P50149
Gene name |
Gnat2 |
Protein name |
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G |
Names |
t subunit alpha-2 , Transducin alpha-2 chain |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:14686 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
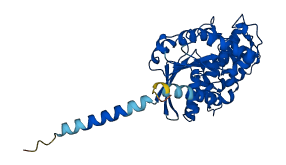
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
184-348 (Ras-like domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Goricanec D et al. (2016) "Conformational dynamics of a G-protein α subunit is tightly regulated by nucleotide binding", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113, E3629-38
- Coleman DE et al. (1999) "Structure of Gialpha1.GppNHp, autoinhibition in a galpha protein-substrate complex", The Journal of biological chemistry, 274, 16669-72
- Lutz S et al. (2007) "Structure of Galphaq-p63RhoGEF-RhoA complex reveals a pathway for the activation of RhoA by GPCRs", Science (New York, N.Y.), 318, 1923-7
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P50149
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P50149-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
17 variants for P50149
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388656060 | 28 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3412897254 | 32 | K>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388659633 | 43 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs13459387 | 77 | V>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388647329 | 89 | S>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3393043963 | 115 | E>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388652010 | 136 | V>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3388646584 | 144 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388658769 | 145 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388647354 | 149 | N>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388656044 | 186 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388647389 | 193 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388653866 | 225 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388660183 | 246 | S>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388655309 | 253 | I>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388652033 | 321 | S>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388639567 | 328 | D>E | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P50149
6 regional properties for P50149
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 331 - 608 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 333 - 599 | IPR001245 |
| domain | PDZ domain | 152 - 239 | IPR001478 |
| domain | Zinc finger, LIM-type | 10 - 70 | IPR001781-1 |
| domain | Zinc finger, LIM-type | 71 - 131 | IPR001781-2 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 337 - 360 | IPR017441 |
Functions
7 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| heterotrimeric G-protein complex | Any of a family of heterotrimeric GTP-binding and hydrolyzing proteins; they belong to a superfamily of GTPases that includes monomeric proteins such as EF-Tu and RAS. Heterotrimeric G-proteins consist of three subunits; the alpha subunit contains the guanine nucleotide binding site and possesses GTPase activity; the beta and gamma subunits are tightly associated and function as a beta-gamma heterodimer; extrinsic plasma membrane proteins (cytoplasmic face) that function as a complex to transduce signals from G protein-coupled receptors to an effector protein. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it and attached to it. |
| photoreceptor inner segment | The inner segment of a vertebrate photoreceptor containing mitochondria, ribosomes and membranes where opsin molecules are assembled and passed to be part of the outer segment discs. |
| photoreceptor outer segment | The outer segment of a vertebrate photoreceptor that contains a stack of membrane discs embedded with photoreceptor proteins. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| synapse | The junction between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron, a muscle fiber or a glial cell. As the axon approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic terminal bouton, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the terminal bouton is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic terminal bouton secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| G protein-coupled receptor binding | Binding to a G protein-coupled receptor. |
| G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding | Binding to a complex of G-protein beta/gamma subunits. |
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
29 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | A G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway in which the signal is transmitted via the activation or inhibition of adenylyl cyclase activity and a subsequent change in the intracellular concentration of cyclic AMP (cAMP). |
| background adaptation | Any process in which an organism changes its pigmentation (lightening in response to a brighter environment or darkening in response to a dimmer environment) in response to a change in light intensity. |
| camera-type eye development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the camera-type eye over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The camera-type eye is an organ of sight that receives light through an aperture and focuses it through a lens, projecting it on a photoreceptor field. |
| cell morphogenesis | The developmental process in which the size or shape of a cell is generated and organized. |
| cone retinal bipolar cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a cone retinal bipolar cell. |
| detection of chemical stimulus involved in sensory perception of bitter taste | The series of events required for a bitter taste stimulus to be received and converted to a molecular signal. |
| detection of light stimulus | The series of events in which a light stimulus (in the form of photons) is received and converted into a molecular signal. |
| detection of light stimulus involved in visual perception | The series of events involved in visual perception in which a light stimulus is received and converted into a molecular signal. |
| dopamine metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving dopamine, a catecholamine neurotransmitter and a metabolic precursor of noradrenaline and adrenaline. |
| G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to its receptor, in which the activated receptor promotes the exchange of GDP for GTP on the alpha-subunit of an associated heterotrimeric G-protein complex. The GTP-bound activated alpha-G-protein then dissociates from the beta- and gamma-subunits to further transmit the signal within the cell. The pathway begins with receptor-ligand interaction, and ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process. The pathway can start from the plasma membrane, Golgi or nuclear membrane. |
| G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway coupled to cGMP nucleotide second messenger | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G protein-coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand, followed by activation of guanylyl cyclase (GC) activity and a subsequent increase in the concentration of cyclic GMP (cGMP). |
| gene expression | The process in which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript and its processing, translation and maturation for protein-coding genes. |
| homeostasis of number of retina cells | Any biological process involved in the maintenance of the steady-state number of cells within a population of cells in the retina. |
| L-glutamate import | The directed movement of L-glutamate, the L-enantiomer of the anion of 2-aminopentanedioic acid, into a cell or organelle. |
| neural tissue regeneration | The regrowth of neural tissue following its loss or destruction. |
