P61586
Gene name |
RHOA |
Protein name |
Transforming protein RhoA |
Names |
Rho cDNA clone 12, h12 |
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:387 |
EC number |
3.6.5.2: Acting on GTP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
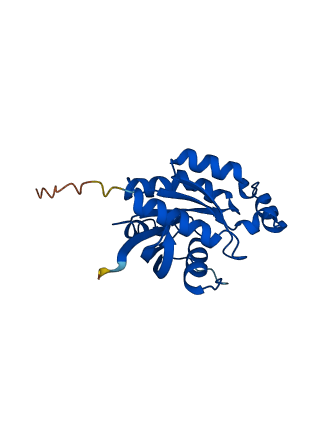
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

114 structures for P61586
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A2B | X-ray | 240 A | A | 1-181 | PDB |
| 1CC0 | X-ray | 500 A | A/C | 1-190 | PDB |
| 1CXZ | X-ray | 220 A | A | 1-181 | PDB |
| 1DPF | X-ray | 200 A | A | 1-180 | PDB |
| 1FTN | X-ray | 210 A | A | 1-193 | PDB |
| 1KMQ | X-ray | 155 A | A | 4-181 | PDB |
| 1LB1 | X-ray | 281 A | B/D/F/H | 1-190 | PDB |
| 1OW3 | X-ray | 180 A | B | 1-193 | PDB |
| 1S1C | X-ray | 260 A | A/B | 1-181 | PDB |
| 1TX4 | X-ray | 165 A | B | 3-179 | PDB |
| 1X86 | X-ray | 322 A | B/D/F/H | 1-193 | PDB |
| 1XCG | X-ray | 250 A | B/F | 3-180 | PDB |
| 2RGN | X-ray | 350 A | C/F | 1-193 | PDB |
| 3KZ1 | X-ray | 270 A | E/F | 1-181 | PDB |
| 3LW8 | X-ray | 185 A | A/B/C/D | 2-181 | PDB |
| 3LWN | X-ray | 228 A | A/B | 2-181 | PDB |
| 3LXR | X-ray | 168 A | A | 2-181 | PDB |
| 3MSX | X-ray | 165 A | A | 1-180 | PDB |
| 3T06 | X-ray | 284 A | B/F | 3-180 | PDB |
| 4D0N | X-ray | 210 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 4XH9 | X-ray | 200 A | B/E | 2-180 | PDB |
| 4XOI | X-ray | 209 A | A/C | 1-180 | PDB |
| 4XSG | X-ray | 180 A | A | 1-179 | PDB |
| 4XSH | X-ray | 250 A | A | 1-179 | PDB |
| 5A0F | X-ray | 200 A | A | 1-181 | PDB |
| 5BWM | X-ray | 250 A | A | 1-179 | PDB |
| 5C2K | X-ray | 142 A | A | 1-193 | PDB |
| 5C4M | X-ray | 130 A | A | 1-193 | PDB |
| 5EZ6 | X-ray | 180 A | B | 1-181 | PDB |
| 5FR1 | X-ray | 275 A | A | 1-193 | PDB |
| 5FR2 | X-ray | 335 A | A | 1-193 | PDB |
| 5HPY | X-ray | 240 A | B/F | 3-181 | PDB |
| 5IRC | X-ray | 172 A | D/F | 2-181 | PDB |
| 5JCP | X-ray | 210 A | A/B | 1-181 | PDB |
| 5JHG | X-ray | 250 A | B/F | 1-181 | PDB |
| 5JHH | X-ray | 230 A | B/F | 1-181 | PDB |
| 5M6X | X-ray | 240 A | B/I | 2-193 | PDB |
| 5M70 | X-ray | 220 A | B/G | 2-193 | PDB |
| 5ZHX | X-ray | 350 A | e/f/g/h | 1-193 | PDB |
| 6BC0 | X-ray | 220 A | F | 1-181 | PDB |
| 6BCA | X-ray | 200 A | C/F | 1-181 | PDB |
| 6BCB | X-ray | 140 A | F | 1-181 | PDB |
| 6KX2 | X-ray | 145 A | A | 1-181 | PDB |
| 6KX3 | X-ray | 198 A | A | 1-181 | PDB |
| 6R3V | X-ray | 175 A | B | 1-193 | PDB |
| 6V6M | X-ray | 139 A | A | 1-181 | PDB |
| 6V6U | X-ray | 116 A | A | 1-181 | PDB |
| 6V6V | X-ray | 140 A | A | 1-181 | PDB |
| 7G80 | X-ray | 167 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G81 | X-ray | 151 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G82 | X-ray | 141 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G83 | X-ray | 131 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G84 | X-ray | 181 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G85 | X-ray | 174 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G86 | X-ray | 170 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G87 | X-ray | 205 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G88 | X-ray | 187 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G89 | X-ray | 190 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8A | X-ray | 150 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8B | X-ray | 142 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8C | X-ray | 218 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8D | X-ray | 194 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8E | X-ray | 179 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8F | X-ray | 142 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8G | X-ray | 192 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8H | X-ray | 167 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8I | X-ray | 247 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8J | X-ray | 199 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8K | X-ray | 149 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8L | X-ray | 160 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8M | X-ray | 203 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8N | X-ray | 232 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8O | X-ray | 158 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8P | X-ray | 221 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8Q | X-ray | 156 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8R | X-ray | 144 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8S | X-ray | 160 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8T | X-ray | 139 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8U | X-ray | 244 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8V | X-ray | 145 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8W | X-ray | 194 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8X | X-ray | 171 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8Y | X-ray | 175 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G8Z | X-ray | 151 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G90 | X-ray | 191 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G91 | X-ray | 229 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G92 | X-ray | 187 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G93 | X-ray | 169 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G94 | X-ray | 147 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G95 | X-ray | 155 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G96 | X-ray | 230 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G97 | X-ray | 230 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G98 | X-ray | 288 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G99 | X-ray | 178 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G9A | X-ray | 258 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G9B | X-ray | 255 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G9C | X-ray | 269 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G9D | X-ray | 266 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G9E | X-ray | 215 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G9F | X-ray | 194 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G9G | X-ray | 208 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G9H | X-ray | 275 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G9I | X-ray | 220 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7G9J | X-ray | 197 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 7QSC | X-ray | 191 A | B/D | 2-193 | PDB |
| 7QTM | X-ray | 225 A | B/I | 2-193 | PDB |
| 7WZA | X-ray | 150 A | A | 1-181 | PDB |
| 7WZC | X-ray | 180 A | A | 1-181 | PDB |
| 8BNT | X-ray | 140 A | A | 1-184 | PDB |
| 8FC7 | EM | 330 A | E/F/G/H | 1-193 | PDB |
| 8FC9 | EM | 375 A | E/F/G/H | 1-193 | PDB |
| 8FCB | EM | 352 A | E/F/G/H | 1-193 | PDB |
| 8T1C | EM | 349 A | E | 1-193 | PDB |
| AF-P61586-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
45 variants for P61586
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
COSM3940568 RCV000432532 CA16602950 rs1057519953 RCV000444013 RCV000425080 RCV000443944 RCV000431457 |
5 | R>L | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Carcinoma of esophagus oesophagus Gastric adenocarcinoma Neoplasm of the large intestine Breast neoplasm [ClinVar, Cosmic] | Yes |
ClinGen cosmic curated ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
RCV000432727 RCV000421840 CA16602949 RCV000422905 RCV000444856 rs1057519953 COSM190569 RCV000440078 |
5 | R>Q | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Carcinoma of esophagus large_intestine Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. Gastric adenocarcinoma Neoplasm of the large intestine haematopoietic_and_lymphoid_tissue Breast neoplasm [ClinVar, Cosmic, NCI-TCGA] | Yes |
ClinGen cosmic curated ClinVar Ensembl NCI-TCGA dbSNP |
|
RCV000430318 RCV000423113 RCV000430517 CA16602948 RCV000420653 RCV000441218 COSM446704 rs1057519952 |
5 | R>W | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Carcinoma of esophagus oesophagus Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. Gastric adenocarcinoma Neoplasm of the large intestine breast Breast neoplasm [ClinVar, Cosmic, NCI-TCGA] | Yes |
ClinGen cosmic curated ClinVar Ensembl NCI-TCGA dbSNP |
|
RCV000435482 RCV000435238 RCV000418248 RCV000428054 CA16602947 rs1057519951 |
40 | E>K | Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. Gastric adenocarcinoma Lung adenocarcinoma Breast neoplasm [ClinVar, NCI-TCGA] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl NCI-TCGA dbSNP |
|
RCV000425677 RCV000425897 COSM125851 CA16602946 rs1057519951 RCV000443212 RCV000436482 |
40 | E>Q | Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck upper_aerodigestive_tract Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. Gastric adenocarcinoma Lung adenocarcinoma breast Breast neoplasm [ClinVar, Cosmic, NCI-TCGA] | Yes |
ClinGen cosmic curated ClinVar Ensembl NCI-TCGA dbSNP |
|
CA16602951 RCV000420783 rs1057519954 RCV000438221 RCV000427520 |
42 | Y>C | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. Gastric adenocarcinoma [ClinVar, NCI-TCGA] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl NCI-TCGA dbSNP |
|
CA16602953 RCV000418559 COSM3357717 RCV000430340 rs1057519954 RCV000440615 |
42 | Y>F | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck Gastric adenocarcinoma haematopoietic_and_lymphoid_tissue [ClinVar, Cosmic] | Yes |
ClinGen cosmic curated ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
RCV000419217 CA16602952 RCV000427521 RCV000436909 rs1057519954 |
42 | Y>S | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. Gastric adenocarcinoma [ClinVar, NCI-TCGA] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl NCI-TCGA dbSNP |
|
VAR_083545 rs1575653629 RCV001526536 RCV001095368 RCV001539108 CA352788014 RCV001526531 |
47 | E>K | Ectodermal dysplasia with facial dysmorphism and acral, ocular, and brain anomalies Hemihypertrophy neuro-ectodermal phenotype EDFAOB; somatic mosaic variant; decreased Rho protein signal transduction; decreased substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading; decreased number of stress fibers assembly; decreased cytoplasmic microtubule organization [ClinVar, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP UniProt |
|
rs1553631976 RCV000623047 CA352786786 |
66 | Y>H | Inborn genetic diseases [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
RCV002221594 VAR_083546 rs1575647025 CA352786720 TCGA novel |
71 | P>S | Ectodermal dysplasia with facial dysmorphism and acral, ocular, and brain anomalies Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. EDFAOB; somatic mosaic variant; decreased Rho protein signal transduction; decreased substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading; decreased stress fibers assembly; decreased cytoplasmic microtubule organization [ClinVar, NCI-TCGA, UniProt] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar NCI-TCGA Ensembl dbSNP UniProt |
|
rs1386884613 CA352788306 |
3 | A>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 3 | A>T | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA352788269 rs1575653732 |
