P41183
Gene name |
Bcl6 (Bcl-6) |
Protein name |
B-cell lymphoma 6 protein homolog |
Names |
|
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:12053 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
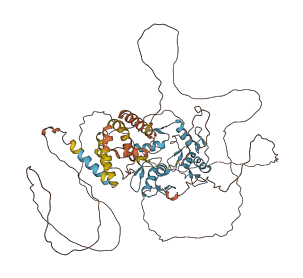
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P41183
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P41183-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
24 variants for P41183
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3389377967 | 57 | F>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389359516 | 59 | S>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389389484 | 65 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3389389459 | 93 | S>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389419310 | 108 | T>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389389467 | 121 | C>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389419337 | 165 | N>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3389410015 | 182 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389357954 | 186 | S>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3389389533 | 212 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389413605 | 233 | C>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389406601 | 273 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs214548355 | 286 | V>A | No | EVA | |
| rs253453572 | 287 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389368923 | 320 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389407706 | 337 | K>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389426726 | 402 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs260091713 | 429 | P>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3389368914 | 521 | C>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389357944 | 537 | H>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389400748 | 557 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3413101207 | 562 | L>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3389378021 | 684 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389325335 | 698 | D>E | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P41183
7 regional properties for P41183
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | BTB/POZ domain | 22 - 129 | IPR000210 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 519 - 547 | IPR013087-1 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 547 - 574 | IPR013087-2 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 575 - 602 | IPR013087-3 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 603 - 630 | IPR013087-4 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 631 - 658 | IPR013087-5 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 659 - 682 | IPR013087-6 |
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| nucleolus | A small, dense body one or more of which are present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is rich in RNA and protein, is not bounded by a limiting membrane, and is not seen during mitosis. Its prime function is the transcription of the nucleolar DNA into 45S ribosomal-precursor RNA, the processing of this RNA into 5.8S, 18S, and 28S components of ribosomal RNA, and the association of these components with 5S RNA and proteins synthesized outside the nucleolus. This association results in the formation of ribonucleoprotein precursors; these pass into the cytoplasm and mature into the 40S and 60S subunits of the ribosome. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| paraspeckles | Discrete subnuclear bodies in the interchromatin nucleoplasmic space, often located adjacent to nuclear specks. 10-20 paraspeckles are typically found in human cell nuclei. |
| replication fork | The Y-shaped region of a replicating DNA molecule, resulting from the separation of the DNA strands and in which the synthesis of new strands takes place. Also includes associated protein complexes. |
13 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| chromatin DNA binding | Binding to DNA that is assembled into chromatin. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity | A transcription regulator activity that modulates transcription of gene sets via selective and non-covalent binding to a specific double-stranded genomic DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within a cis-regulatory region. Regulatory regions include promoters (proximal and distal) and enhancers. Genes are transcriptional units, and include bacterial operons. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a DNA-binding transcription factor, a protein that interacts with a specific DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within the regulatory region of a gene to modulate transcription. |
| DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that represses or decreases the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| intronic transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to an intronic DNA sequence that regulates the transcription of the transcript it is contained within. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific sequence of DNA that is part of a regulatory region that controls the transcription of a gene or cistron by RNA polymerase II. |
| sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
| sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA, e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
| transcription corepressor binding | Binding to a transcription corepressor, a protein involved in negative regulation of transcription via protein-protein interactions with transcription factors and other proteins that negatively regulate transcription. Transcription corepressors do not bind DNA directly, but rather mediate protein-protein interactions between repressing transcription factors and the basal transcription machinery. |
49 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| B cell differentiation | The process in which a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a B cell. A B cell is a lymphocyte of B lineage with the phenotype CD19-positive and capable of B cell mediated immunity. |
| B cell proliferation | The expansion of a B cell population by cell division. Follows B cell activation. |
| cell morphogenesis | The developmental process in which the size or shape of a cell is generated and organized. |
| cell population proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. |
| cell-matrix adhesion | The binding of a cell to the extracellular matrix via adhesion molecules. |
| cellular response to DNA damage stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism. |
| erythrocyte development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an erythrocyte over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| germinal center formation | The process in which germinal centers form. A germinal center is a specialized microenvironment formed when activated B cells enter lymphoid follicles. Germinal centers are the foci for B cell proliferation and somatic hypermutation. |
