P50577
Gene name |
DLX5 (DLX-5) |
Protein name |
Homeobox protein DLX-5 |
Names |
cDlx |
Species |
Gallus gallus (Chicken) |
KEGG Pathway |
gga:373969 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
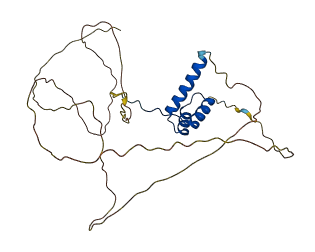
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P50577
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P50577-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
3 variants for P50577
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs740738567 | 12 | I>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs734022615 | 84 | G>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs731937134 | 85 | T>P | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with P50577
6 regional properties for P50577
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| conserved_site | Helix-turn-helix motif | 165 - 190 | IPR000047 |
| domain | Homeobox domain | 134 - 198 | IPR001356 |
| conserved_site | Homeobox, conserved site | 169 - 192 | IPR017970 |
| domain | Homeobox domain, metazoa | 158 - 169 | IPR020479-1 |
| domain | Homeobox domain, metazoa | 173 - 192 | IPR020479-2 |
| domain | Distal-less-like homeobox protein, N-terminal domain | 32 - 116 | IPR022135 |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromatin | The ordered and organized complex of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that forms the chromosome. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that activates or increases transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| HMG box domain binding | Binding to an HMG box domain, a protein domain that consists of three helices in an irregular array. HMG-box domains are found in one or more copies in HMG-box proteins, which form a large, diverse family involved in the regulation of DNA-dependent processes such as transcription, replication, and strand repair, all of which require the bending and unwinding of chromatin. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
19 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anatomical structure formation involved in morphogenesis | The developmental process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome. |
| BMP signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a member of the BMP (bone morphogenetic protein) family to a receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cell population proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. |
| embryonic limb morphogenesis | The process, occurring in the embryo, by which the anatomical structures of the limb are generated and organized. A limb is an appendage of an animal used for locomotion or grasping. |
| endochondral ossification | Replacement ossification wherein bone tissue replaces cartilage. |
| epithelial cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of an epithelial cell, any of the cells making up an epithelium. |
| face morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the face are generated and organized. The face is the ventral division of the head. |
| inner ear morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the inner ear are generated and organized. The inner ear is the structure in vertebrates that contains the organs of balance and hearing. It consists of soft hollow sensory structures (the membranous labyrinth) containing fluid (endolymph) surrounded by fluid (perilymph) and encased in a bony cavity (the bony labyrinth). It consists of two chambers, the sacculus and utriculus, from which arise the cochlea and semicircular canals respectively. |
| interneuron axon guidance | The process in which the migration of an axon growth cone of an interneuron is directed to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. An interneuron is any neuron which is not motor or sensory. Interneurons may also refer to neurons whose axons remain within a particular brain region, as contrasted with projection neurons which have axons projecting to other brain regions. |
| olfactory bulb interneuron differentiation | The process in which a neuroblast acquires specialized features of an interneuron residing in the olfactory bulb. |
| olfactory pit development | The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of the olfactory pit from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the olfactory pit, which is an indentation of the olfactory placode, and ends when the pits hollows out to form the nasopharynx. |
| osteoblast differentiation | The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an osteoblast, a mesodermal or neural crest cell that gives rise to bone. |
| positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of epithelial cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter involved in cellular response to chemical stimulus | Any positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter that is involved in cellular response to chemical stimulus. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| roof of mouth development | The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of the roof of the mouth from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure. The roof of the mouth is the partition that separates the nasal and oral cavities. |
13 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q6RFL5 | BSX | Brain-specific homeobox protein homolog | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P56179 | DLX6 | Homeobox protein DLX-6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O60479 | DLX3 | Homeobox protein DLX-3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P70397 | Dlx6 | Homeobox protein DLX-6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q64205 | Dlx3 | Homeobox protein DLX-3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P70396 | Dlx5 | Homeobox protein DLX-5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P50575 | Dlx5 | Homeobox protein DLX-5 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9FN29 | ATHB-52 | Homeobox-leucine zipper protein ATHB-52 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9M276 | ATHB-12 | Homeobox-leucine zipper protein ATHB-12 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q98875 | dlx1a | Homeobox protein Dlx1a | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q01702 | dlx3b | Homeobox protein Dlx3b | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q98878 | dlx4b | Homeobox protein Dlx4b | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| P50574 | dlx2a | Homeobox protein Dlx2a | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MTAVFDRRVP | GIRSSDFQPP | FQSAAAMHHP | SQESPTLPES | SATDSDYYSP | TGAAPHGYCS |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PTSASYGKAL | NPYQYQYGMN | GSAGTYPAKA | YADYGYGSPY | HQYGGAYGRG | QSSAGQPEKE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VAEPEVRMVN | GKPKKVRKPR | TIYSSFQLAA | LQRRFQKTQY | LALPERAELA | ASLGLTQTQV |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| KIWFQNKRSK | IKKIMKNGEM | PPEHSPSSSD | PMACNSPQSP | AVWEPQGSSR | SLGHHGHGHP |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | ||
| PAANPSPGSY | LESPSAWYPA | ASPLGSHLQP | HGSLQHPLAL | PSGTIY |