or a portion thereof. |
| small protein activating enzyme binding | Binding to a small protein activating enzyme, such as ubiquitin-activating enzyme. |
| transcription factor binding | Binding to a transcription factor, a protein required to initiate or regulate transcription. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | Binding to a ubiquitin protein ligase enzyme, any of the E3 proteins. |
| ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding | Binding to a ubiquitin-like protein ligase, such as ubiquitin-ligase. |
| ubiquitin-specific protease binding | Binding to a ubiquitin-specific protease. |
16 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to cadmium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cadmium (Cd) ion stimulus. |
| cellular response to heat | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a heat stimulus, a temperature stimulus above the optimal temperature for that organism. |
| DNA repair | The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway. |
| negative regulation of action potential | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of action potential creation, propagation or termination. This typically occurs via modulation of the activity or expression of voltage-gated ion channels. |
| negative regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity. |
| negative regulation of DNA binding | Any process that stops or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of DNA binding. DNA binding is any process in which a gene product interacts selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the activity of a transcription factor, any factor involved in the initiation or regulation of transcription. |
| negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| negative regulation of protein import into nucleus | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of proteins from the cytoplasm into the nucleus. |
| negative regulation of transcription by transcription factor localization | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription using a mechanism that involves the localization of a transcription factor. |
| positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, and mediated by the proteasome. |
| positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein complex assembly. |
| protein stabilization | Any process involved in maintaining the structure and integrity of a protein and preventing it from degradation or aggregation. |
| protein sumoylation | The process in which a SUMO protein (small ubiquitin-related modifier) is conjugated to a target protein via an isopeptide bond between the carboxy-terminus of SUMO with an epsilon-amino group of a lysine residue of the target protein. |
| regulation of protein localization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| roof of mouth development | The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of the roof of the mouth from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure. The roof of the mouth is the partition that separates the nasal and oral cavities. |
34 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q12306 | SMT3 | Ubiquitin-like protein SMT3 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | SS |
| Q17QV3 | SUMO3 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 3 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q5E9D1 | SUMO1 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q5ZHQ1 | SUMO3 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q5ZJM9 | SUMO2 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8QGH2 | SUMO1 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q9VCP1 | CG4449 | Uncharacterized protein CG4449 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P61956 | SUMO2 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q6EEV6 | SUMO4 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P55854 | SUMO3 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| G2XKQ0 | SUMO1P1 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P61957 | Sumo2 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z172 | Sumo3 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P63166 | Sumo1 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P61958 | SUMO2 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| A7WLH8 | SUMO1 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| P61959 | Sumo2 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q5XIF4 | Sumo3 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q5I0H3 | Sumo1 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P55857 | SUMO1 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| P55853 | smo-1 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9FKC5 | SUMO4 | Putative small ubiquitin-related modifier 4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9FLP5 | SUMO3 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| P55852 | SUMO1 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q8VZI7 | SUMO5 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| B3H5R8 | SUMO8 | Putative small ubiquitin-related modifier 8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q3E8A8 | SUMO7 | Putative small ubiquitin-related modifier 7 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9FLP6 | SUMO2 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q28H04 | sumo2 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| Q6DEP7 | sumo1 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| Q6DI05 | sumo3 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q6DHL4 | sumo2 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q6NV25 | sumo3l | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 3-like | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q7SZR5 | sumo1 | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSDQEAKPST | EDLGDKKEGE | YIKLKVIGQD | SSEIHFKVKM | TTHLKKLKES | YCQRQGVPMN |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | ||
| SLRFLFEGQR | IADNHTPKEL | GMEEEDVIEV | YQEQTGGHST | V |