P47930
Gene name |
Fosl2 (Fra-2, Fra2) |
Protein name |
Fos-related antigen 2 |
Names |
FRA-2 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:14284 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
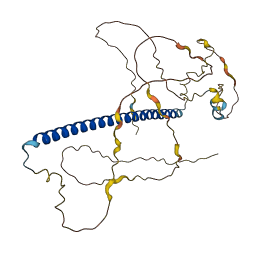
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P47930
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P47930-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
22 variants for P47930
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388735360 | 20 | P>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388759487 | 53 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388726506 | 72 | M>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388749314 | 78 | R>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3388749349 | 83 | S>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388749402 | 91 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388749729 | 102 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388752728 | 109 | T>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388753029 | 113 | R>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3388759519 | 119 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3395340343 | 122 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388749749 | 149 | T>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388735363 | 166 | L>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388738637 | 205 | G>W | No | EVA | |
| rs3388753036 | 276 | G>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388752738 | 277 | T>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388755621 | 279 | N>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388753526 | 289 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3395340304 | 294 | S>* | No | EVA | |
| rs13465639 | 294 | S>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3388752760 | 298 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3394768659 | 302 | K>RTLG* | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P47930
1 regional properties for P47930
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Basic-leucine zipper domain | 122 - 187 | IPR004827 |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex | A transcription factor complex that acts at a regulatory region of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
10 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that activates or increases transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity | A transcription regulator activity that modulates transcription of gene sets via selective and non-covalent binding to a specific double-stranded genomic DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within a cis-regulatory region. Regulatory regions include promoters (proximal and distal) and enhancers. Genes are transcriptional units, and include bacterial operons. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific sequence of DNA that is part of a regulatory region that controls the transcription of a gene or cistron by RNA polymerase II. |
| sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
| transcription cis-regulatory region binding | Binding to a specific sequence of DNA that is part of a regulatory region that controls transcription of that section of the DNA. The transcribed region might be described as a gene, cistron, or operon. |
8 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| keratinocyte development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a keratinocyte over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of multiplication or reproduction of fibroblast cells. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| response to estradiol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of stimulus by estradiol, a C18 steroid hormone hydroxylated at C3 and C17 that acts as a potent estrogen. |
| response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
| transcription by RNA polymerase II | The synthesis of RNA from a DNA template by RNA polymerase II (RNAP II), originating at an RNA polymerase II promoter. Includes transcription of messenger RNA (mRNA) and certain small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O93602 | ATF2 | Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P15336 | ATF2 | Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q02930 | CREB5 | Cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P17544 | ATF7 | Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P15408 | FOSL2 | Fos-related antigen 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8R0S1 | Atf7 | Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P16951 | Atf2 | Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00969 | Atf2 | Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MYQDYPGNFD | TSSRGSSGSP | AHAESYSSGG | GGQQKFRVDM | PGSGSAFIPT | INAITTSQDL |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QWMVQPTVIT | SMSNPYPRSH | PYSPLPGLAS | VPGHMALPRP | GVIKTIGTTV | GRRRRDEQLS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PEEEEKRRIR | RERNKLAAAK | CRNRRRELTE | KLQAETEELE | EEKSGLQKEI | AELQKEKEKL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| EFMLVAHGPV | CKISPEERRS | PPTSGLQSLR | GTGSAVGPVV | VKQEPPEEDS | PSSSAGMDKT |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| QRSVIKPISI | AGGGFYGEEP | LHTPIVVTST | PAITPGTSNL | VFTYPNVLEQ | ESPSSPSESC |
| 310 | 320 | ||||
| SKAHRRSSSS | GDQSSDSLNS | PTLLAL |