P62491
Gene name |
RAB11A |
Protein name |
Ras-related protein Rab-11A |
Names |
Rab-11, YL8 |
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:8766 |
EC number |
3.6.5.2: Acting on GTP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
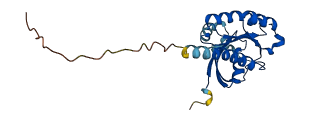
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

29 structures for P62491
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1OIV | X-ray | 198 A | A/B | 1-173 | PDB |
| 1OIW | X-ray | 205 A | A | 1-173 | PDB |
| 1OIX | X-ray | 170 A | A | 1-173 | PDB |
| 1YZK | X-ray | 200 A | A | 8-175 | PDB |
| 2D7C | X-ray | 175 A | A/B | 7-173 | PDB |
| 2GZD | X-ray | 244 A | A/B | 2-173 | PDB |
| 2GZH | X-ray | 247 A | A | 2-173 | PDB |
| 2HV8 | X-ray | 186 A | A/B/C | 6-175 | PDB |
| 4C4P | X-ray | 200 A | A | 1-173 | PDB |
| 4D0L | X-ray | 294 A | B/D/F | 1-216 | PDB |
| 4D0M | X-ray | 600 A | B/D/H/J/N/P/R/T/X/Z/d/h | 1-216 | PDB |
| 4LWZ | X-ray | 255 A | A/C | 1-177 | PDB |
| 4LX0 | X-ray | 219 A | A/C | 1-177 | PDB |
| 4UJ3 | X-ray | 300 A | A/D/G/J/M/P/S/V | 4-186 | PDB |
| 4UJ4 | X-ray | 420 A | A/D/G/J | 4-186 | PDB |
| 4UJ5 | X-ray | 260 A | A/B | 6-186 | PDB |
| 5C46 | X-ray | 265 A | F | 1-216 | PDB |
| 5C4G | X-ray | 320 A | B | 1-216 | PDB |
| 5EUQ | X-ray | 320 A | B | 1-216 | PDB |
| 5EZ5 | X-ray | 240 A | A/B | 8-175 | PDB |
| 5FBL | X-ray | 337 A | B | 1-216 | PDB |
| 5FBQ | X-ray | 379 A | B | 1-216 | PDB |
| 5FBR | X-ray | 328 A | B | 1-216 | PDB |
| 5FBV | X-ray | 329 A | B | 1-216 | PDB |
| 5FBW | X-ray | 349 A | B | 1-216 | PDB |
| 5JCZ | X-ray | 206 A | A/D/I | 1-177 | PDB |
| 6DJL | X-ray | 310 A | A/F/G/H | 1-216 | PDB |
| 6IXV | X-ray | 380 A | E/F/G/H | 1-173 | PDB |
| AF-P62491-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
66 variants for P62491
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
rs1263754517 CA392918973 |
5 | D>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1224127056 CA392918957 |
5 | D>N | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs892660603 CA271610661 |
8 | Y>C | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA TOPMed |
|
CA392919058 rs1240528470 |
9 | D>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 24 | K>Q | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA271613491 rs201712940 |
28 | L>P | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
| TCGA novel | 29 | S>Y | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA392919871 rs1449908676 |
30 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA392919924 rs763409430 |
33 | R>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs374592220 CA271613540 |
34 | N>K | No |
ClinGen ESP TOPMed |
|
|
CA392920365 rs1177010794 |
51 | R>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA392920551 rs1324821460 |
60 | I>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 62 | A>E | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| TCGA novel | 82 | R>C | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| TCGA novel | 82 | R>H | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA392921071 rs1478967473 |
83 | G>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs190571382 CA7621572 |
91 | Y>F | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1324263835 CA392921437 |
100 | E>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA392921583 rs1240762441 |
107 | K>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
| TCGA novel | 108 | E>* | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1434404164 CA392921661 |
111 | D>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs772613563 CA7621579 |
112 | H>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1567137438 CA392921709 |
113 | A>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1190052210 CA392921819 |
117 | I>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
| TCGA novel | 123 | G>D | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| TCGA novel | 124 | N>I | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA392922104 rs1567137460 |
137 | D>H | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs776183548 CA7621582 |
138 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 140 | R>S | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA271613775 rs766250277 |
142 | F>L | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA392923212 rs1412602889 |
150 | F>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1292123777 CA392923220 |
151 | I>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1249496263 CA618663330 |
157 | D>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA392923297 rs1338701122 |
157 | D>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs375521278 CA7621611 |
159 | T>K | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA7621613 rs201908439 |
163 | A>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1241849519 CA392923373 |
163 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA392923469 rs1478817063 |
170 | T>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 171 | E>D | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA392924861 rs1429663909 |
172 | I>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1457090212 CA392924882 |
174 | R>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA7621632 COSM1374151 rs759435629 |
174 | R>H | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. large_intestine [NCI-TCGA, Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
CA392924894 rs1476977752 |
175 | I>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA7621635 rs760325951 |
181 | M>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs752698600 CA7621634 |
181 | M>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA271618250 rs1054774828 |
184 | R>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs764020784 CA7621636 |
185 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs764020784 CA392925022 |
185 | R>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 187 | N>H | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA392925101 rs1237234616 |
190 | S>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA7621639 rs778537719 |
192 | S>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs375723446 CA392925165 |
194 | N>I | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA7621640 rs375723446 |
194 | N>S | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1251632357 CA392925204 |
197 | P>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA7621643 rs748693318 |
199 | H>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA271618270 rs1015728032 |