| histone deacetylation | The modification of histones by removal of acetyl groups. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| isotype switching to IgE isotypes | The switching of activated B cells from IgM biosynthesis to IgE biosynthesis, accomplished through a recombination process involving an intrachromosomal deletion between switch regions that reside 5' of the IgM and IgE constant region gene segments in the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. |
| leukocyte proliferation | The expansion of a leukocyte population by cell division. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of cell growth | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, extent or direction of cell growth. |
| negative regulation of cell-matrix adhesion | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate or extent of cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix. |
| negative regulation of cellular senescence | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cellular senescence. |
| negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| negative regulation of isotype switching to IgE isotypes | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching to IgE isotypes. |
| negative regulation of leukocyte proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte proliferation. |
| negative regulation of mast cell cytokine production | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of mast cell cytokine production. |
| negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the Notch signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of plasma cell differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of plasma cell differentiation. |
| negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of Rho protein signal transduction. |
| negative regulation of T-helper 2 cell differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of T-helper 2 cell differentiation. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| negative regulation of type 2 immune response | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of a type 2 immune response. |
| plasma cell differentiation | The process in which a B cell acquires the specialized features of a plasma cell. A plasma cell is a lymphocyte which develops from a B cell and produces high amounts of antibody. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of B cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of B cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of histone deacetylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the removal of acetyl groups from histones. |
| positive regulation of neuron differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation. |
| positive regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of differentiation of regulatory T cells. |
| protein localization | Any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| pyramidal neuron differentiation | The process in which a neuroblast or one of its progeny commits to a pyramidal neuron fate, migrates from the ventricular zone to the appropriate layer in the cortex and develops into a mature neuron. |
| regulation of cell differentiation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process in which relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features. |
| regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| regulation of cytokine production | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine. |
| regulation of GTPase activity | Any process that modulates the rate of GTP hydrolysis by a GTPase. |
| regulation of immune system process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process. |
| regulation of inflammatory response | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response, the immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. |
| regulation of memory T cell differentiation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of memory T cell differentiation. |
| regulation of T cell proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of T cell proliferation. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| Rho protein signal transduction | The series of molecular signals within the cell that are mediated by a member of the Rho family of proteins switching to a GTP-bound active state. |
| spermatogenesis | The developmental process by which male germ line stem cells self renew or give rise to successive cell types resulting in the development of a spermatozoa. |
| T-helper 2 cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized T cell acquires specialized features of a T-helper 2 (Th2) cell. A Th2 cell is a CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell that has the phenotype GATA-3-positive and produces interleukin-4. |
| transcription by RNA polymerase II | The synthesis of RNA from a DNA template by RNA polymerase II (RNAP II), originating at an RNA polymerase II promoter. Includes transcription of messenger RNA (mRNA) and certain small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). |
| type 2 immune response | An immune response which is associated with resistance to extracellular organisms such as helminths and pathological conditions such as allergy, which is orchestrated by the production of particular cytokines, most notably IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, and IL-13, by any of a variety of cell types including T-helper 2 cells, eosinophils, basophils, mast cells, and nuocytes, resulting in enhanced production of certain antibody isotypes and other effects. |
177 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q08DS3 | OSR1 | Protein odd-skipped-related 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q2VWH6 | FEZF2 | Fez family zinc finger protein 2 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| A6QNZ0 | ZSCAN26 | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 26 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| A7MBI1 | ZFP69 | Zinc finger protein 69 homolog | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q08705 | CTCF | Transcriptional repressor CTCF | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| O42409 | GFI1B | Zinc finger protein Gfi-1b | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| A2T6W2 | ZNF449 | Zinc finger protein 449 | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | PR |
