P54763
Gene name |
Ephb2 |
Protein name |
Ephrin type-B receptor 2 |
Names |
Neural kinase, Nuk receptor tyrosine kinase, Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor EPH-3, Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor SEK-3 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:13844 |
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
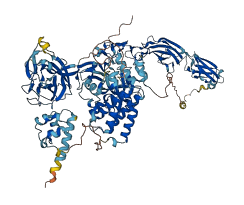
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
621-884 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
763-791 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
621-884 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

8 structures for P54763
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1JPA | X-ray | 191 A | A/B | 587-898 | PDB |
| 1KGY | X-ray | 270 A | A/B/C/D | 20-199 | PDB |
| 1NUK | X-ray | 290 A | A | 20-202 | PDB |
| 1SHW | X-ray | 220 A | B | 19-199 | PDB |
| 2HEN | X-ray | 260 A | A/B/C/D | 614-898 | PDB |
| 3ETP | X-ray | 200 A | A | 20-199 | PDB |
| 7S7K | X-ray | 315 A | A | 19-543 | PDB |
| AF-P54763-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
2 variants for P54763
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs240353516 | 228 | A>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs234527532 | 368 | G>S | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with P54763
14 regional properties for P54763
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 621 - 884 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Ephrin receptor ligand binding domain | 20 - 202 | IPR001090 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 622 - 880 | IPR001245 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class V, conserved site | 178 - 198 | IPR001426-1 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class V, conserved site | 241 - 261 | IPR001426-2 |
| domain | Sterile alpha motif domain | 910 - 977 | IPR001660 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 324 - 434 | IPR003961-1 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 435 - 530 | IPR003961-2 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 742 - 754 | IPR008266 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase ephrin type A/B receptor-like | 268 - 302 | IPR011641 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 627 - 653 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 621 - 880 | IPR020635 |
| domain | Ephrin receptor, transmembrane domain | 544 - 617 | IPR027936 |
| domain | Ephrin type-B receptor 2, ligand binding domain | 19 - 196 | IPR034238 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
15 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| dendritic spine | A small, membranous protrusion from a dendrite that forms a postsynaptic compartment, typically receiving input from a single presynapse. They function as partially isolated biochemical and an electrical compartments. Spine morphology is variable:they can be thin, stubby, mushroom, or branched, with a continuum of intermediate morphologies. They typically terminate in a bulb shape, linked to the dendritic shaft by a restriction. Spine remodeling is though to be involved in synaptic plasticity. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| integral component of postsynaptic membrane | The component of the postsynaptic membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| integral component of presynaptic membrane | The component of the presynaptic membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| synapse | The junction between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron, a muscle fiber or a glial cell. As the axon approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic terminal bouton, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the terminal bouton is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic terminal bouton secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
12 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| amyloid-beta binding | Binding to an amyloid-beta peptide/protein. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| axon guidance receptor activity | Combining with an extracellular messenger and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to results in a change in cellular activity involved in axon guidance. |
| ephrin receptor activity | Combining with an ephrin receptor ligand to initiate a change in cell activity. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| signaling receptor activity | Receiving a signal and transmitting it in the cell to initiate a change in cell activity. A signal is a physical entity or change in state that is used to transfer information in order to trigger a response. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | Combining with a signal and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate. |
| transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity | Combining with a transmembrane ephrin to initiate a change in cell activity. |
62 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| angiogenesis | Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels. |
| animal organ morphogenesis | Morphogenesis of an animal organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process in which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions. |
| axon guidance | The chemotaxis process that directs the migration of an axon growth cone to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| axonal fasciculation | The collection of axons into a bundle of rods, known as a fascicle. |
| B cell activation | The change in morphology and behavior of a mature or immature B cell resulting from exposure to a mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or an antigen for which it is specific. |
| camera-type eye morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the eye are generated and organized. The camera-type eye is an organ of sight that receives light through an aperture and focuses it through a lens, projecting it on a photoreceptor field. |
| cell morphogenesis | The developmental process in which the size or shape of a cell is generated and organized. |
| cellular response to amyloid-beta | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a amyloid-beta stimulus. |
| cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| central nervous system projection neuron axonogenesis | Generation of a long process of a CNS neuron, that carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells in a different central nervous system region. |
| commissural neuron axon guidance | The process in which the migration of an axon growth cone of a commissural neuron is directed to its target in the brain in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| corpus callosum development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the corpus callosum over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The corpus callosum is a thick bundle of nerve fibers comprising a commissural plate connecting the two cerebral hemispheres. It consists of contralateral axon projections that provide communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres. |