| phototransduction | The sequence of reactions within a cell required to convert absorbed photons into a molecular signal. |
| positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration | Any process that increases the concentration of calcium ions in the cytosol. |
| protein localization | Any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| reactive gliosis | A neuroinflammatory response, occurring over several days, during which glial cells undergo nonspecific reactive changes in response to damage to the central nervous system (CNS); typically involves the proliferation or hypertrophy of different types of glial cells. |
| response to light intensity | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a light intensity stimulus. |
| response to light stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a light stimulus, electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths classified as infrared, visible or ultraviolet light. |
| response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| response to UV | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ultraviolet radiation (UV light) stimulus. Ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength in the range of 10 to 380 nanometers. |
| retinal cone cell development | Development of a cone cell, one of the sensory cells in the eye that reacts to the presence of light. Cone cells contain the photopigment iodopsin or cyanopsin and are responsible for photopic (daylight) vision. |
| retinal cone cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a retinal cone cell. |
| retinal rod cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a retinal rod cell. |
| tissue remodeling | The reorganization or renovation of existing tissues. This process can either change the characteristics of a tissue such as in blood vessel remodeling, or result in the dynamic equilibrium of a tissue such as in bone remodeling. |
| visual behavior | The behavior of an organism in response to a visual stimulus. |
| visual perception | The series of events required for an organism to receive a visual stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. Visual stimuli are detected in the form of photons and are processed to form an image. |
58 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P63097 | GNAI1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P0C7Q4 | GNAT3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P04695 | GNAT1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P08239 | GNAO1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P04696 | GNAT2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P50147 | GNAI2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P50146 | GNAI1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P20353 | Galphai | G protein alpha i subunit | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P16378 | Galphao | G protein alpha o subunit | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P25157 | cta | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha homolog | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P11488 | GNAT1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P09471 | GNAO1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q03113 | GNA12 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-12 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P04899 | GNAI2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P63096 | GNAI1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P08754 | GNAI3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| A8MTJ3 | GNAT3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q14344 | GNA13 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P19086 | GNAZ | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P19087 | GNAT2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| B2RSH2 | Gnai1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O70443 | Gnaz | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P08752 | Gnai2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P20612 | Gnat1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P27600 | Gna12 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P27601 | Gna13 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3V3I2 | Gnat3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9DC51 | Gnai3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P21279 | Gnaq | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P30678 | Gna15 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-15 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P18872 | Gnao1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P93564 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Solanum tuberosum (Potato) | SS |
| Q63210 | Gna12 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-12 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P19627 | Gnaz | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P29348 | Gnat3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P04897 | Gnai2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P59215 | Gnao1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P08753 | Gnai3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6Q7Y5 | Gna13 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q0DJ33 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| P51875 | goa-1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q18434 | odr-3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-17 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9BIG4 | gpa-10 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-10 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| P28052 | gpa-3 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-3 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9XTB2 | gpa-13 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-13 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9BIG5 | gpa-4 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-4 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| P28051 | gpa-1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9N2V6 | gpa-16 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-16 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| P91907 | gpa-15 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-15 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q20907 | gpa-8 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-8 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q21917 | gpa-7 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-7 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q93743 | gpa-6 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-6 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| O76584 | gpa-11 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-11 subunit | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| P49084 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | SS |
| P93163 | GPA2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-2 subunit | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | SS |
| O80462 | XLG1 | Extra-large guanine nucleotide-binding protein 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P18064 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| P26981 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGSGISAEDK | ELARRSKELE | KKLQEDADKE | AKTVKLLLLG | AGESGKSTIV | KQMKIIHQDG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| YSPEECLEFK | SVIYGNVLQS | ILAIIRAMST | LGIDYAEPSC | ADAGRQLNNL | ADSTEEGTMP |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PELVDVIRKL | WKDGGVQACF | DRAAEFQLND | SASYYLNQLD | RITDPNYLPN | EQDVLRSRVK |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TTGIIETKFS | VKDLNFRMFD | VGGQRSERKK | WIHCFEGVTC | IIFCAALSAY | DMVLVEDDEV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NRMHESLHLF | NSICNHKFFA | ATSIVLFLNK | KDLFEEKIKK | VHLSICFPEY | DGNNSYEDAG |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | |
| NYIKSQFLDL | NMRKDVKEIY | SHMTCATDTQ | NVKFVFDAVT | DIIIKENLKD | CGLF |