P49840
Gene name |
GSK3A |
Protein name |
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha |
Names |
GSK-3 alpha, Serine/threonine-protein kinase GSK3A |
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:2931 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
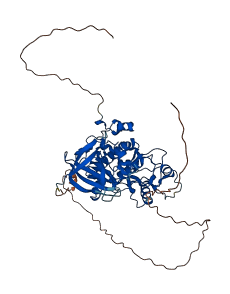
Descriptions
(Annotation based on sequence homology with P49841)
Glycogen synthase kinase 3-beta (GSK3B) is a Ser/Thr protein kinase with key roles in transduction of regulatory and proliferative signals. When the N-terminal peptide is phosphorylated (Ser 9), it autoinhibits GSK-3 by acting as a pseudo-substrate that blocks binding of other substrates. Unique to GSK-3, the binding is associated with a drastic conformational rearrangement of a highly conserved loop that engages the inhibitory peptides in a clamp-like structure. And it shows dose-dependent inhibition of GSK3B kinase activity. In addition, the deletion of the N-terminal residues increased GSK3B catalytic activity by two folds.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
262-284 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
119-403 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

3 structures for P49840
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7SXF | X-ray | 194 A | A | 101-444 | PDB |
| 7SXG | X-ray | 240 A | A | 103-445 | PDB |
| AF-P49840-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
271 variants for P49840
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
RCV000492062 rs1131690798 CA406099046 |
49 | G>A | Primary dilated cardiomyopathy [ClinVar] | Yes |
ClinGen ClinVar Ensembl dbSNP |
|
CA308630959 rs192810927 |
2 | S>N | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes TOPMed |
|
|
CA406100116 rs1250528801 |
2 | S>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1240297777 CA406100108 |
3 | G>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1240297777 CA406100112 |
3 | G>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1483941949 CA406100078 |
5 | G>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406099957 rs1311009534 |
11 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1355890061 CA406099899 |
13 | G>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9471059 rs747505933 |
14 | S>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1256468309 CA406099801 |
17 | A>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1266468058 CA406099641 |
24 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406099514 rs1555748916 |
30 | G>* | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1368819528 CA406099360 |
35 | G>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1035648407 CA308630949 |
35 | G>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs999712211 CA308630946 |
37 | G>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406099252 rs1156505226 |
39 | S>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406099220 rs1256218535 |
42 | G>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1446926033 CA406099199 |
43 | P>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9471056 rs745884025 |
45 | G>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1394889426 CA406099122 |
46 | T>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406099104 rs1599814799 |
47 | G>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406098932 rs1328902462 |
53 | V>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406098900 rs1568467534 |
54 | G>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406098877 rs1266670338 |
55 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1322502216 CA406098827 |
56 | M>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs779095296 CA9471055 |
56 | M>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406098845 rs1164825193 |
56 | M>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA308630927 rs984204862 |
57 | G>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406098812 rs984204862 |
57 | G>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs757519746 CA9471054 |
59 | G>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406098765 rs1325090938 |
60 | V>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406098697 rs1440405889 |
62 | A>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1387601771 CA406098672 |
63 | S>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406098629 rs1286954422 |
64 | S>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406098582 rs1459272124 |
66 | G>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA308630903 rs1028285710 |
68 | G>E | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs763967845 CA9471052 |
68 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs909735120 CA308630894 |
69 | P>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406098445 rs1487197016 |
70 | G>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406098458 rs1266667053 |
70 | G>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406098420 rs1189739306 |
71 | G>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9471050 rs752541196 |
72 | S>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA308630882 rs767318232 |
73 | G>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9471049 rs767318232 |
73 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs759540973 CA9471048 |
76 | G>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 77 | S>N | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1370299102 CA406098226 |
78 | G>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1019306691 CA308630869 |
79 | G>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406098172 rs1568467485 |
80 | P>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA308630846 rs992462361 |
81 | G>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406098055 rs1360888950 |
84 | T>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1360888950 CA406098061 |
84 | T>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1364314334 CA406098045 |
85 | S>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1388234779 CA406097970 |
87 | P>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9471047 rs545519489 |
87 | P>S | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9471046 rs765917283 |
88 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs772910426 CA9471044 |
89 | P>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1285934918 CA406097927 |
89 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1330417314 CA406097911 |
90 | G>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406097917 rs1599814649 |
90 | G>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406097882 rs1211020244 |
91 | V>E | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406097877 rs1211020244 |
91 | V>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs377139858 CA406097855 |
92 | K>N | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9471042 rs747329882 |
94 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs868058377 CA308630826 |
94 | G>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs779904255 CA9471012 |
95 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs749907832 CA9471010 |
98 | G>R | Variant assessed as Somatic; 4.62e-05 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ExAC NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
CA406096320 rs1188285927 |
99 | K>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406096278 rs1599813636 |
