P47069
Gene name |
MPS3 |
Protein name |
Spindle pole body assembly component MPS3 |
Names |
98 kDa nuclear envelope protein, Monopolar spindle protein 3 |
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YJL019W |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
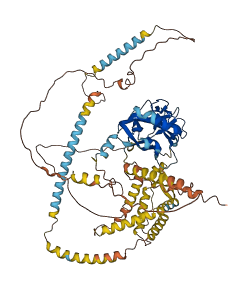
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P47069
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P47069-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
10 variants for P47069
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s10-402998 | 36 | K>R | No | SGRP | |
| s10-403031 | 47 | A>V | No | SGRP | |
| s10-403100 | 70 | S>F | No | SGRP | |
| s10-403184 | 98 | D>G | No | SGRP | |
| s10-403385 | 165 | Y>C | No | SGRP | |
| s10-403519 | 210 | S>G | No | SGRP | |
| s10-403537 | 216 | H>Y | No | SGRP | |
| s10-404555 | 555 | Y>F | No | SGRP | |
| s10-404574 | 561 | F>L | No | SGRP | |
| s10-404620 | 577 | P>A | No | SGRP |
No associated diseases with P47069
1 regional properties for P47069
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | SUN domain | 427 - 616 | IPR012919 |
Functions
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromosome, telomeric region | The end of a linear chromosome, required for the integrity and maintenance of the end. A chromosome telomere usually includes a region of telomerase-encoded repeats the length of which rarely exceeds 20 bp each and that permits the formation of a telomeric loop (T-loop). The telomeric repeat region is usually preceded by a sub-telomeric region that is gene-poor but rich in repetitive elements. Some telomeres only consist of the latter part (for eg. D. melanogaster telomeres). |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| half bridge of spindle pole body | Structure adjacent to the plaques of the spindle pole body. |
| integral component of membrane | The component of a membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| integral component of nuclear inner membrane | The component of the nuclear inner membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| meiotic nuclear membrane microtubule tethering complex | A nuclear membrane protein complex which connects the nuclear outer and inner membranes together, and links links the nuclear lumen to cytoplasmic microtubules during meiosis. |
| nuclear envelope | The double lipid bilayer enclosing the nucleus and separating its contents from the rest of the cytoplasm; includes the intermembrane space, a gap of width 20-40 nm (also called the perinuclear space). |
| nuclear periphery | The portion of the nuclear lumen proximal to the inner nuclear membrane. |
| spindle pole body | The microtubule organizing center in fungi; functionally homologous to the animal cell centrosome. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| protein-membrane adaptor activity | The binding activity of a molecule that brings together a protein or a protein complex with a membrane, or bringing together two membranes, either via membrane lipid binding or by interacting with a membrane protein, to establish or maintain the localization of the protein, protein complex or organelle. |
10 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| establishment of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion | The process in which the sister chromatids of a replicated chromosome become joined along the entire length of the chromosome during S phase during a mitotic cell cycle. |
| homologous chromosome pairing at meiosis | The meiotic cell cycle process where side by side pairing and physical juxtaposition of homologous chromosomes is created during meiotic prophase. Homologous chromosome pairing begins when the chromosome arms begin to pair from the clustered telomeres and ends when synaptonemal complex or linear element assembly is complete. |
| karyogamy | The creation of a single nucleus from multiple nuclei as a result of fusing the lipid bilayers that surround each nuclei. |
| meiotic telomere clustering | The cell cycle process in which the dynamic reorganization of telomeres occurs in early meiotic prophase, during which meiotic chromosome ends are gathered in a bouquet arrangement at the inner surface of the nuclear envelope proximal to the spindle pole body. This plays an important role in progression through meiosis and precedes synapsis. |
| mitotic sister chromatid cohesion | The cell cycle process in which the sister chromatids of a replicated chromosome are joined along the entire length of the chromosome, from their formation in S phase through metaphase during a mitotic cell cycle. This cohesion cycle is critical for high fidelity chromosome transmission. |
| nuclear envelope organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the nuclear envelope. |
| nuclear migration involved in conjugation with cellular fusion | The microtubule-based movement of nuclei towards one another as a prelude to karyogamy in organisms undergoing conjugation with cellular fusion. |
| spindle pole body duplication | Construction of a new spindle pole body. |
| subtelomeric heterochromatin assembly | The compaction of chromatin into heterochromatin at the subtelomeric region. |
| telomere tethering at nuclear periphery | The process in which a telomere is maintained in a specific location at the nuclear periphery. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9UH99 | SUN2 | SUN domain-containing protein 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q8TC36 | SUN5 | SUN domain-containing protein 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O94901 | SUN1 | SUN domain-containing protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q8BJS4 | Sun2 | SUN domain-containing protein 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q9DA32 | Sun5 | SUN domain-containing protein 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9D666 | Sun1 | SUN domain-containing protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MNNSNEHRRE | EAGAANEQMP | YNKAVKSAYA | DVLKDKMNRE | QEISLRAIKK | GIYTDGGETD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NYDMDKENDS | AYEMFKKNLD | FPLDQHNDDD | DDDPYIEDNG | QETDGYSDED | YTDEADKSFI |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| EDSDSDSYDL | ESNSDFEENL | ESSGEAKKLK | WRTYIFYGGL | FFVFYFFGSF | LMTTVKNNDL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| ESHSSGATSS | PGKSFSNLQK | QVNHLYSELS | KRDEKHSSEL | DKTVKIIVSQ | FEKNIKRLLP |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SNLVNFENDI | NSLTKQVETI | STSMSELQRR | NHKFTVENVT | QWQDQLVKQL | DTHLPQEIPV |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| VINNSSSLLI | IPELHNYLSA | LISDVIESPG | IGTAGSAESR | WEYDLNRYVK | EILSNELQYI |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| DKDYFIQEMN | RRLQSNKQEI | WEEITNRLET | QQQQQQQQVQ | QDYSNVPQQY | SSILMKRLIH |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| QIYNSNQHQW | EDDLDFATYV | QGTKLLNHLT | SPTWRQGSGV | QPIELLTDSK | QSSSTYWQCE |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| NEPGCSWAIR | FKTPLYLTKI | SYMHGRFTNN | LHIMNSAPRL | ISLYVKLSQT | KEIKALQTLA |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| NQYGFGQHHK | RDRNYIKIAK | FEYRLTDSRI | RQQMYLPPWF | IQLKPLVRSI | VFQVDENYGN |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| KKFISLRKFI | INGVTPQDLQ | IIENNEFPVL | LGDTPEYGVT | QNTDEGKRKV | LLSKPPYASS |
| 670 | 680 | ||||
| STSTKFHPAS | NVPSFGQDEL | DQ |