P46108
Gene name |
CRK |
Protein name |
Adapter molecule crk |
Names |
Proto-oncogene c-Crk, p38 |
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:1398 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
SH2-SH3 ADAPTOR PROTEIN-RELATED (PTHR19969) |
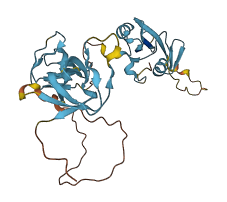
Descriptions
CRK regulates transcription and cytoskeletal reorganization for cell growth and motility by linking tyrosine kinases to small G proteins. The SH2 and nSH3 domains are used to recruit their target proteins. In CRKII, the intramolecular interactions of the SH domains with the inter-domain linker between nSH3 and cSH3 (inter-SH3 region) result in a compact structure.The binding site of SH2 in CRKII is exposed, but nSH3 is masked by SH2. In addition, cSH3 acts as a stabilizer of the assembled structure and thus as a negative regulator of CRKII function. Mutations disrupting the core structure of CRKII disturb the assembly of the SH domains, allowing nSH3 to effectively bind target proteins and transmit signals, thus promoting cell growth and motility.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
135-189 (N-terminal Src Homology 3 domain of Ct10 Regulator of Kinase adaptor proteins) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Mutagenesis experiment, Structural analysis |
Target domain |
135-189 (N-terminal Src Homology 3 domain of Ct10 Regulator of Kinase adaptor proteins) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment, Structural analysis |
Target domain |
135-189 (N-terminal Src Homology 3 domain of Ct10 Regulator of Kinase adaptor proteins) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Kobashigawa Y et al. (2007) "Structural basis for the transforming activity of human cancer-related signaling adaptor protein CRK", Nature structural & molecular biology, 14, 503-10
- Ogawa S et al. (1994) "The C-terminal SH3 domain of the mouse c-Crk protein negatively regulates tyrosine-phosphorylation of Crk associated p130 in rat 3Y1 cells", Oncogene, 9, 1669-78
- Sriram G et al. (2012) "Commentary: The carboxyl-terminal Crk SH3 domain: Regulatory strategies and new perspectives", FEBS letters, 586, 2615-8
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure
11 structures for P46108
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1JU5 | NMR | - | A | 12-120 | PDB |
| 2DVJ | NMR | - | A | 1-228 | PDB |
| 2EYV | NMR | - | A | 6-124 | PDB |
| 2EYW | NMR | - | A | 125-198 | PDB |
| 2EYX | NMR | - | A | 232-298 | PDB |
| 2EYY | NMR | - | A | 1-204 | PDB |
| 2EYZ | NMR | - | A | 1-304 | PDB |
| 2MS4 | NMR | - | B | 216-224 | PDB |
| 5UL6 | X-ray | 145 A | A | 134-191 | PDB |
| 6ATV | X-ray | 175 A | A | 134-191 | PDB |
| AF-P46108-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
159 variants for P46108
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CA397536663 rs774008957 |
4 | N>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA397536659 rs1242640031 |
4 | N>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA8266560 rs774008957 |
4 | N>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266561 rs774008957 |
4 | N>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA286802918 rs889227428 |
7 | S>L | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs748457687 CA8266558 |
9 | E>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA286802916 rs1029064679 |
9 | E>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1281300310 CA397536570 |
10 | R>G | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA397536563 rs1222327170 |
10 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA397536567 rs1281300310 |
10 | R>W | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs781767989 CA8266557 |
11 | S>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266556 rs755532427 |
11 | S>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA286802913 rs996619270 |
14 | Y>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs2229075 CA286802908 |
17 | R>G | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266554 rs779969139 |
18 | L>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs765456902 CA8266551 |
21 | Q>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1413934422 CA397536310 |
23 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs775103823 CA8266546 |
26 | L>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA397536133 rs1598308740 |
33 | G>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs773880876 CA8266543 |
34 | V>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1317489137 CA397536116 |
34 | V>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs770651188 CA8266542 |
39 | D>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1567504480 CA397536021 |
39 | D>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA397535870 rs1346380897 |
47 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1164473030 CA397535745 |
56 | R>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1008110814 CA286802847 |
57 | V>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1181134938 CA397535675 |
58 | S>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1181134938 CA397535659 |
58 | S>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA286802839 rs1046738642 |
62 | I>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1291990121 CA397535551 |
65 | S>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA397535542 rs897819678 |
65 | S>I | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA286802823 rs897819678 |
65 | S>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA286802807 rs532720077 |
67 | P>R | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
CA397535502 rs1247693524 |
68 | R>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266532 rs201145609 |
68 | R>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs756091066 CA8266530 |
70 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA397535443 rs1291174190 |
71 | V>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA397535450 rs1291174190 |
71 | V>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266528 rs767423900 |
72 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs767423900 CA286802791 |
72 | P>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266529 rs752609926 |
72 | P>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA286802788 rs927840235 |
76 | A>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA8266527 rs758982759 |
76 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266525 rs766205321 |
77 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs766205321 CA8266526 |
77 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs762667910 CA8266524 |