9 | V>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA74517701 COSM3824157 rs11552761 |
17 | G>A | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. breast [NCI-TCGA, Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated Ensembl NCI-TCGA |
|
CA74517702 rs11552761 |
17 | G>E | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen Ensembl NCI-TCGA |
| TCGA novel | 22 | L>F | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA74517671 rs11552762 |
32 | E>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
| TCGA novel | 32 | E>G | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA352787998 rs1259336198 |
49 | D>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1575647051 RCV001029738 CA352786855 |
61 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
| TCGA novel | 67 | D>N | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
COSM3736658 rs866298036 CA74513482 |
75 | P>S | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. skin [NCI-TCGA, Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated Ensembl NCI-TCGA |
|
rs372868120 CA352786644 |
78 | D>E | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 78 | D>N | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1381401434 CA352786588 |
86 | I>N | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1386276711 CA352786592 |
86 | I>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA74513411 rs1019221398 |
87 | D>N | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs866333389 CA74508739 |
108 | P>L | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen Ensembl NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1260716785 CA352785839 |
114 | L>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA352785703 rs1200080340 |
129 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1420305556 CA352785678 |
132 | A>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA2397838 rs779873892 |
134 | M>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs371460390 CA74508707 |
134 | M>T | No |
ClinGen ESP TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1376671049 CA352784450 |
137 | E>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs773583237 CA352784445 |
137 | E>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs775207141 CA2397788 |
141 | P>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 143 | E>A | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs745317533 CA2397786 |
146 | D>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1357783668 CA352784369 |
147 | M>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA352784370 rs1260250679 |
147 | M>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA352784342 rs1465894043 |
151 | I>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA352784336 rs1250486455 COSM1328154 |
152 | G>C | ovary Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [Cosmic, NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
| TCGA novel | 153 | A>T | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| rs11552757 | 161 | A>V | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
1 associated diseases with P61586
[MIM: 618727]: Ectodermal dysplasia with facial dysmorphism and acral, ocular, and brain anomalies (EDFAOB)
A neuroectodermal syndrome characterized by linear hypopigmentation, alopecia, apparently asymptomatic leukoencephalopathy, and facial, ocular, dental and acral anomalies. Patients show no intellectual or neurologic impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31570889}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Without disease ID
- A neuroectodermal syndrome characterized by linear hypopigmentation, alopecia, apparently asymptomatic leukoencephalopathy, and facial, ocular, dental and acral anomalies. Patients show no intellectual or neurologic impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31570889}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
1 regional properties for P61586
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Small GTP-binding protein domain | 5 - 159 | IPR005225 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.5.2 | Acting on GTP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
26 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical junction complex | A functional unit located near the cell apex at the points of contact between epithelial cells, which in vertebrates is composed of the tight junction, the zonula adherens, and desmosomes and in some invertebrates, such as Drosophila, is composed of the subapical complex (SAC), the zonula adherens and the septate junction. Functions in the regulation of cell polarity, tissue integrity and intercellular adhesion and permeability. |
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| cell cortex | The region of a cell that lies just beneath the plasma membrane and often, but not always, contains a network of actin filaments and associated proteins. |
| cell junction | A cellular component that forms a specialized region of connection between two or more cells, or between a cell and the extracellular matrix, or between two membrane-bound components of a cell, such as flagella. |
| cell periphery | The part of a cell encompassing the cell cortex, the plasma membrane, and any external encapsulating structures. |
| cell projection | A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon. |
