P63013
Gene name |
Prrx1 (Pmx, Pmx1) |
Protein name |
Paired mesoderm homeobox protein 1 |
Names |
Homeobox protein K-2, Homeobox protein mHox, Paired-related homeobox protein 1, PRX-1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:18933 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
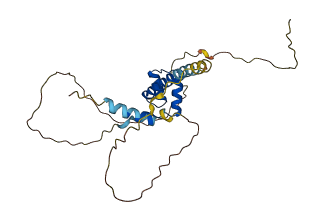
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P63013
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P63013-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
9 variants for P63013
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388512411 | 3 | S>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388507824 | 118 | Y>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388510099 | 135 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388509949 | 164 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3388510617 | 178 | P>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388514374 | 180 | V>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388509887 | 183 | P>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388514411 | 200 | S>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388513053 | 214 | P>VSDG* | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P63013
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that activates or increases transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that represses or decreases the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| HMG box domain binding | Binding to an HMG box domain, a protein domain that consists of three helices in an irregular array. HMG-box domains are found in one or more copies in HMG-box proteins, which form a large, diverse family involved in the regulation of DNA-dependent processes such as transcription, replication, and strand repair, all of which require the bending and unwinding of chromatin. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor activity | A general transcription initiation factor activity that contributes to transcription start site selection and transcription initiation of genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II. The general transcription factors for RNA polymerase II include TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE, TFIIF, TFIIH and TATA-binding protein (TBP). In most species, RNA polymerase II transcribes all messenger RNAs (mRNAs), most untranslated regulatory RNAs, the majority of the snoRNAs, four of the five snRNAs (U1, U2, U4, and U5), and other small noncoding RNAs. For some small RNAs there is variability between species as to whether it is transcribed by RNA polymerase II or RNA polymerase III. However there are also rare exceptions, such as Trypanosoma brucei, where RNA polymerase I transcribes certain mRNAs in addition to its normal role in rRNA transcription. |
| RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a sequence-specific DNA binding RNA polymerase II transcription factor, any of the factors that interact selectively and non-covalently with a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. |
20 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| artery morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of arterial blood vessels are generated and organized. Arteries are blood vessels that transport blood from the heart to the body and its organs. |
| cartilage development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cartilage element over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cartilage elements are skeletal elements that consist of connective tissue dominated by extracellular matrix containing collagen type II and large amounts of proteoglycan, particularly chondroitin sulfate. |
| embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the cranial skeleton are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. |
| embryonic limb morphogenesis | The process, occurring in the embryo, by which the anatomical structures of the limb are generated and organized. A limb is an appendage of an animal used for locomotion or grasping. |
| embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. |
| inner ear morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the inner ear are generated and organized. The inner ear is the structure in vertebrates that contains the organs of balance and hearing. It consists of soft hollow sensory structures (the membranous labyrinth) containing fluid (endolymph) surrounded by fluid (perilymph) and encased in a bony cavity (the bony labyrinth). It consists of two chambers, the sacculus and utriculus, from which arise the cochlea and semicircular canals respectively. |
| mesenchymal cell proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a mesenchymal cell population. A mesenchymal cell is a cell that normally gives rise to other cells that are organized as three-dimensional masses, rather than sheets. |
| middle ear morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the middle ear are generated and organized. The middle ear is the air-filled cavity within the skull of vertebrates that lies between the outer ear and the inner ear. It is linked to the pharynx (and therefore to outside air) via the Eustachian tube and in mammals contains the three ear ossicles, which transmit auditory vibrations from the outer ear (via the tympanum) to the inner ear (via the oval window). |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| neuron fate determination | The process in which a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into a neuron regardless of its environment; upon determination, the cell fate cannot be reversed. |
| neuronal stem cell population maintenance | Any process in by an organism or tissue maintains a population of neuronal stem cells. |
| positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation | The process of activating or increasing the rate or extent of mesenchymal cell proliferation. Mesenchymal cells are loosely organized embryonic cells. |
| positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of smoothened signaling. |
| positive regulation of stem cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of stem cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| regulation of neuron projection regeneration | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection regeneration, the regrowth of neuronal processes such as axons or dendrites following their loss or damage. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| roof of mouth development | The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of the roof of the mouth from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure. The roof of the mouth is the partition that separates the nasal and oral cavities. |
| smoothened signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of activation of the transmembrane protein Smoothened. |
| stem cell proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of stem cells, resulting in the expansion of a stem cell population. A stem cell is a cell that retains the ability to divide and proliferate throughout life to provide progenitor cells that can differentiate into specialized cells. |
23 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0JNI8 | LHX9 | LIM/homeobox protein Lhx9 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q90881 | LHX9 | LIM/homeobox protein Lhx9 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| F1NEA7 | DMBX1 | Diencephalon/mesencephalon homeobox protein 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q90963 | PRRX2 | Paired mesoderm homeobox protein 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q8IRC7 | Awh | LIM/homeobox protein Awh | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q8NHV9 | RHOXF1 | Rhox homeobox family member 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9NQ69 | LHX9 | LIM/homeobox protein Lhx9 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O95076 | ALX3 | Homeobox protein aristaless-like 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9BQY4 | RHOXF2 | Rhox homeobox family member 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P50458 | LHX2 | LIM/homeobox protein Lhx2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O15266 | SHOX | Short stature homeobox protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q99811 | PRRX2 | Paired mesoderm homeobox protein 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O14813 | PHOX2A | Paired mesoderm homeobox protein 2A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8VIH1 | Nobox | Homeobox protein NOBOX | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O88933 | Esx1 | Extraembryonic, spermatogenesis, homeobox 1 (Homeobox protein SPX1) (Homeodomain protein EPX) | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q9WUH2 | Lhx9 | LIM/homeobox protein Lhx9 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q06348 | Prrx2 | Paired mesoderm homeobox protein 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62066 | Phox2a | Paired mesoderm homeobox protein 2A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q80W90 | Lhx9 | LIM/homeobox protein Lhx9 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P36198 | Lhx2 | LIM/homeobox protein Lhx2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q28G02 | siamois | Homeobox protein siamois | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| Q566X8 | dmbx1b | Diencephalon/mesencephalon homeobox protein 1-B | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q1LWV4 | lhx9 | LIM/homeobox protein Lhx9 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MTSSYGHVLE | RQPALGGRLD | SPGNLDTLQA | KKNFSVSHLL | DLEEAGDMVA | AQADESVGEA |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GRSLLESPGL | TSGSDTPQQD | NDQLNSEEKK | KRKQRRNRTT | FNSSQLQALE | RVFERTHYPD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| AFVREDLARR | VNLTEARVQV | WFQNRRAKFR | RNERAMLANK | NASLLKSYSG | DVTAVEQPIV |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| PRPAPRPTDY | LSWGTASPYS | AMATYSATCA | NNSPAQGINM | ANSIANLRLK | AKEYSLQRNQ |
| VPTVN |