78 | P>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266521 rs761058721 |
80 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs770045198 CA8266494 |
82 | V>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA286794549 rs897014160 |
82 | V>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs747960532 CA8266493 |
84 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1035514589 CA286794548 |
85 | S>F | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs781014005 CA8266492 |
85 | S>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs200440102 CA8266491 |
86 | R>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1462597299 CA397532695 |
87 | L>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs780103155 CA8266489 |
88 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs757985067 CA8266488 |
91 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1398022661 CA397532615 |
93 | E>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA397532578 rs1420488676 |
96 | S>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs749892558 CA8266487 |
106 | I>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA286794546 rs11544140 |
107 | H>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1041967 CA286794545 |
109 | L>W | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA397532295 rs1343545080 |
113 | T>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA397532291 rs1255487598 |
113 | T>M | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA397532268 rs753041568 |
115 | I>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs753041568 CA8266484 |
115 | I>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA286794544 rs905572417 |
115 | I>V | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs767900527 CA8266483 |
116 | E>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266481 rs774845596 |
122 | R>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA397532177 rs1267204398 |
122 | R>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs766815891 CA8266480 |
123 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266479 rs763079680 |
125 | S>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266476 rs748384553 |
126 | G>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs769953070 CA8266477 |
126 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs748384553 CA397532121 |
126 | G>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs776671383 CA8266475 |
128 | I>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1301251656 CA397532101 |
129 | L>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs904025018 CA286794543 |
130 | R>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA286794542 rs947045345 |
132 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs375463605 CA286794541 |
134 | A>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs772107356 CA8266472 |
134 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs745434190 CA8266470 |
137 | V>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266469 rs778455201 |
138 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1242359268 CA397531900 |
148 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA397531850 rs1318927794 |
152 | P>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA286794538 rs745921349 |
158 | I>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA286794537 rs187208794 |
161 | I>V | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
rs1332350809 COSM1479244 CA397531706 |
162 | R>Q | breast [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated TOPMed |
|
CA8266465 rs755350622 |
162 | R>W | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1223714291 CA397531664 |
165 | P>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA8266462 rs763419842 |
175 | S>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs773332314 CA397531481 |
175 | S>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs867650824 CA286794535 |
176 | E>A | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA8266460 rs370837590 |
176 | E>K | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs761760691 CA8266459 |
183 | P>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs776920144 CA8266458 |
187 | V>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs145983279 CA8266456 |
188 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1200376984 CA397531169 |
192 | P>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1270600646 CA397531150 |
194 | S>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266453 rs745777068 |
195 | A>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs372978924 CA8266449 |
198 | S>L | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs748690203 CA8266450 |
198 | S>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA397531071 rs1490963705 |
201 | I>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA397530969 rs1422122098 |
207 | G>C | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA397530941 rs1568014296 |
208 | S>F | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs758717980 CA8266445 |
209 | H>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1307021911 CA397530915 |
210 | P>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs765599295 CA8266443 |
212 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1273441505 CA397530854 |
215 | G>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1451293325 CA397530856 |
215 | G>W | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266441 rs753846735 |
216 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266439 rs774455135 |
222 | A>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs980590664 CA286794531 |
222 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1272608968 CA397530735 |
224 | P>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266437 rs772014783 |
226 | V>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs911274067 CA286794530 |
227 | N>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs774348217 CA8266435 |
227 | N>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs748897674 COSM975638 CA8266433 |
229 | P>L | endometrium [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
CA397530621 rs1225277427 |
233 | L>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs747824545 CA8266430 |
237 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs747824545 CA397530592 |
237 | P>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs372495262 CA286794529 |
238 | I>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1180209088 CA397530587 |
238 | I>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266428 rs569957933 |
238 | I>V | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA397530573 rs1237445672 |