100 | V>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406096291 rs1441919598 |
100 | V>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs965827350 CA308629973 |
101 | T>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9471009 rs764778729 |
102 | T>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs148059197 CA9471008 |
104 | V>I | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs148059197 CA9471007 |
104 | V>L | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1268572541 CA406096147 |
107 | L>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406096136 rs1374518673 |
108 | G>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs35978177 CA9471006 VAR_051625 |
109 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen UniProt ESP ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
|
CA406096082 rs1285630690 |
110 | G>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs754164769 CA9471005 |
110 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406096076 rs1285630690 |
110 | G>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs774878085 CA9471004 |
113 | R>C | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ExAC NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs771524236 CA9471003 |
113 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9471001 rs773402220 |
114 | S>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs112179240 CA308629963 |
115 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs769972399 CA9471000 |
116 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs748311925 CA9470999 |
120 | T>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
COSM77819 CA9470998 rs781405859 |
122 | I>M | ovary [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC gnomAD |
|
rs1472502410 CA406095753 |
125 | I>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 126 | G>D | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA406095710 rs1209337771 |
127 | N>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406095533 rs1181645225 |
134 | Y>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs771018222 CA9470995 |
137 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470994 rs758313664 |
139 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs995391049 CA308629945 |
141 | T>A | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA9470993 rs377767121 |
141 | T>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1175239860 CA406095332 |
142 | R>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
| TCGA novel | 151 | L>F | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs753302903 CA9470990 |
156 | F>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs188273923 CA9470961 |
163 | I>V | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs538814192 CA308628845 |
164 | M>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406094086 rs1183969392 |
165 | R>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 166 | K>T | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA406093992 rs1231853362 |
172 | I>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 182 | S>I | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs759795011 CA9470933 |
188 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406093637 rs1357968048 |
195 | L>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1228185101 CA406093624 |
195 | L>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406093474 rs1330546749 |
202 | V>A | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
| TCGA novel | 202 | V>M | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs946576843 CA308628745 |
203 | Y>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406093432 rs1156515117 |
204 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs961346905 CA308628743 |
204 | R>W | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1425030772 CA406093403 |
206 | A>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470930 rs762941632 |
207 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470929 rs374117558 |
207 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470928 rs780627193 |
213 | K>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs747609490 CA9470927 |
215 | T>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406093266 rs1599811792 |
215 | T>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs780876254 CA9470926 |
216 | I>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs370744168 CA9470922 |
220 | Y>F | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs986885157 CA308627913 |
223 | V>A | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1226685012 CA406092447 |
224 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1480971718 CA406092443 |
225 | M>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs759265893 CA9470899 |
225 | M>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 228 | L>P | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| TCGA novel | 229 | F>L | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| TCGA novel | 229 | F>W | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs908624912 CA308627899 |
235 | I>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 238 | Q>G | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1212146016 CA406092338 |
239 | G>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs766460072 CA9470895 |
240 | V>M | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ExAC NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
COSM1209114 rs1249544838 CA406092314 |
243 | R>C | large_intestine [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated gnomAD |
| TCGA novel | 249 | N>D | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs750207489 CA9470893 |
253 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1176260955 CA406092244 |
253 | D>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406092240 rs1157501093 |
254 | P>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9470891 rs761840963 |
256 | T>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1415606112 CA406092210 |
258 | V>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
| TCGA novel | 263 | D>N | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs760709783 CA9470870 |
269 | Q>P | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ExAC NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs760709783 CA406091950 |
269 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs774840736 CA9470869 |
272 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 278 | S>Y | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs759105475 CA9470867 |
283 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1035974110 CA406091671 COSM997282 |
283 | R>H | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. large_intestine endometrium [NCI-TCGA, Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs1035974110 CA308627852 |
283 | R>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs981266433 CA308627849 |
286 | R>W | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
| TCGA novel | 288 | P>L | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA406091488 rs1428107658 |
292 | F>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
| TCGA novel | 303 | V>G | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA406091274 rs1161565330 |
304 | W>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406091277 rs779175432 |
304 | W>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470838 rs779175432 |
