P61329
Gene name |
Fgf12 (Fhf1) |
Protein name |
Fibroblast growth factor 12 |
Names |
FGF-12, Fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 1, FHF-1, Myocyte-activating factor |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:14167 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
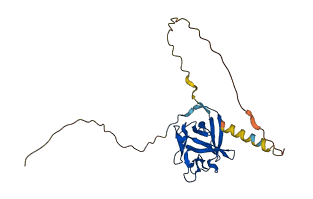
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P61329
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P61329-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
4 variants for P61329
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3389407714 | 29 | R>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3406702057 | 55 | C>W | No | EVA | |
| rs3406451063 | 131 | G>E | No | EVA | |
| rs1134333690 | 134 | Y>* | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P61329
No regional properties for P61329
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for P61329 | |||
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| synapse | The junction between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron, a muscle fiber or a glial cell. As the axon approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic terminal bouton, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the terminal bouton is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic terminal bouton secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| growth factor activity | The function that stimulates a cell to grow or proliferate. Most growth factors have other actions besides the induction of cell growth or proliferation. |
| heparin binding | Binding to heparin, a member of a group of glycosaminoglycans found mainly as an intracellular component of mast cells and which consist predominantly of alternating alpha-(1->4)-linked D-galactose and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-6-sulfate residues. |
| sodium channel regulator activity | Binds to and modulates the activity of a sodium channel. |
| transmembrane transporter binding | Binding to a transmembrane transporter, a protein or protein complex that enables the transfer of a substance, usually a specific substance or a group of related substances, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
11 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adult locomotory behavior | Locomotory behavior in a fully developed and mature organism. |
| chemical synaptic transmission | The vesicular release of classical neurotransmitter molecules from a presynapse, across a chemical synapse, the subsequent activation of neurotransmitter receptors at the postsynapse of a target cell (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) and the effects of this activation on the postsynaptic membrane potential and ionic composition of the postsynaptic cytosol. This process encompasses both spontaneous and evoked release of neurotransmitter and all parts of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Evoked transmission starts with the arrival of an action potential at the presynapse. |
| JNK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a JNK (a MAPK), a JNKK (a MAPKK) and a JUN3K (a MAP3K). The cascade can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinases in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| negative regulation of cation channel activity | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cation channel activity. |
| neuromuscular process | Any process pertaining to the functions of the nervous and muscular systems of an organism. |
| positive regulation of sodium ion transport | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| regulation of membrane depolarization | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of membrane depolarization. Membrane depolarization is the process in which membrane potential changes in the depolarizing direction from the resting potential, usually from negative to positive. |
| regulation of neuronal action potential | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of action potential creation, propagation or termination in a neuron. This typically occurs via modulation of the activity or expression of voltage-gated ion channels. |
| regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of sodium ion transmembrane transport. |
| regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity. |
| regulation of voltage-gated sodium channel activity | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of voltage-gated sodium channel activity. |
28 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P48801 | FGF3 | Fibroblast growth factor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P08620 | FGF4 | Fibroblast growth factor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9NP95 | FGF20 | Fibroblast growth factor 20 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9HCT0 | FGF22 | Fibroblast growth factor 22 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P10767 | FGF6 | Fibroblast growth factor 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O15520 | FGF10 | Fibroblast growth factor 10 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q92914 | FGF11 | Fibroblast growth factor 11 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P11487 | FGF3 | Fibroblast growth factor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P31371 | FGF9 | Fibroblast growth factor 9 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O43320 | FGF16 | Fibroblast growth factor 16 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV SS |
| Q9NSA1 | FGF21 | Fibroblast growth factor 21 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9JJN1 | Fgf21 | Fibroblast growth factor 21 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9ESS2 | Fgf22 | Fibroblast growth factor 22 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O35565 | Fgf10 | Fibroblast growth factor 10 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54130 | Fgf9 | Fibroblast growth factor 9 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P21658 | Fgf6 | Fibroblast growth factor 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P11403 | Fgf4 | Fibroblast growth factor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9ESL8 | Fgf16 | Fibroblast growth factor 16 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9ESL9 | Fgf20 | Fibroblast growth factor 20 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05524 | Fgf3 | Fibroblast growth factor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q95L12 | FGF9 | Fibroblast growth factor 9 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q9EST9 | Fgf20 | Fibroblast growth factor 20 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O54769 | Fgf16 | Fibroblast growth factor 16 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P36364 | Fgf9 | Fibroblast growth factor 9 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P70492 | Fgf10 | Fibroblast growth factor 10 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6PBT8 | fgf1 | Putative fibroblast growth factor 1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q2HXK8 | fgf16 | Fibroblast growth factor 16 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| P48802 | fgf3 | Fibroblast growth factor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAAAIASSLI | RQKRQARESN | SDRVSASKRR | SSPSKDGRSL | CERHVLGVFS | KVRFCSGRKR |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PVRRRPEPQL | KGIVTRLFSQ | QGYFLQMHPD | GTIDGTKDEN | SDYTLFNLIP | VGLRVVAIQG |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VKASLYVAMN | GEGYLYSSDV | FTPECKFKES | VFENYYVIYS | STLYRQQESG | RAWFLGLNKE |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GQIMKGNRVK | KTKPSSHFVP | KPIEVCMYRE | PSLHEIGEKQ | GRSRKSSGTP | TMNGGKVVNQ |
| DST |