240 | A>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1204201258 CA397530551 |
244 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs750699283 CA8266427 |
244 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266426 rs779528692 |
246 | R>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266425 rs757697743 |
246 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266424 rs753987675 |
249 | N>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1378140776 CA397530505 |
251 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs760787562 CA8266422 |
252 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266421 rs752999684 |
253 | K>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266420 rs767779302 |
257 | A>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs771230814 CA8266383 |
261 | G>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA286792522 rs771230814 |
261 | G>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266384 rs775156732 |
261 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1460550029 CA397527853 |
264 | V>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs954838481 CA286792521 |
267 | T>M | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA397527817 rs1598290683 |
267 | T>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs145094200 CA286792520 |
270 | N>D | No |
ClinGen ESP |
|
|
rs1260863082 CA397527699 |
276 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA397527679 rs1398231816 |
277 | G>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs748279653 CA8266379 |
279 | C>Y | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266378 rs781401346 |
280 | N>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266376 rs751763519 |
281 | G>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs755037548 CA8266377 |
281 | G>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs766559218 CA8266375 |
283 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA397527576 rs1568005864 |
287 | P>S | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1477228518 CA397527562 |
289 | T>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs765221724 CA8266372 |
292 | R>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266371 rs761704148 |
292 | R>H | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs765221724 CA397527524 |
292 | R>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1421174730 CA397527512 |
293 | L>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs963953252 CA286792518 |
295 | D>H | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA8266370 rs371718957 |
296 | Q>H | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1278918643 CA397527442 |
298 | N>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs140388019 CA286792517 |
300 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ESP TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA8266367 rs775008230 |
301 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs146555797 CA8266366 |
304 | S>N | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
No associated diseases with P46108
5 regional properties for P46108
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | SH2 domain | 11 - 118 | IPR000980 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 132 - 192 | IPR001452-1 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 235 - 296 | IPR001452-2 |
| domain | CRK, N-terminal SH3 domain | 135 - 189 | IPR035457 |
| domain | CRK, C-terminal SH3 domain | 237 - 293 | IPR035458 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR19969 | SH2-SH3 ADAPTOR PROTEIN-RELATED |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR19969:SF8 | ADAPTER MOLECULE CRK |
| PANTHER Protein Class | scaffold/adaptor protein | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category |
Integrin signalling pathway Crk CCKR signaling map CRK Angiogenesis Crk |
|
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton | The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of actin and associated proteins. Includes actin cytoskeleton-associated complexes. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| extracellular exosome | A vesicle that is released into the extracellular region by fusion of the limiting endosomal membrane of a multivesicular body with the plasma membrane. Extracellular exosomes, also simply called exosomes, have a diameter of about 40-100 nm. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| membrane raft | Any of the small (10-200 nm), heterogeneous, highly dynamic, sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that compartmentalize cellular processes. Small rafts can sometimes be stabilized to form larger platforms through protein-protein and protein-lipid interactions. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
15 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoskeletal protein binding | Binding to a protein component of a cytoskeleton (actin, microtubule, or intermediate filament cytoskeleton). |
| ephrin receptor binding | Binding to an ephrin receptor. |
| insulin-like growth factor receptor binding | Binding to an insulin-like growth factor receptor. |
| kinase binding | Binding to a kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group. |
| phosphotyrosine residue binding | Binding to a phosphorylated tyrosine residue within a protein. |
| protein phosphorylated amino acid binding | Binding to a phosphorylated amino acid residue within a protein. |
| protein self-association | Binding to a domain within the same polypeptide. |
| protein tyrosine kinase binding | Binding to protein tyrosine kinase. |
| receptor tyrosine kinase binding | Binding to a receptor that possesses protein tyrosine kinase activity. |
| scaffold protein binding | Binding to a scaffold protein. Scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signaling pathways. Although not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signaling pathway, tethering them into complexes. |
| SH2 domain binding | Binding to a SH2 domain (Src homology 2) of a protein, a protein domain of about 100 amino-acid residues and belonging to the alpha + beta domain class. |
| SH3 domain binding | Binding to a SH3 domain (Src homology 3) of a protein, small protein modules containing approximately 50 amino acid residues found in a great variety of intracellular or membrane-associated proteins. |
| signaling adaptor activity | The binding activity of a molecule that brings together two or more molecules in a signaling pathway, permitting those molecules to function in a coordinated way. Adaptor molecules themselves do not have catalytic activity. |