| cleavage furrow | The cleavage furrow is a plasma membrane invagination at the cell division site. The cleavage furrow begins as a shallow groove and eventually deepens to divide the cytoplasm. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| cytoskeleton | A cellular structure that forms the internal framework of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton includes intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendritic spine | A small, membranous protrusion from a dendrite that forms a postsynaptic compartment, typically receiving input from a single presynapse. They function as partially isolated biochemical and an electrical compartments. Spine morphology is variable:they can be thin, stubby, mushroom, or branched, with a continuum of intermediate morphologies. They typically terminate in a bulb shape, linked to the dendritic shaft by a restriction. Spine remodeling is though to be involved in synaptic plasticity. |
| endoplasmic reticulum membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| extracellular exosome | A vesicle that is released into the extracellular region by fusion of the limiting endosomal membrane of a multivesicular body with the plasma membrane. Extracellular exosomes, also simply called exosomes, have a diameter of about 40-100 nm. |
| extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The component of a plasma membrane consisting of gene products and protein complexes that are loosely bound to its cytoplasmic surface, but not integrated into the hydrophobic region. |
| ficolin-1-rich granule membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a ficolin-1-rich granule. |
| focal adhesion | A cell-substrate junction that anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix and that forms a point of termination of actin filaments. In insects focal adhesion has also been referred to as hemi-adherens junction (HAJ). |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| lamellipodium | A thin sheetlike process extended by the leading edge of a migrating cell or extending cell process; contains a dense meshwork of actin filaments. |
| midbody | A thin cytoplasmic bridge formed between daughter cells at the end of cytokinesis. The midbody forms where the contractile ring constricts, and may persist for some time before finally breaking to complete cytokinesis. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynapse | The part of a synapse that is part of the post-synaptic cell. |
| ruffle membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a ruffle. |
| secretory granule membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a secretory granule. |
| vesicle | Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| G protein activity | A molecular function regulator that cycles between active GTP-bound and inactive GDP-bound states. In its active state, binds to a variety of effector proteins to regulate cellular processes. Intrinsic GTPase activity returns the G protein to its GDP-bound state. The return to the GDP-bound state can be accelerated by the action of a GTPase-activating protein (GAP). |
| GDP binding | Binding to GDP, guanosine 5'-diphosphate. |
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
| myosin binding | Binding to a myosin; myosins are any of a superfamily of molecular motor proteins that bind to actin and use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to generate force and movement along actin filaments. |
| protein domain specific binding | Binding to a specific domain of a protein. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor binding | Binding to a Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor protein. |
93 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| actin cytoskeleton reorganization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in dynamic structural changes to the arrangement of constituent parts of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| actin filament organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments. Includes processes that control the spatial distribution of actin filaments, such as organizing filaments into meshworks, bundles, or other structures, as by cross-linking. |
| alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment | The process in which a pro-T cell becomes committed to becoming an alpha-beta T cell. |
| androgen receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by androgen binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| angiotensin-mediated vasoconstriction involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure | The decrease in blood vessel diameter as a result of the release of angiotensin into the blood stream. |
| apical junction assembly | The formation of an apical junction, a functional unit located near the cell apex at the points of contact between epithelial cells composed of the tight junction, the zonula adherens junction and the desmosomes, by the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of its constituents. |
| apolipoprotein A-I-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by apolipoprotein A-I binding to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| beta selection | The process in which successful recombination of a T cell receptor beta chain into a translatable protein coding sequence leads to rescue from apoptosis and subsequent proliferation of an immature T cell. |
| cell junction assembly | A cellular process that results in the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a cell junction. |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| cell-matrix adhesion | The binding of a cell to the extracellular matrix via adhesion molecules. |
| cellular response to chemokine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemokine stimulus. |