304 | W>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1411642033 CA406091257 |
306 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs866283999 CA308627538 |
311 | A>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs867510755 CA308627536 |
312 | E>* | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406091173 rs1167070200 |
314 | L>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 316 | G>S | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs749580672 CA9470836 |
319 | I>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs777426805 CA9470835 |
320 | F>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406091041 rs1599809999 |
324 | S>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs376641475 CA406090994 |
327 | D>E | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1206035457 CA406091016 |
327 | D>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1272927888 CA406090949 |
330 | V>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA308627496 rs868320301 |
336 | L>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
| TCGA novel | 337 | G>E | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA406090717 rs1408231243 |
339 | P>S | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs1337074844 CA406090682 |
341 | R>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1337074844 CA406090681 |
341 | R>Q | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
CA308627493 rs907284414 |
341 | R>W | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA TOPMed |
|
CA308627489 rs377171569 |
343 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470818 rs377171569 |
343 | Q>K | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs773423786 CA9470817 |
349 | P>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406090487 rs1160899097 |
350 | N>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406090432 rs1175974409 |
352 | T>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406090418 rs1244295204 |
353 | E>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1460275285 CA406090307 |
357 | P>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA308627478 rs566849543 |
361 | A>S | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
rs779531784 CA9470811 |
362 | H>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406088921 rs1474572177 |
362 | H>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1382575097 CA406088537 |
368 | F>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 369 | K>T | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1215626593 CA406088463 |
371 | R>* | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs1215626593 CA406088465 |
371 | R>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1360787446 CA406088455 |
371 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1295983715 CA406088431 |
372 | T>M | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs746066994 CA308627353 |
373 | P>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406088376 rs1456790864 |
374 | P>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406088362 rs1300952322 |
375 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9470793 rs779920504 |
376 | A>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs758365091 COSM997274 CA9470792 |
378 | A>T | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. endometrium [NCI-TCGA, Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC NCI-TCGA TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs745355981 CA9470791 |
378 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406088251 rs1467035531 |
380 | C>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1490532781 CA406088261 |
380 | C>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406088215 rs763845338 |
381 | S>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs763845338 CA9470787 |
381 | S>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA406088194 rs1220366398 |
382 | S>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 384 | L>R | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| TCGA novel | 386 | Y>H | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1227824774 CA406088090 |
387 | T>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs766951143 CA9470784 |
399 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470783 rs763409196 |
399 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470781 rs765287420 |
401 | S>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 407 | R>* | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA308627339 rs574208169 |
407 | R>P | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406087505 rs574208169 |
407 | R>Q | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs1422015490 CA406087492 |
408 | C>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470778 rs768891597 |
409 | L>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1252547692 CA406087302 |
415 | N>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs775308267 CA9470776 |
416 | N>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs745851660 CA9470774 |
417 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
COSM997272 rs1205340289 CA406087251 |
417 | R>H | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. endometrium [NCI-TCGA, Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
CA406087217 rs1176142177 |
419 | L>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs770282435 CA9470772 |
421 | P>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs770282435 CA406087157 |
421 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs980287763 CA308627329 |
427 | A>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA308627327 rs971574526 |
428 | G>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406086865 rs1417966495 |
431 | S>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs777463616 CA9470749 |
432 | I>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs954624999 CA308627252 |
432 | I>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1165441689 CA406086807 |
434 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 435 | S>P | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
| TCGA novel | 436 | L>Q | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs562611851 CA406086726 |
437 | N>K | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406086744 rs1236744225 |
437 | N>Y | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406086715 rs780458200 |
438 | A>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470746 rs780458200 |
438 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
| TCGA novel | 439 | I>T | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
CA406086636 rs1350924549 |
441 | I>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1294546069 CA406086619 |
442 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs557869303 CA308627246 |
443 | P>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA9470744 rs773016062 |
445 | L>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406086538 rs1359151387 |
446 | R>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1195958363 CA406086506 |
447 | S>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9470742 rs201338063 |
448 | P>S | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470741 rs201338063 |
448 | P>T | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470739 rs756325459 |
449 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406086454 rs1464135401 |
450 | G>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406086412 rs1395202956 |