| Q9U405 | grau | Transcription factor grauzone | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q7K0S9 | sug | Zinc finger protein GLIS2 homolog | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P20385 | Cf2 | Chorion transcription factor Cf2 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q86P48 | ATbp | AT-rich binding protein | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P28698 | MZF1 | Myeloid zinc finger 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9NTW7 | ZFP64 | Zinc finger protein 64 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O14978 | ZNF263 | Zinc finger protein 263 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O60304 | ZNF500 | Zinc finger protein 500 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P08151 | GLI1 | Zinc finger protein GLI1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9UFB7 | ZBTB47 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 47 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P18146 | EGR1 | Early growth response protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9Y5W3 | KLF2 | Krueppel-like factor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9UNY5 | ZNF232 | Zinc finger protein 232 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96SZ4 | ZSCAN10 | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 10 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P17028 | ZNF24 | Zinc finger protein 24 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P57682 | KLF3 | Krueppel-like factor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P25490 | YY1 | Transcriptional repressor protein YY1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O43296 | ZNF264 | Zinc finger protein 264 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P49711 | CTCF | Transcriptional repressor CTCF | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9NQX1 | PRDM5 | PR domain zinc finger protein 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9HBE1 | PATZ1 | POZ-, AT hook-, and zinc finger-containing protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8TAX0 | OSR1 | Protein odd-skipped-related 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9UL58 | ZNF215 | Zinc finger protein 215 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8TBJ5 | FEZF2 | Fez family zinc finger protein 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96SR6 | ZNF382 | Zinc finger protein 382 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96IT1 | ZNF496 | Zinc finger protein 496 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96N95 | ZNF396 | Zinc finger protein 396 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9ULJ3 | ZBTB21 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 21 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O75840 | KLF7 | Krueppel-like factor 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9H9D4 | ZNF408 | Zinc finger protein 408 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q13127 | REST | RE1-silencing transcription factor | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8IZM8 | ZNF654 | Zinc finger protein 654 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q14526 | HIC1 | Hypermethylated in cancer 1 protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P17022 | ZNF18 | Zinc finger protein 18 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q86XF7 | ZNF575 | Zinc finger protein 575 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q06889 | EGR3 | Early growth response protein 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8NAM6 | ZSCAN4 | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q08ER8 | ZNF543 | Zinc finger protein 543 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P17029 | ZKSCAN1 | Zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8N680 | ZBTB2 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O95625 | ZBTB11 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 11 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9NPC7 | MYNN | Myoneurin | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96BV0 | ZNF775 | Zinc finger protein 775 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8NF99 | ZNF397 | Zinc finger protein 397 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q63HK3 | ZKSCAN2 | Zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q5FWF6 | ZNF789 | Zinc finger protein 789 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q15776 | ZKSCAN8 | Zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 8 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q53GI3 | ZNF394 | Zinc finger protein 394 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O95125 | ZNF202 | Zinc finger protein 202 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q05516 | ZBTB16 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9H116 | GZF1 | GDNF-inducible zinc finger protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8N0Y2 | ZNF444 | Zinc finger protein 444 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6P9G9 | ZNF449 | Zinc finger protein 449 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8IW36 | ZNF695 | Zinc finger protein 695 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q5VTD9 | GFI1B | Zinc finger protein Gfi-1b | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6PG37 | ZNF790 | Zinc finger protein 790 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9NQV6 | PRDM10 | PR domain zinc finger protein 10 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9Y2D9 | ZNF652 | Zinc finger protein 652 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q5TC79 | ZBTB37 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 37 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9Y4E5 | ZNF451 | E3 SUMO-protein ligase ZNF451 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8ND82 | ZNF280C | Zinc finger protein 280C | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q49AA0 | ZFP69 | Zinc finger protein 69 homolog | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O43298 | ZBTB43 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 43 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9Y330 | ZBTB12 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 12 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q13105 | ZBTB17 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 17 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P51508 | ZNF81 | Zinc finger protein 81 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q5JNZ3 | ZNF311 | Zinc finger protein 311 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9BRR0 | ZKSCAN3 | Zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q969J2 | ZKSCAN4 | Zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P49910 | ZNF165 | Zinc finger protein 165 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9Y4X4 | KLF12 | Krueppel-like factor 12 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P10074 | ZBTB48 | Telomere zinc finger-associated protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P17010 | ZFX | Zinc finger X-chromosomal protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9H5H4 | ZNF768 | Zinc finger protein 768 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6NSZ9 | ZSCAN25 | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 25 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9Y2L8 | ZKSCAN5 | Zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q86UZ6 | ZBTB46 