| cellular response to cytokine stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cytokine stimulus. |
| cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| cerebral cortex cell migration | The orderly movement of cells from one site to another in the cerebral cortex. |
| cleavage furrow formation | Generation of the cleavage furrow, a shallow groove in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate that marks the site of cytokinesis. This process includes the recruitment and localized activation of signals such as RhoA at the site of the future furrow to ensure that furrowing initiates at the correct site in the cell. |
| cortical cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures in the cell cortex, i.e. just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| cytoplasmic microtubule organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of structures formed of microtubules and associated proteins in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| endothelial cell migration | The orderly movement of an endothelial cell into the extracellular matrix to form an endothelium. |
| endothelial tube lumen extension | Any endothelial tube morphogenesis process by which the tube is increased in length. |
| establishment of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity | The specification and formation of the apicobasal polarity of an epithelial cell. |
| establishment or maintenance of cell polarity | Any cellular process that results in the specification, formation or maintenance of anisotropic intracellular organization or cell growth patterns. |
| forebrain radial glial cell differentiation | The process in which neuroepithelial cells of the neural tube give rise to radial glial cells, specialized bipotential progenitors cells of the forebrain. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate. |
| GTP metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| kidney development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the kidney over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The kidney is an organ that filters the blood and/or excretes the end products of body metabolism in the form of urine. |
| mitotic cleavage furrow formation | Any cleavage furrow formation that is involved in mitotic cell cycle. |
| mitotic spindle assembly | Mitotic bipolar spindle assembly begins with spindle microtubule nucleation from the separated spindle pole body, includes spindle elongation during prometaphase, and is complete when all kinetochores are stably attached the spindle, and the spindle assembly checkpoint is satisfied. |
| motor neuron apoptotic process | Any apoptotic process in a motor neuron, an efferent neuron that passes from the central nervous system or a ganglion toward or to a muscle and conducts an impulse that causes movement. |
| negative chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell or organism towards a lower concentration of a chemical. |
| negative regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis. Cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis is the orderly movement of endothelial cells into the extracellular matrix in order to form new blood vessels contributing to the process of sprouting angiogenesis. |
| negative regulation of cell size | Any process that reduces cell size. |
| negative regulation of cell-substrate adhesion | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of cell-substrate adhesion. Cell-substrate adhesion is the attachment of a cell to the underlying substrate via adhesion molecules. |
| negative regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of -kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| negative regulation of intracellular steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the activity of any intracellular steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of motor neuron apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of motor neuron apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of neuron differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation. |
| negative regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| negative regulation of oxidative phosphorylation | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP that accompanies the oxidation of a metabolite through the operation of the respiratory chain. Oxidation of compounds establishes a proton gradient across the membrane, providing the energy for ATP synthesis. |
| negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process. |
| negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration. |
| negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. |
| neuron migration | The characteristic movement of an immature neuron from germinal zones to specific positions where they will reside as they mature. |
| neuron projection morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of a neuron projection are generated and organized. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites. |
| odontogenesis | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tooth or teeth over time, from formation to the mature structure(s). A tooth is any hard bony, calcareous, or chitinous organ found in the mouth or pharynx of an animal and used in procuring or masticating food. |
| ossification involved in bone maturation | The formation of bone or of a bony substance, or the conversion of fibrous tissue or of cartilage into bone, involved in the progression of the skeleton from its formation to its mature state. |