453 | T>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA9470737 rs11550536 |
454 | L>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406086387 rs1165380071 |
454 | L>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308627237 rs950317218 |
455 | T>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA308627239 rs764690826 |
455 | T>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA9470736 rs759204057 |
456 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs766194328 CA9470734 |
458 | S>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406086311 rs1476282315 |
459 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs376057161 CA9470733 |
460 | A>P | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs35454502 CA9470721 VAR_040539 |
461 | L>F | No |
ClinGen UniProt ExAC TOPMed dbSNP gnomAD |
|
|
CA9470722 rs778258162 |
461 | L>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs201310907 CA308626757 |
464 | T>I | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
CA308626759 rs201310907 |
464 | T>N | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
rs201310907 CA406084639 |
464 | T>S | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
rs752845859 CA9470720 |
465 | P>L | Variant assessed as Somatic; 0.0 impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No |
ClinGen ExAC NCI-TCGA gnomAD |
|
rs1403697782 CA406084618 |
466 | T>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406084567 rs1257760220 |
469 | D>E | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA406084551 rs1325877352 |
470 | W>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA406084559 rs1197150211 |
470 | W>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs868094081 CA308626752 |
471 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs755266233 CA9470718 |
472 | S>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1448054868 CA406084512 |
473 | T>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1375007525 CA406084500 |
474 | D>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs766254532 CA9470716 |
475 | A>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308626741 rs867989593 |
476 | T>K | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406084470 rs1599808511 |
476 | T>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1347260842 CA406084443 |
478 | T>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA406084441 rs1347260842 |
478 | T>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
| TCGA novel | 479 | L>F | Variant assessed as Somatic; impact. [NCI-TCGA] | No | NCI-TCGA |
|
rs1198737800 CA406084418 |
480 | T>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs773213319 CA9470714 |
481 | N>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA308626739 rs866755387 |
482 | S>F | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA406084388 rs1599808478 |
482 | S>P | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
No associated diseases with P49840
4 regional properties for P49840
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 119 - 403 | IPR000719 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 240 - 252 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 125 - 149 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Glycogen synthase kinase 3, catalytic domain | 114 - 406 | IPR039192 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
11 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical dendrite | A dendrite that emerges near the apical pole of a neuron. In bipolar neurons, apical dendrites are located on the opposite side of the soma from the axon. |
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| beta-catenin destruction complex | A cytoplasmic protein complex containing glycogen synthase kinase-3-beta (GSK-3-beta), the adenomatous polyposis coli protein (APC), and the scaffolding protein axin, among others; phosphorylates beta-catenin, targets it for degradation by the proteasome. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| microtubule | Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| postsynapse | The part of a synapse that is part of the post-synaptic cell. |
| proximal dendrite | The dendrite of the dendritic tree that is closest to the neuronal cell body (the soma). |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding | Binding to one or both of the catalytic subunits of protein kinase A. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| tau protein binding | Binding to tau protein. tau is a microtubule-associated protein, implicated in Alzheimer's disease, Down Syndrome and ALS. |
| tau-protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + tau-protein = ADP + O-phospho-tau-protein. |
53 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| aging | A developmental process that is a deterioration and loss of function over time. Aging includes loss of functions such as resistance to disease, homeostasis, and fertility, as well as wear and tear. Aging includes cellular senescence, but is more inclusive. May precede death and may succeed developmental maturation (GO:0021700). |
| cardiac left ventricle morphogenesis | The process in which the left cardiac ventricle is generated and organized. |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| cellular response to glucocorticoid stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucocorticoid stimulus. Glucocorticoids are hormonal C21 corticosteroids synthesized from cholesterol with the ability to bind with the cortisol receptor and trigger similar effects. Glucocorticoids act primarily on carbohydrate and protein metabolism, and have anti-inflammatory effects. |
| cellular response to insulin stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin stimulus. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in mammals, and by the homologous organs of other organisms. |
| cellular response to interleukin-3 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-3 stimulus. |
| cellular response to lithium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lithium (Li+) ion stimulus. |
| dopamine receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a dopamine receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands. |
| excitatory postsynaptic potential | A process that leads to a temporary increase in postsynaptic potential due to the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell. The flow of ions that causes an EPSP is an excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) and makes it easier for the neuron to fire an action potential. |
| extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals in which a signal is conveyed from the cell surface to trigger the apoptotic death of a cell. The pathway starts with either a ligand binding to a cell surface receptor, or a ligand being withdrawn from a cell surface receptor (e.g. in the case of signaling by dependence receptors), and ends when the execution phase of apoptosis is triggered. |
| extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand | The series of molecular signals in which a signal is conveyed from the cell surface to trigger the apoptotic death of a cell. The pathway starts with withdrawal of a ligand from a cell surface receptor, and ends when the execution phase of apoptosis is triggered. |