| dendritic spine development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendritic spine over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A dendritic spine is a protrusion from a dendrite and a specialized subcellular compartment involved in synaptic transmission. |
| dendritic spine morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of a dendritic spine are generated and organized. A dendritic spine is a protrusion from a dendrite and a specialized subcellular compartment involved in synaptic transmission. |
| ephrin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by ephrin binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| hindbrain tangential cell migration | The migration of a cell in the hindbrain in which cells move orthogonal to the direction of radial migration. |
| inner ear morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the inner ear are generated and organized. The inner ear is the structure in vertebrates that contains the organs of balance and hearing. It consists of soft hollow sensory structures (the membranous labyrinth) containing fluid (endolymph) surrounded by fluid (perilymph) and encased in a bony cavity (the bony labyrinth). It consists of two chambers, the sacculus and utriculus, from which arise the cochlea and semicircular canals respectively. |
| learning | Any process in an organism in which a relatively long-lasting adaptive behavioral change occurs as the result of experience. |
| learning or memory | The acquisition and processing of information and/or the storage and retrieval of this information over time. |
| negative regulation of axonogenesis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis. |
| negative regulation of cell adhesion | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell adhesion. |
| negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response. |
| negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| negative regulation of NMDA glutamate receptor activity | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of NMDA glutamate receptor activity. |
| negative regulation of protein kinase activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity. |
| negative regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of Ras protein signal transduction. |
| neuron projection retraction | The organization process which results in the disassembly (either partial or complete) of constituent parts of a neuron projection. A neuron projection is a prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| optic nerve morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structure of the optic nerve is generated and organized. The sensory optic nerve originates from the bipolar cells of the retina and conducts visual information to the brainstem. The optic nerve exits the back of the eye in the orbit, enters the optic canal, and enters the central nervous system at the optic chiasm (crossing) where the nerve fibers become the optic tract just prior to entering the hindbrain. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| positive regulation of B cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of B cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of dendritic spine morphogenesis, the process in which the anatomical structures of a dendritic spine are generated and organized. A dendritic spine is a protrusion from a dendrite and a specialized subcellular compartment involved in synaptic transmission. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of immunoglobulin production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of immunoglobulin production. |
| positive regulation of kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| positive regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity | A process that increases long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity, the ability of neuronal synapses to change long-term as circumstances require. Long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity generally involves increase or decrease in actual synapse numbers. |
| positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of long-term synaptic potentiation. |
| positive regulation of NMDA glutamate receptor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of NMDA glutamate receptor activity. |
| positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to plasma membrane. |
| positive regulation of synapse assembly | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the frequency, rate or extent of synapse assembly, the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a synapse. |
| positive regulation of synaptic plasticity | A process that increases synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to change as circumstances require. They may alter function, such as increasing or decreasing their sensitivity, or they may increase or decrease in actual numbers. |
| positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of tumor necrosis factor production. |
| postsynaptic membrane assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a postsynaptic membrane, a specialized area of membrane facing the presynaptic membrane on the tip of the nerve ending and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft). |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of axonogenesis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis, the generation of an axon, the long process of a neuron. |
| regulation of behavioral fear response | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of behavioral fear response. |
| regulation of blood coagulation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation. |
| regulation of body fluid levels | Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids. |
| regulation of filopodium assembly | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly of a filopodium, a thin, stiff protrusion extended by the leading edge of a motile cell such as a crawling fibroblast or amoeba, or an axonal growth cone. |
| regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity | A process that modulates neuronal synaptic plasticity, the ability of neuronal synapses to change as circumstances require. They may alter function, such as increasing or decreasing their sensitivity, or they may increase or decrease in actual numbers. |
| regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of receptor signaling via JAK-STAT. |
| regulation of synapse assembly | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of synapse assembly, the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a synapse. |
| regulation of T-helper 17 type immune response | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of T-helper 17 type immune response. |