| positive regulation of actin filament polymerization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of actin polymerization. |
| positive regulation of alpha-beta T cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of alpha-beta T cell differentiation. |
| positive regulation of cell growth | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, extent or direction of cell growth. |
| positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the activity of a cysteine-type endopeptidase involved in the apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of cytokinesis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the division of the cytoplasm of a cell, and its separation into two daughter cells. |
| positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| positive regulation of leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cell | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cell. |
| positive regulation of lipase activity | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of lipase activity, the hydrolysis of a lipid or phospholipid. |
| positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death of neurons by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of neuron differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation. |
| positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| positive regulation of podosome assembly | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of podosome assembly. |
| positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of protein serine/threonine kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of stress fiber assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly of a stress fiber, a bundle of microfilaments and other proteins found in fibroblasts. |
| positive regulation of T cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of T cell migration. |
| positive regulation of translation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of proteins by the translation of mRNA or circRNA. |
| positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of vascular smooth muscle contraction. |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of calcium ion transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of calcium ions into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| regulation of cell migration | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| regulation of dendrite development | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of dendrite development. |
| regulation of focal adhesion assembly | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of focal adhesion formation, the establishment and maturation of focal adhesions. |
| regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of modification of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of modification of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton. |
| regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neural precursor cell proliferation. |
| regulation of osteoblast proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast proliferation. |
| regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by endothelin | The process in which endothelin modulates the force with which blood passes through the circulatory system. Endothelin is a hormone that is released by the endothelium, and it is a vasoconstrictor. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| response to amino acid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an amino acid stimulus. An amino acid is a carboxylic acids containing one or more amino groups. |
| response to ethanol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ethanol stimulus. |
| response to glucocorticoid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucocorticoid stimulus. Glucocorticoids are hormonal C21 corticosteroids synthesized from cholesterol with the ability to bind with the cortisol receptor and trigger similar effects. Glucocorticoids act primarily on carbohydrate and protein metabolism, and have anti-inflammatory effects. |
| response to glucose | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucose stimulus. |
| response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
| response to mechanical stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a mechanical stimulus. |
| response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| Rho protein signal transduction | The series of molecular signals within the cell that are mediated by a member of the Rho family of proteins switching to a GTP-bound active state. |
| Roundabout signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a SLIT protein binding to a Roundabout (ROBO) family receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| skeletal muscle satellite cell migration | The orderly movement of a skeletal muscle satellite cell from one site to another. Migration of these cells is a key step in the process of growth and repair of skeletal muscle cells. |
| skeletal muscle tissue development | The developmental sequence of events leading to the formation of adult skeletal muscle tissue. The main events are: the fusion of myoblasts to form myotubes that increase in size by further fusion to them of myoblasts, the formation of myofibrils within their cytoplasm and the establishment of functional neuromuscular junctions with motor neurons. At this stage they can be regarded as mature muscle fibers. |
| stress fiber assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a stress fiber. A stress fiber is a contractile actin filament bundle that consists of short actin filaments with alternating polarity. |