200 | V>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA392925274 rs1376052565 |
202 | P>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA392925307 rs1280621310 |
204 | T>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA271618273 rs11556461 |
205 | E>K | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs770049340 CA7621644 |
206 | N>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA271618281 rs4920 |
207 | K>N | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs778257251 CA392925437 |
210 | V>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs778257251 CA7621645 |
210 | V>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1442206199 CA392925426 |
210 | V>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs749489126 CA7621646 |
215 | N>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs749489126 CA271618292 |
215 | N>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
No associated diseases with P62491
1 regional properties for P62491
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Small GTP-binding protein domain | 10 - 168 | IPR005225 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.5.2 | Acting on GTP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
23 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| centriolar satellite | A small (70-100 nm) cytoplasmic granule that contains a number of centrosomal proteins; centriolar satellites traffic toward microtubule minus ends and are enriched near the centrosome. |
| centriole | A cellular organelle, found close to the nucleus in many eukaryotic cells, consisting of a small cylinder with microtubular walls, 300-500 nm long and 150-250 nm in diameter. It contains nine short, parallel, peripheral microtubular fibrils, each fibril consisting of one complete microtubule fused to two incomplete microtubules. Cells usually have two centrioles, lying at right angles to each other. At division, each pair of centrioles generates another pair and the twin pairs form the pole of the mitotic spindle. |
| centrosome | A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle. |
| cleavage furrow | The cleavage furrow is a plasma membrane invagination at the cell division site. The cleavage furrow begins as a shallow groove and eventually deepens to divide the cytoplasm. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| extracellular exosome | A vesicle that is released into the extracellular region by fusion of the limiting endosomal membrane of a multivesicular body with the plasma membrane. Extracellular exosomes, also simply called exosomes, have a diameter of about 40-100 nm. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| intracellular membrane-bounded organelle | Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane. |
| multivesicular body | A type of endosome in which regions of the limiting endosomal membrane invaginate to form internal vesicles; membrane proteins that enter the internal vesicles are sequestered from the cytoplasm. |
| phagocytic vesicle | A membrane-bounded intracellular vesicle that arises from the ingestion of particulate material by phagocytosis. |
| postsynaptic recycling endosome | A recycling endosome of the postsynapse. In postsynaptic terminals with dendritic spines, it is typically located at the base of a dendritic spine. It is involved in recycling of neurotransmitter receptors to the postsynaptic membrane. In some cases at least, this recycling is activated by postsynaptic signalling and so can play a role in long term potentiation. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
| recycling endosome | An organelle consisting of a network of tubules that functions in targeting molecules, such as receptors transporters and lipids, to the plasma membrane. |
| recycling endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a recycling endosome. |
| spindle pole | Either of the ends of a spindle, where spindle microtubules are organized; usually contains a microtubule organizing center and accessory molecules, spindle microtubules and astral microtubules. |
| trans-Golgi network | The network of interconnected tubular and cisternal structures located within the Golgi apparatus on the side distal to the endoplasmic reticulum, from which secretory vesicles emerge. The trans-Golgi network is important in the later stages of protein secretion where it is thought to play a key role in the sorting and targeting of secreted proteins to the correct destination. |
| transport vesicle | Any of the vesicles of the constitutive secretory pathway, which carry cargo from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi, between Golgi cisternae, from the Golgi to the ER (retrograde transport) or to destinations within or outside the cell. |
| vesicle | Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| G protein activity | A molecular function regulator that cycles between active GTP-bound and inactive GDP-bound states. In its active state, binds to a variety of effector proteins to regulate cellular processes. Intrinsic GTPase activity returns the G protein to its GDP-bound state. The return to the GDP-bound state can be accelerated by the action of a GTPase-activating protein (GAP). |
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
| microtubule binding | Binding to a microtubule, a filament composed of tubulin monomers. |
| myosin V binding | Binding to a class V myosin; myosin V is a dimeric molecule involved in intracellular transport. |
| syntaxin binding | Binding to a syntaxin, a SNAP receptor involved in the docking of synaptic vesicles at the presynaptic zone of a synapse. |
22 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| amyloid-beta clearance by transcytosis | The process in which amyloid-beta is removed from extracellular brain regions by cell surface receptor-mediated endocytosis, followed by transcytosis across the blood-brain barrier. |
| astral microtubule organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of astral microtubules, any of the spindle microtubules that radiate in all directions from the spindle poles. |
| establishment of protein localization to membrane | The directed movement of a protein to a specific location in a membrane. |
| establishment of protein localization to organelle | The directed movement of a protein to a specific location on or in an organelle. Encompasses establishment of localization in the membrane or lumen of a membrane-bounded organelle. |
