P46460
Gene name |
Nsf (Skd2) |
Protein name |
Vesicle-fusing ATPase |
Names |
N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein, NEM-sensitive fusion protein, Suppressor of K(+) transport growth defect 2, Protein SKD2, Vesicular-fusion protein NSF |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:18195 |
EC number |
3.6.4.6: Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
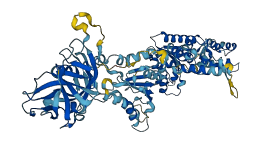
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
252-395 (D1 domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P46460
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P46460-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P46460
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P46460 | |||||
No associated diseases with P46460
7 regional properties for P46460
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | CDC48, N-terminal subdomain | 5 - 86 | IPR003338 |
| domain | AAA+ ATPase domain | 252 - 399 | IPR003593-1 |
| domain | AAA+ ATPase domain | 535 - 671 | IPR003593-2 |
| domain | ATPase, AAA-type, core | 256 - 396 | IPR003959-1 |
| domain | ATPase, AAA-type, core | 539 - 668 | IPR003959-2 |
| conserved_site | ATPase, AAA-type, conserved site | 367 - 385 | IPR003960 |
| domain | CDC48, domain 2 | 111 - 183 | IPR004201 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.4.6 | Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
7 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendritic shaft | Cylindric portion of the dendrite, directly stemming from the perikaryon, and carrying the dendritic spines. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| Golgi stack | The set of thin, flattened membrane-bounded compartments, called cisternae, that form the central portion of the Golgi complex. The stack usually comprises cis, medial, and trans cisternae; the cis- and trans-Golgi networks are not considered part of the stack. |
| myelin sheath | An electrically insulating fatty layer that surrounds the axons of many neurons. It is an outgrowth of glial cells: Schwann cells supply the myelin for peripheral neurons while oligodendrocytes supply it to those of the central nervous system. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
15 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| ATP-dependent protein binding | Binding to a protein or protein complex using energy from ATP hydrolysis. |
| D1 dopamine receptor binding | Binding to a D1 dopamine receptor. |
| ionotropic glutamate receptor binding | Binding to an ionotropic glutamate receptor. Ionotropic glutamate receptors bind glutamate and exert an effect through the regulation of ion channels. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| PDZ domain binding | Binding to a PDZ domain of a protein, a domain found in diverse signaling proteins. |
| protein C-terminus binding | Binding to a protein C-terminus, the end of a peptide chain at which the 1-carboxyl function of a constituent amino acid is not attached in peptide linkage to another amino-acid residue. |
| protein disaggregase activity | An ATP-dependent molecular chaperone activity that mediates the solubilization of ordered protein aggregates. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| small GTPase binding | Binding to a small monomeric GTPase. |
| SNARE binding | Binding to a SNARE (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attached protein receptor) protein. |
| syntaxin binding | Binding to a syntaxin, a SNAP receptor involved in the docking of synaptic vesicles at the presynaptic zone of a synapse. |
| syntaxin-1 binding | Binding to a syntaxin-1 SNAP receptor. |
13 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport | The directed movement of proteins from the Golgi to the plasma membrane in transport vesicles that move from the trans-Golgi network to the plasma membrane. |
| Golgi vesicle docking | The initial attachment of a Golgi transport vesicle membrane to a target membrane, mediated by proteins protruding from the membrane of the Golgi vesicle and the target membrane. |
| intra-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | The directed movement of substances within the Golgi, mediated by small transport vesicles. These either fuse with the cis-Golgi or with each other to form the membrane stacks known as the cis-Golgi reticulum (network). |
| intracellular protein transport | The directed movement of proteins in a cell, including the movement of proteins between specific compartments or structures within a cell, such as organelles of a eukaryotic cell. |
| positive regulation of protein catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by the destruction of the native, active configuration, with or without the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. |
| positive regulation of receptor recycling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of receptor recycling. |
| potassium ion transport | The directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| protein transport | The directed movement of proteins into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| protein-containing complex disassembly | The disaggregation of a protein-containing macromolecular complex into its constituent components. |
| regulation of exocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of exocytosis. |
| regulation of receptor internalization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of receptor internalization. |
| SNARE complex disassembly | The disaggregation of the SNARE protein complex into its constituent components. The SNARE complex is a protein complex involved in membrane fusion; a stable ternary complex consisting of a four-helix bundle, usually formed from one R-SNARE and three Q-SNAREs with an ionic layer sandwiched between hydrophobic layers. |
| vesicle-mediated transport | A cellular transport process in which transported substances are moved in membrane-bounded vesicles; transported substances are enclosed in the vesicle lumen or located in the vesicle membrane. The process begins with a step that directs a substance to the forming vesicle, and includes vesicle budding and coating. Vesicles are then targeted to, and fuse with, an acceptor membrane. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P46461 | comt | Vesicle-fusing ATPase 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P54351 | Nsf2 | Vesicle-fusing ATPase 2 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P46459 | NSF | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9QUL6 | Nsf | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q94392 | nsf-1 | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9M0Y8 | NSF | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAGRTMQAAR | CPTDELSLSN | CAVVNEKDFQ | SGQHVMVRTS | PNHKYIFTLR | THPSVVPGCI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| AFSLPQRKWA | GLSIGQDIEV | ALYSFDKAKQ | CIGTMTIEID | FLQKKNIDSN | PYDTDKMAAE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| FIQQFNNQAF | SVGQQLVFSF | NDKLFGLLVK | DIEAMDPSIL | KGEPASGKRQ | KIEVGLVVGN |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SQVAFEKAEN | SSLNLIGKAK | TKENRQSIIN | PDWNFEKMGI | GGLDKEFSDI | FRRAFASRVF |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| PPEIVEQMGC | KHVKGILLYG | PPGCGKTLLA | RQIGKMLNAR | EPKVVNGPEI | LNKYVGESEA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| NIRKLFADAE | EEQRRLGANS | GLHIIIFDEI | DAICKQRGSM | AGSTGVHDTV | VNQLLSKIDG |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VEQLNNILVI | GMTNRPDLID | EALLRPGRLE | VKMEIGLPDE | KGRLQILHIH | TARMRGHQLL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| SADVDIKELA | VETKNFSGAE | LEGLVRAAQS | TAMNRHIKAS | TKVEVDMEKA | ESLQVTRGDF |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| LASLENDIKP | AFGTNQEDYA | SYIMNGIIKW | GDPVTRVLDD | GELLVQQTKN | SDRTPLVSVL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LEGPPHSGKT | ALAAKIAEES | NFPFIKICSP | DKMIGFSETA | KCQAMKKIFD | DAYKSQLSCV |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| VVDDIERLLD | YVPIGPRFSN | LVLQALLVLL | KKAPPQGRKL | LIIGTTSRKD | VLQEMEMLNA |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| FSTTIHVPNI | ATGEQLLEAL | ELLGNFKDKE | RTTIAQQVKG | KKVWIGIKKL | LMLIEMSLQM |
| 730 | 740 | ||||
| DPEYRVRKFL | ALMREEGASP | LDFD |