| retinal ganglion cell axon guidance | The process in which the migration of an axon growth cone of a retinal ganglion cell (RGC) is directed to its target in the brain in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| roof of mouth development | The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of the roof of the mouth from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure. The roof of the mouth is the partition that separates the nasal and oral cavities. |
| tight junction assembly | A cellular process that results in the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a tight junction. A tight junction seals cells together in an epithelium in a way that prevents even small molecules from leaking from one side of the sheet to the other. |
| trans-synaptic signaling by trans-synaptic complex, modulating synaptic transmission | Cell-cell signaling between presynapse and postsynapse, mediated by transynaptic protein complexes, that modulates the synaptic transmission properties of the synapse. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| urogenital system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the urogenital system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| vesicle-mediated intercellular transport | A cellular transport process in which transported substances are moved in extracellular vesicles between cells; transported substances are enclosed in the vesicle lumen or located in the extracellular vesicle membrane. |
49 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q07496 | EPHA4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07494 | EPHB1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P29318 | EPHA3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| O42422 | EPHA7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P54755 | EPHA5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07498 | EPHB3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07497 | EPHB5 | Ephrin type-B receptor 5 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P28693 | EPHB2 | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P0C0K6 | EPHB6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | SS |
| P29322 | EPHA8 | Ephrin type-A receptor 8 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P21709 | EPHA1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54764 | EPHA4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54753 | EPHB3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29320 | EPHA3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P54760 | EPHB4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29317 | EPHA2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q15375 | EPHA7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q5JZY3 | EPHA10 | Ephrin type-A receptor 10 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9UF33 | EPHA6 | Ephrin type-A receptor 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54762 | EPHB1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54756 | EPHA5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O15197 | EPHB6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29323 | EPHB2 | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q03145 | Epha2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60629 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60750 | Epha1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54761 | Ephb4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61772 | Epha7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8CBF3 | Ephb1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O09127 | Epha8 | Ephrin type-A receptor 8 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03137 | Epha4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54754 | Ephb3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8BYG9 | Epha10 | Ephrin type-A receptor 10 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O08644 | Ephb6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62413 | Epha6 | Ephrin type-A receptor 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P29319 | Epha3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54757 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P54759 | Epha7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09759 | Ephb1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P0C0K7 | Ephb6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08680 | Epha3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O61460 | vab-1 | Ephrin receptor 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q8VZJ9 | CRCK2 | Calmodulin-binding receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LMN7 | WAK5 | Wall-associated receptor kinase 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LSV3 | WAKL16 | Putative wall-associated receptor kinase-like 16 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9M342 | WAKL15 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 15 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O13147 | ephb3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O73878 | ephb4b | Ephrin type-B receptor 4b | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O13146 | epha3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAVRRLGAAL | LLLPLLAAVE | ETLMDSTTAT | AELGWMVHPP | SGWEEVSGYD | ENMNTIRTYQ |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| VCNVFESSQN | NWLRTKFIRR | RGAHRIHVEM | KFSVRDCSSI | PSVPGSCKET | FNLYYYEADF |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DLATKTFPNW | MENPWVKVDT | IAADESFSQV | DLGGRVMKIN | TEVRSFGPVS | RNGFYLAFQD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| YGGCMSLIAV | RVFYRKCPRI | IQNGAIFQET | LSGAESTSLV | AARGSCIANA | EEVDVPIKLY |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| CNGDGEWLVP | IGRCMCKAGF | EAVENGTVCR | GCPSGTFKAN | QGDEACTHCP | INSRTTSEGA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TNCVCRNGYY | RADLDPLDMP | CTTIPSAPQA | VISSVNETSL | MLEWTPPRDS | GGREDLVYNI |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| ICKSCGSGRG | ACTRCGDNVQ | YAPRQLGLTE | PRIYISDLLA | HTQYTFEIQA | VNGVTDQSPF |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| SPQFASVNIT | TNQAAPSAVS | IMHQVSRTVD | SITLSWSQPD | QPNGVILDYE | LQYYEKELSE |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| YNATAIKSPT | NTVTVQGLKA | GAIYVFQVRA | RTVAGYGRYS | GKMYFQTMTE | AEYQTSIKEK |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LPLIVGSSAA | GLVFLIAVVV | IAIVCNRRGF | ERADSEYTDK | LQHYTSGHMT | PGMKIYIDPF |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| TYEDPNEAVR | EFAKEIDISC | VKIEQVIGAG | EFGEVCSGHL | KLPGKREIFV | AIKTLKSGYT |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| EKQRRDFLSE | ASIMGQFDHP | NVIHLEGVVT | KSTPVMIITE | FMENGSLDSF | LRQNDGQFTV |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| IQLVGMLRGI | AAGMKYLADM | NYVHRDLAAR | NILVNSNLVC | KVSDFGLSRF | LEDDTSDPTY |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| TSALGGKIPI | RWTAPEAIQY | RKFTSASDVW | SYGIVMWEVM | SYGERPYWDM | TNQDVINAIE |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| QDYRLPPPMD | CPSALHQLML | DCWQKDRNHR | PKFGQIVNTL | DKMIRNPNSL | KAMAPLSSGI |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| NLPLLDRTIP | DYTSFNTVDE | WLEAIKMGQY | KESFANAGFT | SFDVVSQMMM | EDILRVGVTL |
| 970 | 980 | ||||
| AGHQKKILNS | IQVMRAQMNQ | IQSVEV |