P49186
Gene name |
Mapk9 (Jnk2, Prkm9) |
Protein name |
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 9 |
Names |
MAP kinase 9, MAPK 9, SAPK-alpha, Stress-activated protein kinase JNK2, c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2, p54-alpha |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:50658 |
EC number |
2.7.11.24: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
168-190 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
26-321 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
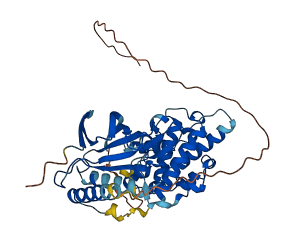
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P49186
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P49186-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P49186
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P49186 | |||||
No associated diseases with P49186
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.24 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perikaryon | The portion of the cell soma (neuronal cell body) that excludes the nucleus. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process | Binds to and increases the rate of proteolysis catalyzed by a cysteine-type endopeptidase involved in the apoptotic process. |
| JUN kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: JUN + ATP = JUN phosphate + ADP. This reaction is the phosphorylation and activation of members of the JUN family, a gene family that encodes nuclear transcription factors. |
| MAP kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: protein + ATP = protein phosphate + ADP. This reaction is the phosphorylation of proteins. Mitogen-activated protein kinase; a family of protein kinases that perform a crucial step in relaying signals from the plasma membrane to the nucleus. They are activated by a wide range of proliferation- or differentiation-inducing signals; activation is strong with agonists such as polypeptide growth factors and tumor-promoting phorbol esters, but weak (in most cell backgrounds) by stress stimuli. |
| mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase binding | Binding to a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase, a protein that can phosphorylate a MAP kinase kinase. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
49 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals which triggers the apoptotic death of a cell. The pathway starts with reception of a signal, and ends when the execution phase of apoptosis is triggered. |
| cellular hyperosmotic response | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of detection of, or exposure to, a hyperosmotic environment, i.e. an environment with a higher concentration of solutes than the organism or cell. |
| cellular response to amyloid-beta | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a amyloid-beta stimulus. |
| cellular response to cadmium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cadmium (Cd) ion stimulus. |
| cellular response to growth factor stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a growth factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to interleukin-1 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-1 stimulus. |
| cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| cellular response to reactive oxygen species | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a reactive oxygen species stimulus. Reactive oxygen species include singlet oxygen, superoxide, and oxygen free radicals. |
| cellular response to tumor necrosis factor | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a tumor necrosis factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to UV | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ultraviolet radiation (UV light) stimulus. Ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength in the range of 10 to 380 nanometers. |
| central nervous system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain and spinal cord. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| JNK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a JNK (a MAPK), a JNKK (a MAPKK) and a JUN3K (a MAP3K). The cascade can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinases in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| JUN phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a JUN protein. |
| neuron development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell. |
| neuron projection development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell morphogenesis contributing to cell differentiation. Cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation is the change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. |
| positive regulation of chemokine production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of chemokine production. |
| positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the activity of a cysteine-type endopeptidase involved in the apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation. Macrophage derived foam cell differentiation is the process in which a macrophage acquires the specialized features of a foam cell. A foam cell is a type of cell containing lipids in small vacuoles and typically seen in atherosclerotic lesions, as well as other conditions. |
| positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nitric oxide. |
| positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a nitric oxide synthase enzyme. |
| positive regulation of podosome assembly | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of podosome assembly. |
| positive regulation of prostaglandin biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of prostaglandin. |
| positive regulation of prostaglandin secretion | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a prostaglandin from a cell. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of protein ubiquitination | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the addition of ubiquitin groups to a protein. |
| positive regulation of transcription factor catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription factor catabolic process. |
| protein localization to tricellular tight junction | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a location within a tricellular tight junction. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| protein targeting to mitochondrion | The process of directing proteins towards and into the mitochondrion, usually mediated by mitochondrial proteins that recognize signals contained within the imported protein. |
| regulation of circadian rhythm | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a circadian rhythm. A circadian rhythm is a biological process in an organism that recurs with a regularity of approximately 24 hours. |
| regulation of JNK cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the JNK cascade. |
| regulation of protein ubiquitination | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the addition of ubiquitin groups to a protein. |
| release of cytochrome c from mitochondria | The process that results in the movement of cytochrome c from the mitochondrial intermembrane space into the cytosol, which is part of the apoptotic signaling pathway and leads to caspase activation. |
| response to amine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an amine stimulus. An amine is a compound formally derived from ammonia by replacing one, two or three hydrogen atoms by hydrocarbyl groups. |
| response to cadmium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cadmium (Cd) ion stimulus. |
| response to mechanical stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a mechanical stimulus. |
| response to nerve growth factor | A process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a nerve growth factor stimulus. |
| response to organic substance | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic substance stimulus. |
| response to toxic substance | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a toxic stimulus. |
| response to water deprivation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a water deprivation stimulus, prolonged deprivation of water. |
| response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| rhythmic process | Any process pertinent to the generation and maintenance of rhythms in the physiology of an organism. |
30 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P32485 | HOG1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase HOG1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| P79996 | MAPK9 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 9 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P53779 | MAPK10 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 10 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P45983 | MAPK8 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P45984 | MAPK9 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 9 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q91Y86 | Mapk8 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9WTU6 | Mapk9 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 9 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P20793 | Mak | Serine/threonine-protein kinase MAK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9Z2A6 | Mapk15 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 15 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P21708 | Mapk3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P63086 | Mapk1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P27704 | Mapk6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63538 | Mapk12 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 12 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P0C865 | Mapk7 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 7 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WTY9 | Mapk13 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P70618 | Mapk14 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63454 | Mapk4 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q336X9 | MPK6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q5J4W4 | MPK2 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 2 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q84UI5 | MPK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q10N20 | MPK5 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 5 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| O44408 | kgb-1 | GLH-binding kinase 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q39023 | MPK3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q39026 | MPK6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q39025 | MPK5 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q39024 | MPK4 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9M1Z5 | MPK10 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 10 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q8GYQ5 | MPK12 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 12 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9LMM5 | MPK11 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 11 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9LQQ9 | MPK13 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSDSKSDGQF | YSVQVADSTF | TVLKRYQQLK | PIGSGAQGIV | CAAFDTVLGI | NVAVKKLSRP |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| FQNQTHAKRA | YRELVLLKCV | NHKNIISLLN | VFTPQKTLEE | FQDVYLVMEL | MDANLCQVIH |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| MELDHERMSY | LLYQMLCGIK | HLHSAGIIHR | DLKPSNIVVK | SDCTLKILDF | GLARTACTNF |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| MMTPYVVTRY | YRAPEVILGM | GYKENVDIWS | VGCIMGELVK | GCVIFQGTDH | IDQWNKVIEQ |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LGTPSAEFMK | KLQPTVRNYV | ENRPKYPGIK | FEELFPDWIF | PSESERDKIK | TSQARDLLSK |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| MLVIDPDKRI | SVDEALRHPY | ITVWYDPAEA | EAPPPQIYDA | QLEEREHAIE | EWKELIYKEV |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| MDWEERSKNG | VKDQPSDAAV | SSKATPSQSS | SINDISSMST | EHTLASDTDS | SLDASTGPLE |
| GCR |