P42644
Gene name |
GRF3 |
Protein name |
14-3-3-like protein GF14 psi |
Names |
General regulatory factor 3, Protein RARE COLD INDUCIBLE 1A |
Species |
Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) |
KEGG Pathway |
ath:AT5G38480 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
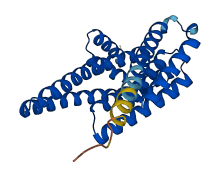
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P42644
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P42644-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
8 variants for P42644
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tmp_5_15410347_T_C | 24 | V>A | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH12180323 | 25 | E>D | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH03282074 | 36 | V>D | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH03282073 | 36 | V>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_5_15410507_C_G | 77 | N>K | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_5_15410520_G_T | 82 | A>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_5_15410839_C_T | 162 | T>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_5_15411076_G_A | 212 | G>D | No | 1000Genomes |
No associated diseases with P42644
3 regional properties for P42644
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| conserved_site | 14-3-3 protein, conserved site | 44 - 54 | IPR023409-1 |
| conserved_site | 14-3-3 protein, conserved site | 216 - 235 | IPR023409-2 |
| domain | 14-3-3 domain | 4 - 247 | IPR023410 |
11 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chloroplast | A chlorophyll-containing plastid with thylakoids organized into grana and frets, or stroma thylakoids, and embedded in a stroma. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plant-type cell wall | A more or less rigid stucture lying outside the cell membrane of a cell and composed of cellulose and pectin and other organic and inorganic substances. |
| plant-type vacuole | A closed structure that is completely surrounded by a unit membrane, contains liquid, and retains the same shape regardless of cell cycle phase. An example of this structure is found in Arabidopsis thaliana. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| plasmodesma | A fine cytoplasmic channel, found in all higher plants, that connects the cytoplasm of one cell to that of an adjacent cell. |
| plastid | Any member of a family of organelles found in the cytoplasm of plants and some protists, which are membrane-bounded and contain DNA. Plant plastids develop from a common type, the proplastid. |
1 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
10 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to nitrogen starvation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of deprivation of nitrogen. |
| cellular response to phosphate starvation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of deprivation of phosphate. |
| cellular response to potassium ion starvation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of deprivation of potassium ions. |
| cold acclimation | Any process that increases freezing tolerance of an organism in response to low, nonfreezing temperatures. |
| ethylene-activated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated by the reception of ethylene (ethene, C2H4) by a receptor and ending with modulation of a cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| protein localization | Any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| regulation of metabolic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism. |
| response to cold | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cold stimulus, a temperature stimulus below the optimal temperature for that organism. |
| response to freezing | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a freezing stimulus, temperatures below 0 degrees Celsius. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
38 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q04917 | YWHAH | 14-3-3 protein eta | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P61981 | YWHAG | 14-3-3 protein gamma | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P31946 | YWHAB | 14-3-3 protein beta/alpha | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P27348 | YWHAQ | 14-3-3 protein theta | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P63104 | YWHAZ | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P49106 | GRF1 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-6 | Zea mays (Maize) | PR |
| Q01526 | GRF2 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-12 | Zea mays (Maize) | PR |
| P68510 | Ywhah | 14-3-3 protein eta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P63101 | Ywhaz | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P93784 | HOX | 14-3-3-like protein 16R | Solanum tuberosum (Potato) | PR |
| Q41418 | 14-3-3-like protein | Solanum tuberosum (Potato) | PR | |
| P63102 | Ywhaz | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q06967 | GF14F | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-F | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q2R2W2 | GF14D | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-D | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q6EUP4 | GF14E | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-E | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q6ZKC0 | GF14C | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-C | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q7XTE8 | GF14B | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-B | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q84J55 | GF14A | 14-3-3-like protein GF14-A | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q96452 | GF14C | 14-3-3-like protein C | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | PR |
| Q96453 | GF14D | 14-3-3-like protein D | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | PR |
| Q96450 | GF14A | 14-3-3-like protein A | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | PR |
| P42645 | GRF5 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 upsilon | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P46077 | GRF4 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 phi | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q01525 | GRF2 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 omega | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q96299 | GRF9 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 mu | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q96300 | GRF7 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 nu | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9C5W6 | GRF12 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 iota | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9S9Z8 | GRF11 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 omicron | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P42643 | GRF1 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 chi | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P93212 | TFT7 | 14-3-3 protein 7 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93209 | TFT3 | 14-3-3 protein 3 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93207 | TFT10 | 14-3-3 protein 10 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93214 | TFT9 | 14-3-3 protein 9 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93211 | TFT6 | 14-3-3 protein 6 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93206 | TFT1 | 14-3-3 protein 1 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93213 | TFT8 | 14-3-3 protein 8 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P93208 | TFT2 | 14-3-3 protein 2 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| P42652 | TFT4 | 14-3-3 protein 4 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSTREENVYM | AKLAEQAERY | EEMVEFMEKV | AKTVDVEELS | VEERNLLSVA | YKNVIGARRA |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| SWRIISSIEQ | KEESKGNEDH | VAIIKDYRGK | IESELSKICD | GILNVLEAHL | IPSASPAESK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VFYLKMKGDY | HRYLAEFKAG | AERKEAAEST | LVAYKSASDI | ATAELAPTHP | IRLGLALNFS |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| VFYYEILNSP | DRACSLAKQA | FDDAIAELDT | LGEESYKDST | LIMQLLRDNL | TLWTSDMTDE |
| 250 | |||||
| AGDEIKEASK | PDGAE |