P46461
Gene name |
comt |
Protein name |
Vesicle-fusing ATPase 1 |
Names |
N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein 1, NEM-sensitive fusion protein 1, Protein comatose, Vesicular-fusion protein NSF1, dNsf-1, NSF-1 |
Species |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
KEGG Pathway |
dme:Dmel_CG1618 |
EC number |
3.6.4.6: Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
252-399 (D1 domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
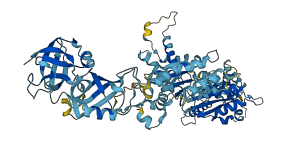
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P46461
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P46461-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P46461
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P46461 | |||||
No associated diseases with P46461
8 regional properties for P46461
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | CDC48, N-terminal subdomain | 4 - 86 | IPR003338 |
| domain | AAA+ ATPase domain | 252 - 399 | IPR003593-1 |
| domain | AAA+ ATPase domain | 535 - 671 | IPR003593-2 |
| domain | ATPase, AAA-type, core | 256 - 396 | IPR003959-1 |
| domain | ATPase, AAA-type, core | 539 - 662 | IPR003959-2 |
| conserved_site | ATPase, AAA-type, conserved site | 367 - 385 | IPR003960 |
| domain | CDC48, domain 2 | 111 - 183 | IPR004201 |
| domain | AAA ATPase, AAA+ lid domain | 423 - 459 | IPR041569 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.4.6 | Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| Golgi stack | The set of thin, flattened membrane-bounded compartments, called cisternae, that form the central portion of the Golgi complex. The stack usually comprises cis, medial, and trans cisternae; the cis- and trans-Golgi networks are not considered part of the stack. |
| neuromuscular junction | The junction between the axon of a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. In response to the arrival of action potentials, the presynaptic button releases molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane of the muscle fiber, leading to a change in post-synaptic potential. |
| neuromuscular junction of somatic muscle | A neuromuscular junction in which the target muscle cell is a somatic muscle cell, such as those found in nematodes and arthropods. |
| presynaptic cytosol | The region of the cytosol consisting of all cytosol that is part of the presynapse. |
| terminal bouton | Terminal inflated portion of the axon, containing the specialized apparatus necessary to release neurotransmitters. The axon terminus is considered to be the whole region of thickening and the terminal bouton is a specialized region of it. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
15 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| autophagy | The cellular catabolic process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm; allows for both recycling of macromolecular constituents under conditions of cellular stress and remodeling the intracellular structure for cell differentiation. |
| Golgi organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the Golgi apparatus. |
| Golgi to lysosome transport | The directed movement of substances from the Golgi to lysosomes. |
| Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport | The directed movement of proteins from the Golgi to the plasma membrane in transport vesicles that move from the trans-Golgi network to the plasma membrane. |
| Golgi vesicle docking | The initial attachment of a Golgi transport vesicle membrane to a target membrane, mediated by proteins protruding from the membrane of the Golgi vesicle and the target membrane. |
| intra-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | The directed movement of substances within the Golgi, mediated by small transport vesicles. These either fuse with the cis-Golgi or with each other to form the membrane stacks known as the cis-Golgi reticulum (network). |
| neuromuscular synaptic transmission | The process of synaptic transmission from a neuron to a muscle, across a synapse. |
| neuron cellular homeostasis | The cellular homeostatic process that preserves a neuron in a stable, differentiated functional and structural state. |
| neurotransmitter secretion | The regulated release of neurotransmitter from the presynapse into the synaptic cleft via calcium-regulated exocytosis during synaptic transmission. |
| regulation of neuromuscular synaptic transmission | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neuromuscular synaptic transmission. |
| regulation of short-term neuronal synaptic plasticity | A process that modulates short-term neuronal synaptic plasticity, the ability of neuronal synapses to change in the short-term as circumstances require. Short-term neuronal synaptic plasticity generally involves increasing or decreasing synaptic sensitivity. |
| SNARE complex disassembly | The disaggregation of the SNARE protein complex into its constituent components. The SNARE complex is a protein complex involved in membrane fusion; a stable ternary complex consisting of a four-helix bundle, usually formed from one R-SNARE and three Q-SNAREs with an ionic layer sandwiched between hydrophobic layers. |
| synaptic vesicle cycle | A biological process in which synaptic vesicles are loaded with neurotransmitters, move to the active zone, exocytose and are then recycled via endocytosis, ultimately leading to reloading with neurotransmitters. |
| synaptic vesicle fusion to presynaptic active zone membrane | Fusion of the membrane of a synaptic vesicle with the presynaptic active zone membrane, thereby releasing its cargo neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. |
| synaptic vesicle priming | A process that converts synaptic vesicles to a state of competence for calcium triggered fusion with the active zone membrane by bringing the two membranes into very close proximity. Priming typically (but not always) occurs after docking (Jahn and Fasshauer, 2012). Primed vesicles are also capable of spontaneously fusing with the active zone membrane. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P54351 | Nsf2 | Vesicle-fusing ATPase 2 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P46459 | NSF | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P46460 | Nsf | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9QUL6 | Nsf | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q94392 | nsf-1 | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9M0Y8 | NSF | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAYILKATKC | PTDELSLTNR | AIVNVGDFPE | EIKYADISPA | PGQHFIFALE | KTVEVPSGYV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GFSLVQRKWA | MVSINQELEV | RPYRFDASSD | VITCVSFETD | FLQKKTVSQE | PYDSDQMAKE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| FIMQFAGMAL | TVGQSLVFNF | KDKKLLGLAV | KSLEAIDPKS | LGEGKDTAMR | NVRFGRILGN |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TVVQFEKAEN | SSLNLQGKSK | GKVVRQSIIN | PDWDFGKMGI | GGLDKEFNSI | FRRAFASRVF |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| PPELVEQLGC | KHVKGILLYG | PPGTGKTLMA | RQIGTMLNAR | EPKIVNGPQI | LDKYVGESEA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| NVRRLFAEAE | EEEKRLGPNS | GLHIIIFDEI | DAICKQRGSV | AGNSGVHDTV | VNQLLTKIDG |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VDQLNNILVI | GMTNRRDMID | EALLRPGRLE | VQMEISLPNE | QGRVQILNIH | TKRMREFNKI |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| NDDVDNKEIA | ALTKNFSGAE | LEGLVRAAQS | SAMNRLIKAD | AKVTVDPEAM | EKLKVNRDDF |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| LHSLEHDIKP | AFGTAQEILD | NMLARGVINW | GAPVSNLLED | GMLYVQQAKA | PESSGLVSVL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| VAGAPNSGKT | ALAAQLAKMS | DFPFVKVCSP | EDMVGYTESA | KCLHIRKIFD | DAYRSMLSCI |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| VVDNVERLLD | YGSIGPRYSN | MTLQALLVLL | KKQPPKGRKL | LILCTSSRRE | VLEEMEMLTA |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| FTSVLHVPNL | SKPDHVLAVL | ENTDIFSKGE | IQAIGKKMAG | KRVFIGIKKL | LGLIDMARQT |
| 730 | 740 | ||||
| EQSQRAIKFL | SKMEEEGGLD | MVARQ |