P57080
Gene name |
Usp25 |
Protein name |
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 25 |
Names |
EC 3.4.19.12 , Deubiquitinating enzyme 25 , Ubiquitin thioesterase 25 , Ubiquitin-specific-processing protease 25 , mUSP25 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:30940 |
EC number |
3.4.19.12: Omega peptidases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
169-655 (Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase) |
Relief mechanism |
Others |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Sauer F et al. (2019) "Differential Oligomerization of the Deubiquitinases USP25 and USP28 Regulates Their Activities", Molecular cell, 74, 421-435.e10
- Gersch M et al. (2019) "Distinct USP25 and USP28 Oligomerization States Regulate Deubiquitinating Activity", Molecular cell, 74, 436-451.e7
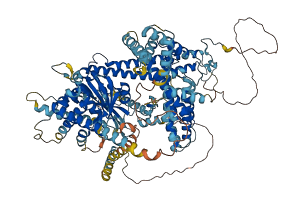
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for P57080
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1VDL | NMR | - | A | 1-67 | PDB |
| AF-P57080-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
23 variants for P57080
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3389433741 | 28 | T>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389422310 | 153 | R>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389371956 | 272 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3412991836 | 310 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389371895 | 437 | L>V | No | EVA | |
| rs265655380 | 500 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3389403235 | 502 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389426265 | 503 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs259759688 | 509 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3389413856 | 537 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389433730 | 579 | E>V | No | EVA | |
| rs239556814 | 706 | T>A | No | EVA | |
| rs255378838 | 706 | T>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3389430167 | 825 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3389424410 | 849 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389415922 | 863 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389381934 | 964 | P>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3389371891 | 981 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389371969 | 986 | R>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389403226 | 1000 | N>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389426264 | 1033 | A>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3389371887 | 1035 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3407151063 | 1039 | R>L | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P57080
5 regional properties for P57080
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Myosin head, motor domain | 51 - 773 | IPR001609 |
| domain | Myosin, N-terminal, SH3-like | 2 - 53 | IPR004009 |
| domain | Myosin VI, cargo binding domain | 1137 - 1227 | IPR032412 |
| domain | Class VI myosin, motor domain | 71 - 760 | IPR036114 |
| domain | Myosin VI, lever arm | 771 - 918 | IPR049016 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.4.19.12 | Omega peptidases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| proteasome complex | A large multisubunit complex which catalyzes protein degradation, found in eukaryotes, archaea and some bacteria. In eukaryotes, this complex consists of the barrel shaped proteasome core complex and one or two associated proteins or complexes that act in regulating entry into or exit from the core. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cysteine-type deubiquitinase activity | An thiol-dependent isopeptidase activity that cleaves ubiquitin from a target protein to which it is conjugated. |
| SUMO binding | Binding to the small ubiquitin-like protein SUMO. |
7 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| immune response | Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat. |
| interleukin-17-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by interleukin-17 binding to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| mRNA metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving mRNA, messenger RNA, which is responsible for carrying the coded genetic 'message', transcribed from DNA, to sites of protein assembly at the ribosomes. |
| regulation of protein stability | Any process that affects the structure and integrity of a protein, altering the likelihood of its degradation or aggregation. |
| response to oxidative stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of oxidative stress, a state often resulting from exposure to high levels of reactive oxygen species, e.g. superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals. |
| stress-activated protein kinase signaling cascade | The series of molecular signals in which a stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) cascade relays a signal. |
| ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of a ubiquitin group, or multiple ubiquitin groups, to the protein. |
4 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q93009 | USP7 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9UHP3 | USP25 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 25 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q6A4J8 | Usp7 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P56399 | Usp5 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MTVEQNVLQQ | SAAQKHQQTF | LNQLREITGI | NDAQILQQAL | KDSNGNLELA | VAFLTAKNAK |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| TPPQEETGYY | QTALPGNDRY | ISVGSQADAN | VIDLTGDDKD | DLQRAIALSL | AESNRAFRET |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| GITDEEQAIS | RVLEASIAEN | KACLKRTPIE | VWRDSRNPYD | RKRQEKAPVG | LKNVGNTCWF |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SAVIQSLFNL | LEFRRLVLNY | KPPSNAQDLP | RNQKEHRNLP | FMRELRYLFA | LLVGTKRKYV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| DPSRAVEILK | DAFKSNDSQQ | QDVSEFTHKL | LDWLEDAFQM | KAEEETDEEK | PKNPMVELFY |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| GRFLAMGVLE | GKKFENTEMF | GQYPLQVNGF | KDLHECLEAA | MIEGEIESLH | SDNSGKSGQE |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| HWFTELPPVL | TFELSRFEFN | QALGRPEKIH | NKLEFPQVLY | LDRYMHRNRE | ITRIKREEIK |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| RLKDYLTVLQ | QRLERYLSYG | SGPKRFPLVD | VLQYALEFAS | SKPVCTSPVD | DIDASSSASG |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| PLPSQSLPST | TEQQGPCASD | LPGSSSPASG | AALPLRSVIH | KPFTQSRIPP | DLPMHPAPRH |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| ITEEELCVLE | SCLHRWRTEI | ENDTRDLQES | ISRIHRTIEL | MYSDKSMIQV | PYRLHAVLVH |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| EGQANAGHYW | AYIFDHRESR | WMKYNDIAVT | KSSWEELVRD | SFGGYRNASA | YCLMYIDDKA |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| QFLIQEEFNK | ETGQALVGME | TLPPDLRDFV | EEDNQRFEKE | LEEWDTQLAQ | RSLQEKLLAA |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| PKLREAEASA | TTAQAGGADY | LEQPSRSDLS | KHWKEETLRV | IAKASHDLED | KGPETVLQSA |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| IKLEYSRLVK | LAQEDTPPET | DYRLHHVLVY | FIQNQAPKKI | IEKTLLEQFG | DRNLSFDERC |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| HNIMKVAQAK | LEMIKPEEVN | LEEYEEWHAD | YKKFRETTMY | LITGLENFQR | ESYIDSLLFL |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| LCAYQNNKEL | LSKGPYRGHD | GELISHYRRE | CLLKLNEQAA | ELFESGEDGD | VNNGLIIMNE |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| FIVPFLPLLL | VDDMEEKDIL | AVEDMRNRWC | SYLGQEMEAN | LQEKLTDFLP | KLLDCSTEIK |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | |||
| GFHEPPKLPS | YSAHELCERF | ARIMLSLSRT | PADGR |