P53042
Gene name |
Ppp5c |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 5 |
Names |
PP5, Protein phosphatase T, PPT |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:65179 |
EC number |
3.1.3.16: Phosphoric monoester hydrolases |
Protein Class |
SERINE/THREONINE-PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE 5-RELATED (PTHR45668) |
Descriptions
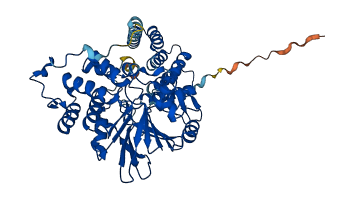
Protein phosphatase 5 (PP5) is a serine/threonine protein phosphatase comprising a regulatory tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain N-terminal to its phosphatase domain. PP5 functions in signaling pathways that control cellular responses to stress, glucocorticoids and DNA damage. Its phosphatase activity is suppressed by an autoinhibited conformation maintained by the TPR domain and a C-terminal region. The TPR domain engages with the catalytic channel of the phosphate domain, restricting access to the catalytic site. This autoinhibited conformation of PP5 is stabilized by the C-terminal αJ helix. In a study with rat PPP5C (P53042), the protein also contains a C-terminal regulatory region that may interact with the TPR domain.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
203-479 (Phosphatase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
Mutagenesis experiment |
Target domain |
203-479 (Phosphatase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Kang H et al. (2001) "Identification of amino acids in the tetratricopeptide repeat and C-terminal domains of protein phosphatase 5 involved in autoinhibition and lipid activation", Biochemistry, 40, 10485-90
- Oberoi J et al. (2016) "Structural and functional basis of protein phosphatase 5 substrate specificity", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113, 9009-14
- Chen MX et al. (1997) "Activation of protein phosphatase 5 by limited proteolysis or the binding of polyunsaturated fatty acids to the TPR domain", FEBS letters, 400, 136-40
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

3 structures for P53042
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4JA7 | X-ray | 200 A | A | 16-499 | PDB |
| 4JA9 | X-ray | 230 A | A | 16-499 | PDB |
| AF-P53042-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P53042
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P53042 | |||||
No associated diseases with P53042
5 regional properties for P53042
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | DEP domain | 111 - 186 | IPR000591 |
| domain | Cyclic nucleotide-binding domain | 245 - 364 | IPR000595 |
| domain | Ras-like guanine nucleotide exchange factor, N-terminal | 383 - 521 | IPR000651 |
| domain | Ras guanine-nucleotide exchange factors catalytic domain | 661 - 918 | IPR001895 |
| conserved_site | Ras guanine-nucleotide exchange factor, conserved site | 807 - 836 | IPR019804 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.1.3.16 | Phosphoric monoester hydrolases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR45668 | SERINE/THREONINE-PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE 5-RELATED |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR45668:SF5 | SERINE_THREONINE-PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE 5 |
| PANTHER Protein Class |
protein phosphatase
protein modifying enzyme |
|
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
11 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell periphery | The part of a cell encompassing the cell cortex, the plasma membrane, and any external encapsulating structures. |
| chaperone complex | A protein complex required for the non-covalent folding or unfolding, maturation, stabilization or assembly or disassembly of macromolecular structures. Usually active during or immediately after completion of translation. Many chaperone complexes contain heat shock proteins. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perikaryon | The portion of the cell soma (neuronal cell body) that excludes the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
| proximal dendrite | The dendrite of the dendritic tree that is closest to the neuronal cell body (the soma). |
13 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ADP binding | Binding to ADP, adenosine 5'-diphosphate. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| G-protein alpha-subunit binding | Binding to a G-protein alpha subunit. The alpha subunit binds a guanine nucleotide. |
| heat shock protein binding | Binding to a heat shock protein, a protein synthesized or activated in response to heat shock. |
| Hsp90 protein binding | Binding to Hsp90 proteins, any of a group of heat shock proteins around 90kDa in size. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| microtubule binding | Binding to a microtubule, a filament composed of tubulin monomers. |
| phosphatase activity | Catalysis of the hydrolysis of phosphoric monoesters, releasing inorganic phosphate. |
| phosphoprotein phosphatase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: a phosphoprotein + H2O = a protein + phosphate. Together with protein kinases, these enzymes control the state of phosphorylation of cellular proteins and thereby provide an important mechanism for regulating cellular activity. |
| protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: protein serine phosphate + H2O = protein serine + phosphate, and protein threonine phosphate + H2O = protein threonine + phosphate. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| RNA binding | Binding to an RNA molecule or a portion thereof. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to cadmium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cadmium (Cd) ion stimulus. |
| cellular response to hydrogen peroxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulus. |
| histone dephosphorylation | OBSOLETE. The modification of histones by removal of phosphate groups. |
| negative regulation of cell death | Any process that decreases the rate or frequency of cell death. Cell death is the specific activation or halting of processes within a cell so that its vital functions markedly cease, rather than simply deteriorating gradually over time, which culminates in cell death. |
| negative regulation of neuron death | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neuron death. |
| negative regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| peptidyl-serine dephosphorylation | The removal of phosphoric residues from peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine to form peptidyl-serine. |
| positive regulation of glucocorticoid receptor signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of glucocorticoid receptor signaling pathway. |
| protein dephosphorylation | The process of removing one or more phosphoric residues from a protein. |
| response to arachidonic acid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an arachidonic acid stimulus. |
| response to lead ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lead ion stimulus. |
| response to morphine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a morphine stimulus. Morphine is an opioid alkaloid, isolated from opium, with a complex ring structure. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P53043 | PPT1 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase T | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | SS |
| P53041 | PPP5C | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q60676 | Ppp5c | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9NES8 | pph-5 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 5 | Caenorhabditis elegans | EV |
| Q84XU2 | PAPP5 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q84K11 | PP5 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 5 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAMAEGERTE | CAEPPRDEPP | AEGTLKRAEE | LKTQANDYFK | AKDYENAIKF | YSQAIELNPS |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NAIYYGNRSL | AYLRTECYGY | ALGDATRAIE | LDKKYIKGYY | RRAASNMALG | KFRAALRDYE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| TVVKVKPNDK | DAKMKYQECS | KIVKQKAFER | AIAGDEHRRS | VVDSLDIESM | TIEDEYSGPK |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LEDGKVTITF | MKDLMQWYKD | QKKLHRKCAY | QILVQVKEVL | CKLSTLVETT | LKETEKITVC |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| GDTHGQFYDL | LNIFELNGLP | SETNPYIFNG | DFVDRGSFSV | EVILTLFGFK | LLYPDHFHLL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| RGNHETDNMN | QIYGFEGEVK | AKYTAQMYEL | FSEVFEWLPL | AQCINGKVLI | MHGGLFSEDG |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VTLDDIRKIE | RNRQPPDSGP | MCDLLWSDPQ | PQNGRSVSKR | GVSCQFGPDV | TKAFLEENQL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| DYIIRSHEVK | AEGYEVAHGG | RCVTVFSAPN | YCDQMGNKAS | YIHLQGSDLR | PQFHQFTAVP |
| 490 | |||||
| HPNVKPMAYA | NTLLQLGMM |