| glycogen metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycogen, a polydisperse, highly branched glucan composed of chains of D-glucose residues in alpha-(1->4) glycosidic linkage, joined together by alpha-(1->6) glycosidic linkages. |
| hypermethylation of CpG island | An increase in the epigenetic methylation of cytosine and adenosine residues in a CpG island in DNA. CpG islands are genomic regions that contain a high frequency of the CG dinucleotide and are often associated with the transcription start site of genes. |
| insulin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of the insulin receptor binding to insulin. |
| negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| negative regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of the growth of a cardiac muscle cell, where growth contributes to the progression of the cell over time from its initial formation to its mature state. |
| negative regulation of dendrite development | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of dendrite development. |
| negative regulation of glucose import | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the import of the hexose monosaccharide glucose into a cell or organelle. |
| negative regulation of glycogen (starch) synthase activity | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of glycogen (starch) synthase activity. |
| negative regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of glycogen. |
| negative regulation of glycogen synthase activity, transferring glucose-1-phosphate | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of glycogen synthase activity, transferring glucose-1-phosphate. |
| negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of insulin receptor signaling. |
| negative regulation of TOR signaling | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of TOR signaling. |
| negative regulation of type B pancreatic cell development | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of pancreatic B cell development. |
| negative regulation of UDP-glucose catabolic process | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of UDP-glucose catabolism. UDP-glucose catabolic processes are the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of UDP-glucose, uridinediphosphoglucose, a substance composed of glucose in glycosidic linkage with uridine diphosphate. |
| nervous system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-threonine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-threonine. |
| positive regulation of adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor protein signaling pathway. An adrenergic receptor signaling pathway is the series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of an adrenergic receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands. |
| positive regulation of adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of amyloid-beta formation. |
| positive regulation of autophagy | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of autophagy. Autophagy is the process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of glycogen (starch) synthase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of glycogen (starch) synthase activity. |
| positive regulation of heart contraction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of heart contraction. |
| positive regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death of neurons by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation. Peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation is the phosphorylation of peptidyl-threonine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-threonine. |
| positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, and mediated by the proteasome. |
| positive regulation of protein catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by the destruction of the native, active configuration, with or without the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. |
| positive regulation of protein targeting to mitochondrion | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein targeting to mitochondrion. |
| positive regulation of protein ubiquitination | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the addition of ubiquitin groups to a protein. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, and mediated by the proteasome. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of mitochondrion degradation by an autophagic process. |
| regulation of gene expression by genomic imprinting | An epigenetic mechanism of regulation of gene expression in which epigenetic modifications (imprints) are established during gametogenesis. For a given gene to show parentally biased expression, the imprint are established exclusively in one of the two parental genomes, thus generating an asymmetry between the maternal and paternal alleles. |
| regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure | The process that modulates the force with which blood travels through the systemic arterial circulatory system. The process is controlled by a balance of processes that increase pressure and decrease pressure. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
| viral protein processing | Any protein maturation process achieved by the cleavage of a peptide bond or bonds within a viral protein. |
| Wnt signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell and ending with a change in cell state. |
11 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P18431 | sgg | Protein kinase shaggy | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P49841 | GSK3B | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q80YS9 | Stkld1 | Serine/threonine kinase-like domain-containing protein STKLD1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9WV60 | Gsk3b | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q2NL51 | Gsk3a | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P18266 | Gsk3b | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P18265 | Gsk3a | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q09595 | R03D7.5 | Putative serine/threonine-protein kinase R03D7.5 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9U2Q9 | gsk-3 | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q39019 | ASK10 | Shaggy-related protein kinase kappa | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FVS6 | ASK4 | Shaggy-related protein kinase delta | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSGGGPSGGG | PGGSGRARTS | SFAEPGGGGG | GGGGGPGGSA | SGPGGTGGGK | ASVGAMGGGV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GASSSGGGPG | GSGGGGSGGP | GAGTSFPPPG | VKLGRDSGKV | TTVVATLGQG | PERSQEVAYT |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DIKVIGNGSF | GVVYQARLAE | TRELVAIKKV | LQDKRFKNRE | LQIMRKLDHC | NIVRLRYFFY |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SSGEKKDELY | LNLVLEYVPE | TVYRVARHFT | KAKLTIPILY | VKVYMYQLFR | SLAYIHSQGV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| CHRDIKPQNL | LVDPDTAVLK | LCDFGSAKQL | VRGEPNVSYI | CSRYYRAPEL | IFGATDYTSS |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| IDVWSAGCVL | AELLLGQPIF | PGDSGVDQLV | EIIKVLGTPT | REQIREMNPN | YTEFKFPQIK |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| AHPWTKVFKS | RTPPEAIALC | SSLLEYTPSS | RLSPLEACAH | SFFDELRCLG | TQLPNNRPLP |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| PLFNFSAGEL | SIQPSLNAIL | IPPHLRSPAG | TTTLTPSSQA | LTETPTSSDW | QSTDATPTLT |
| NSS |