| signaling receptor complex adaptor activity | The binding activity of a molecule that provides a physical support for the assembly of a multiprotein receptor signaling complex. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | Binding to a ubiquitin protein ligase enzyme, any of the E3 proteins. |
41 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| activation of GTPase activity | Any process that initiates the activity of an inactive GTPase through the replacement of GDP by GTP. |
| cell chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| cellular response to endothelin | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an endothelin stimulus. Endothelin is any of three secretory vasoconstrictive peptides (endothelin-1, -2, -3). |
| cellular response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin-like growth factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus | A process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a nerve growth factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to nitric oxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a nitric oxide stimulus. |
| cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a transforming growth factor beta stimulus. |
| cerebellar neuron development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cerebellar neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell. |
| cerebral cortex development | The progression of the cerebral cortex over time from its initial formation until its mature state. The cerebral cortex is the outer layered region of the telencephalon. |
| dendrite development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendrite over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| ephrin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by ephrin binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| establishment of cell polarity | The specification and formation of anisotropic intracellular organization or cell growth patterns. |
| helper T cell diapedesis | The passage of a helper T cell between the tight junctions of endothelial cells lining blood vessels, typically the fourth and final step of cellular extravasation. |
| hippocampus development | The progression of the hippocampus over time from its initial formation until its mature state. |
| lipid metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent. Includes fatty acids; neutral fats, other fatty-acid esters, and soaps; long-chain (fatty) alcohols and waxes; sphingoids and other long-chain bases; glycolipids, phospholipids and sphingolipids; and carotenes, polyprenols, sterols, terpenes and other isoprenoids. |
| negative regulation of cell motility | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell motility. |
| negative regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate of natural killer mediated cytotoxicity. |
| negative regulation of wound healing | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of the series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury. |
| neuron migration | The characteristic movement of an immature neuron from germinal zones to specific positions where they will reside as they mature. |
| positive regulation of cell growth | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, extent or direction of cell growth. |
| positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the frequency, rate or extent of smooth muscle cell migration. |
| positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading. |
| reelin-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of reelin (a secreted glycoprotein) to a receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of cell adhesion mediated by integrin. |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| regulation of dendrite development | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of dendrite development. |
| regulation of GTPase activity | Any process that modulates the rate of GTP hydrolysis by a GTPase. |
| regulation of intracellular signal transduction | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of intracellular signal transduction. |
| regulation of protein binding | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of protein binding. |
| regulation of Rac protein signal transduction | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of Rac protein signal transduction. |
| regulation of signal transduction | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction. |
| regulation of T cell migration | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of T cell migration. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| response to cholecystokinin | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cholecystokinin stimulus. |
| response to hepatocyte growth factor | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hepatocyte growth factor stimulus. |
| response to hydrogen peroxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulus. |
| response to yeast | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a yeast species. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
10 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q04929 | CRK | Adapter molecule crk | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q9XYM0 | Crk | Adapter molecule Crk | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| O43639 | NCK2 | Cytoplasmic protein NCK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P16333 | NCK1 | Cytoplasmic protein NCK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P46109 | CRKL | Crk-like protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P47941 | Crkl | Crk-like protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q64010 | Crk | Adapter molecule crk | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV SS |
| Q5U2U2 | Crkl | Crk-like protein | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63768 | Crk | Adapter molecule crk | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9NHC3 | ced-2 | Cell death abnormality protein 2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAGNFDSEER | SSWYWGRLSR | QEAVALLQGQ | RHGVFLVRDS | STSPGDYVLS | VSENSRVSHY |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| IINSSGPRPP | VPPSPAQPPP | GVSPSRLRIG | DQEFDSLPAL | LEFYKIHYLD | TTTLIEPVSR |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| SRQGSGVILR | QEEAEYVRAL | FDFNGNDEED | LPFKKGDILR | IRDKPEEQWW | NAEDSEGKRG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| MIPVPYVEKY | RPASASVSAL | IGGNQEGSHP | QPLGGPEPGP | YAQPSVNTPL | PNLQNGPIYA |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| RVIQKRVPNA | YDKTALALEV | GELVKVTKIN | VSGQWEGECN | GKRGHFPFTH | VRLLDQQNPD |
| EDFS |