| stress-activated protein kinase signaling cascade | The series of molecular signals in which a stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) cascade relays a signal. |
| substantia nigra development | The progression of the substantia nigra over time from its initial formation until its mature state. The substantia nigra is the layer of gray substance that separates the posterior parts of the cerebral peduncles (tegmentum mesencephali) from the anterior parts; it normally includes a posterior compact part with many pigmented cells (pars compacta) and an anterior reticular part whose cells contain little pigment (pars reticularis). |
| substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading | The morphogenetic process that results in flattening of a cell as a consequence of its adhesion to a substrate. |
| trabecula morphogenesis | The process of shaping a trabecula in an organ. A trabecula is a small, often microscopic, tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod, which generally has a mechanical function. Trabecula are usually but not necessarily, composed of dense collagenous tissue. |
| Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where activated receptors signal via downstream effectors including C-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) to modulate cytoskeletal elements and control cell polarity. |
| wound healing, spreading of cells | The migration of a cell along or through a wound gap that contributes to the reestablishment of a continuous surface. |
38 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q00246 | RHO4 | GTP-binding protein RHO4 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q17QI8 | Rhov | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoV | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q2HJ68 | RND1 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein Rho6 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q3ZBW5 | RHOB | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P61585 | RHOA | Transforming protein RhoA | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q1RMJ6 | RHOC | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q9PSX7 | RHOC | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P24406 | RHOA | Transforming protein RhoA | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| P48148 | Rho1 | Ras-like GTP-binding protein Rho1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| O94955 | RHOBTB3 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O94844 | RHOBTB1 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P08134 | RHOC | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P61587 | RND3 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P62745 | RHOB | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q92730 | RND1 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein Rho6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96L33 | RHOV | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoV | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8BLR7 | Rnd1 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein Rho6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P61588 | Rnd3 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9DAK3 | Rhobtb1 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9CTN4 | Rhobtb3 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8VDU1 | Rhov | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoV | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62159 | Rhoc | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P62746 | Rhob | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9QUI0 | Rhoa | Transforming protein RhoA | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O77683 | RND3 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| Q6SA80 | Rnd3 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9Z1Y0 | Rhov | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoV | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P61589 | Rhoa | Transforming protein RhoA | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P62747 | Rhob | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9SSX0 | RAC1 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein 1 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q6Z808 | RAC3 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein 3 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q68Y52 | RAC2 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein 2 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q67VP4 | RAC4 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein 4 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q22038 | rho-1 | Ras-like GTP-binding protein rhoA | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9SU67 | ARAC8 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O82480 | ARAC7 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC7 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q38903 | ARAC2 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O82481 | ARAC10 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC10 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAAIRKKLVI | VGDGACGKTC | LLIVFSKDQF | PEVYVPTVFE | NYVADIEVDG | KQVELALWDT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| AGQEDYDRLR | PLSYPDTDVI | LMCFSIDSPD | SLENIPEKWT | PEVKHFCPNV | PIILVGNKKD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LRNDEHTRRE | LAKMKQEPVK | PEEGRDMANR | IGAFGYMECS | AKTKDGVREV | FEMATRAALQ |
| 190 | |||||
| ARRGKKKSGC | LVL |