P63101
Gene name |
Ywhaz |
Protein name |
14-3-3 protein zeta/delta |
Names |
Protein kinase C inhibitor protein 1, KCIP-1, SEZ-2 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:22631 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
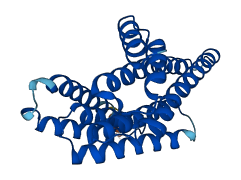
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for P63101
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7EXE | X-ray | 275 A | A/B | 2-245 | PDB |
| AF-P63101-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
9 variants for P63101
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3389358654 | 26 | M>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389358714 | 36 | L>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3389367444 | 152 | A>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389373320 | 172 | L>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389356824 | 176 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3389364152 | 183 | N>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389309561 | 196 | F>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389360661 | 225 | L>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389278560 | 243 | G>W | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P63101
3 regional properties for P63101
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| conserved_site | 14-3-3 protein, conserved site | 41 - 51 | IPR023409-1 |
| conserved_site | 14-3-3 protein, conserved site | 211 - 230 | IPR023409-2 |
| domain | 14-3-3 domain | 3 - 242 | IPR023410 |
11 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell leading edge | The area of a motile cell closest to the direction of movement. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse | One of the giant synapses that form between the mossy fiber axons of dentate gyrus granule cells and the large complex spines of CA3 pyramidal cells. It consists of a giant bouton known as the mossy fiber expansion, synapsed to the complex, multiheaded spine (thorny excresence) of a CA3 pyramidal cell. |
| melanosome | A tissue-specific, membrane-bounded cytoplasmic organelle within which melanin pigments are synthesized and stored. Melanosomes are synthesized in melanocyte cells. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a DNA-binding transcription factor, a protein that interacts with a specific DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within the regulatory region of a gene to modulate transcription. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| phosphoserine residue binding | Binding to a phosphorylated serine residue within a protein. |
| protein domain specific binding | Binding to a specific domain of a protein. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein sequestering activity | Binding to a protein to prevent it from interacting with other partners or to inhibit its localization to the area of the cell or complex where it is active. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| transmembrane transporter binding | Binding to a transmembrane transporter, a protein or protein complex that enables the transfer of a substance, usually a specific substance or a group of related substances, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | Binding to a ubiquitin protein ligase enzyme, any of the E3 proteins. |
19 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| angiogenesis | Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels. |
| ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least ERK1 or ERK2 (MAPKs), a MEK (a MAPKK) and a MAP3K. The cascade may involve 4 different kinases, as it can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| establishment of Golgi localization | The directed movement of the Golgi to a specific location. |
| Golgi reassembly | The reformation of the Golgi following its breakdown and partitioning contributing to Golgi inheritance. |
| histamine secretion by mast cell | The regulated release of histamine by a mast cell or group of mast cells. |
| lung development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the lung over time, from its formation to the mature structure. In all air-breathing vertebrates the lungs are developed from the ventral wall of the oesophagus as a pouch which divides into two sacs. In amphibians and many reptiles the lungs retain very nearly this primitive sac-like character, but in the higher forms the connection with the esophagus becomes elongated into the windpipe and the inner walls of the sacs become more and more divided, until, in the mammals, the air spaces become minutely divided into tubes ending in small air cells, in the walls of which the blood circulates in a fine network of capillaries. In mammals the lungs are more or less divided into lobes, and each lung occupies a separate cavity in the thorax. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| protein localization | Any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| protein targeting | The process of targeting specific proteins to particular regions of the cell, typically membrane-bounded subcellular organelles. Usually requires an organelle specific protein sequence motif. |
| protein targeting to mitochondrion | The process of directing proteins towards and into the mitochondrion, usually mediated by mitochondrial proteins that recognize signals contained within the imported protein. |
| regulation of cell death | Any process that modulates the rate or frequency of cell death. Cell death is the specific activation or halting of processes within a cell so that its vital functions markedly cease, rather than simply deteriorating gradually over time, which culminates in cell death. |
| regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| regulation of synapse maturation | Any process that modulates the extent of synapse maturation, the process that organizes a synapse so that it attains its fully functional state. |
| respiratory system process | A process carried out by the organs or tissues of the respiratory system. The respiratory system is an organ system responsible for respiratory gaseous exchange. |
| response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
| synaptic target recognition | The process in which a neuronal cell in a multicellular organism interprets signals produced by potential target cells, with which it may form synapses. |
| tube formation | Creation of the central hole of a tube in an anatomical structure through which gases and/or liquids flow. |
37 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q04917 | YWHAH | 14-3-3 protein eta | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P61981 | YWHAG | 14-3-3 protein gamma | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P31946 | YWHAB | 14-3-3 protein beta/alpha | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P27348 | YWHAQ | 14-3-3 protein theta | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P63104 | YWHAZ | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P49106 | GRF1 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-6 | Zea mays (Maize) | PR |
| P68510 | Ywhah | 14-3-3 protein eta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P93784 | HOX | 14-3-3-like protein 16R | Solanum tuberosum (Potato) | PR |
| Q41418 | 14-3-3-like protein | Solanum tuberosum (Potato) | PR | |
| P63102 | Ywhaz | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q6EUP4 | GF14E | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-E | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q06967 | GF14F | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-F | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q7XTE8 | GF14B | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-B | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q6ZKC0 | GF14C | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-C | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q84J55 | GF14A | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-A | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q2R2W2 | GF14D | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-D | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q2R1D5 | GF14H | Putative 14-3-3-like protein GF14-H | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q96450 | GF14A | 14-3-3-like protein A | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | PR |
| Q96453 | GF14D | 14-3-3-like protein D | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | PR |
| Q96452 | GF14C | 14-3-3-like protein C | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | PR |
| Q9C5W6 | GRF12 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 iota | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9S9Z8 | GRF11 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 omicron | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P46077 | GRF4 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 phi | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q01525 | GRF2 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 omega | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q96300 | GRF7 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 nu | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P42645 | GRF5 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 upsilon | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P42644 | GRF3 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 psi | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q96299 | GRF9 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 mu | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P42652 | TFT4 | 14-3-3 protein 4 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93212 | TFT7 | 14-3-3 protein 7 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93209 | TFT3 | 14-3-3 protein 3 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93207 | TFT10 | 14-3-3 protein 10 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93211 | TFT6 | 14-3-3 protein 6 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93206 | TFT1 | 14-3-3 protein 1 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93208 | TFT2 | 14-3-3 protein 2 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93213 | TFT8 | 14-3-3 protein 8 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93214 | TFT9 | 14-3-3 protein 9 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MDKNELVQKA | KLAEQAERYD | DMAACMKSVT | EQGAELSNEE | RNLLSVAYKN | VVGARRSSWR |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| VVSSIEQKTE | GAEKKQQMAR | EYREKIETEL | RDICNDVLSL | LEKFLIPNAS | QPESKVFYLK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| MKGDYYRYLA | EVAAGDDKKG | IVDQSQQAYQ | EAFEISKKEM | QPTHPIRLGL | ALNFSVFYYE |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| ILNSPEKACS | LAKTAFDEAI | AELDTLSEES | YKDSTLIMQL | LRDNLTLWTS | DTQGDEAEAG |
| EGGEN |