| establishment of vesicle localization | The directed movement of a vesicle to a specific location. |
| exocytosis | A process of secretion by a cell that results in the release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle. Exocytosis can occur either by full fusion, when the vesicle collapses into the plasma membrane, or by a kiss-and-run mechanism that involves the formation of a transient contact, a pore, between a granule (for exemple of chromaffin cells) and the plasma membrane. The latter process most of the time leads to only partial secretion of the granule content. Exocytosis begins with steps that prepare vesicles for fusion with the membrane (tethering and docking) and ends when molecules are secreted from the cell. |
| exosomal secretion | The process whereby a membrane-bounded vesicle is released into the extracellular region by fusion of the limiting endosomal membrane of a multivesicular body with the plasma membrane. |
| melanosome transport | The directed movement of melanosomes into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| mitotic metaphase plate congression | The cell cycle process in which chromosomes are aligned at the metaphase plate, a plane halfway between the poles of the mitotic spindle, during mitosis. |
| mitotic spindle assembly | Mitotic bipolar spindle assembly begins with spindle microtubule nucleation from the separated spindle pole body, includes spindle elongation during prometaphase, and is complete when all kinetochores are stably attached the spindle, and the spindle assembly checkpoint is satisfied. |
| multivesicular body assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a multivesicular body, a type of late endosome in which regions of the limiting endosomal membrane invaginate to form internal vesicles; membrane proteins that enter the internal vesicles are sequestered from the cytoplasm. |
| neuron projection development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| neurotransmitter receptor transport, endosome to postsynaptic membrane | The directed movement of neurotransmitter receptor from the postsynaptic endosome to the postsynaptic membrane in transport vesicles. |
| plasma membrane to endosome transport | Transport of a vesicle from the plasma membrane to the endosome. |
| positive regulation of epithelial cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of epithelial cell migration. |
| positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle | Any signalling pathway that activates or increases the activity of a cell cycle cyclin-dependent protein kinase to modulate the switch from G2 phase to M phase of the mitotic cell cycle. |
| protein localization to cell surface | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a location within the external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| protein localization to plasma membrane | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location in the plasma membrane. |
| regulation of cytokinesis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the division of the cytoplasm of a cell and its separation into two daughter cells. |
| regulation of multivesicular body size | Any process that modulates the volume of a multivesicular body, a type of late endosome in which regions of the limiting endosomal membrane invaginate to form internal vesicles. |
| regulation of vesicle-mediated transport | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of vesicle-mediated transport, the directed movement of substances, either within a vesicle or in the vesicle membrane, into, out of or within a cell. |
| vesicle-mediated transport | A cellular transport process in which transported substances are moved in membrane-bounded vesicles; transported substances are enclosed in the vesicle lumen or located in the vesicle membrane. The process begins with a step that directs a substance to the forming vesicle, and includes vesicle budding and coating. Vesicles are then targeted to, and fuse with, an acceptor membrane. |
20 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q3MHP2 | RAB11B | Ras-related protein Rab-11B | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q2TA29 | RAB11A | Ras-related protein Rab-11A | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q5ZJN2 | RAB11A | Ras-related protein Rab-11A | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P62490 | RAB11A | Ras-related protein Rab-11A | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| Q8WUD1 | RAB2B | Ras-related protein Rab-2B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P61019 | RAB2A | Ras-related protein Rab-2A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P20338 | RAB4A | Ras-related protein Rab-4A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P61018 | RAB4B | Ras-related protein Rab-4B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q15907 | RAB11B | Ras-related protein Rab-11B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P46638 | Rab11b | Ras-related protein Rab-11B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P62492 | Rab11a | Ras-related protein Rab-11A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q52NJ1 | RAB11A | Ras-related protein Rab-11A | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| O35509 | Rab11b | Ras-related protein Rab-11B | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P62494 | Rab11a | Ras-related protein Rab-11A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O04486 | RABA2A | Ras-related protein RABA2a | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FE79 | RABA4C | Ras-related protein RABA4c | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LH50 | RABA4D | Ras-related protein RABA4d | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LNK1 | RABA3 | Ras-related protein RABA3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LNW1 | RABA2B | Ras-related protein RABA2b | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O49513 | RABA1E | Ras-related protein RABA1e | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGTRDDEYDY | LFKVVLIGDS | GVGKSNLLSR | FTRNEFNLES | KSTIGVEFAT | RSIQVDGKTI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| KAQIWDTAGQ | ERYRAITSAY | YRGAVGALLV | YDIAKHLTYE | NVERWLKELR | DHADSNIVIM |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LVGNKSDLRH | LRAVPTDEAR | AFAEKNGLSF | IETSALDSTN | VEAAFQTILT | EIYRIVSQKQ |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | |||
| MSDRRENDMS | PSNNVVPIHV | PPTTENKPKV | QCCQNI |