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 46 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9NX65 | ZSCAN32 | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 32 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O14771 | ZNF213 | Zinc finger protein 213 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8IWY8 | ZSCAN29 | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 29 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8NCP5 | ZBTB44 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 44 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9NQX0 | PRDM6 | Putative histone-lysine N-methyltransferase PRDM6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9BU19 | ZNF692 | Zinc finger protein 692 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q08AG5 | ZNF844 | Zinc finger protein 844 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6R2W3 | ZBED9 | SCAN domain-containing protein 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P98182 | ZNF200 | Zinc finger protein 200 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9UK11 | ZNF223 | Zinc finger protein 223 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O15156 | ZBTB7B | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6ZMS7 | ZNF783 | Zinc finger protein 783 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P59923 | ZNF445 | Zinc finger protein 445 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8N859 | ZNF713 | Zinc finger protein 713 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q99612 | KLF6 | Krueppel-like factor 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8TD17 | ZNF398 | Zinc finger protein 398 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P52739 | ZNF131 | Zinc finger protein 131 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| A6NGD5 | ZSCAN5C | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 5C | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q05215 | EGR4 | Early growth response protein 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q7Z398 | ZNF550 | Zinc finger protein 550 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9Y2K1 | ZBTB1 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96N20 | ZNF75A | Zinc finger protein 75A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| A6NJL1 | ZSCAN5B | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 5B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| A1YPR0 | ZBTB7C | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7C | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9NWS9 | ZNF446 | Zinc finger protein 446 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P24278 | ZBTB25 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 25 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96N38 | ZNF714 | Zinc finger protein 714 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q86YH2 | ZNF280B | Zinc finger protein 280B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P41182 | BCL6 | B-cell lymphoma 6 protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O08584 | Klf6 | Krueppel-like factor 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61164 | Ctcf | Transcriptional repressor CTCF | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q810A1 | Znf18 | Zinc finger protein 18 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8BGS3 | Zkscan1 | Zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q00899 | Yy1 | Transcriptional repressor protein YY1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9DAI4 | Zbtb43 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 43 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O70237 | Gfi1b | Zinc finger protein Gfi-1b | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q99KZ6 | Znf639 | Zinc finger protein 639 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9Z1D9 | Znf394 | Zinc finger protein 394 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9CXE0 | Prdm5 | PR domain zinc finger protein 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P43300 | Egr3 | Early growth response protein 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9DAU9 | Znf654 | Zinc finger protein 654 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9R1Y5 | Hic1 | Hypermethylated in cancer 1 protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8R0T2 | Znf768 | Zinc finger protein 768 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9WVG7 | Osr1 | Protein odd-skipped-related 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8BI73 | Znf775 | Zinc finger protein 775 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VCZ7 | Zbtb7c | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91VN1 | Znf24 | Zinc finger protein 24 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9DB38 | Znf580 | Zinc finger protein 580 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| A7KBS4 | Zscan4d | Zinc finger and SCAN domain containing protein 4D | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91VW9 | Zkscan3 | Zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P10925 | Zfy1 | Zinc finger Y-chromosomal protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P08046 | Egr1 | Early growth response protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q3TTC2 | Yy2 | Transcription factor YY2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q3UTQ7 | Prdm10 | PR domain zinc finger protein 10 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q6P3Y5 | Znf280c | Zinc finger protein 280C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VIG1 | Rest | RE1-silencing transcription factor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9Z1D8 | Zkscan5 | Zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8BID6 | Zbtb46 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 46 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P17012 | Zfx | Zinc finger X-chromosomal protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9WUK6 | Zbtb18 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 18 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O35738 | Klf12 | Krueppel-like factor 12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| B2RXC5 | Znf382 | Zinc finger protein 382 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O08900 | Ikzf3 | Zinc finger protein Aiolos | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q5DU09 | Znf652 | Zinc finger protein 652 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q5RJ54 | Zscan26 | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 26 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8BLM0 | Klf8 | Krueppel-like factor 8 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q99JB0 | Klf7 | Krueppel-like factor 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8R0A2 | Zbtb44 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 44 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P20662 | Zfy2 | Zinc finger Y-chromosomal protein 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q80VJ6 | Zscan4c | Zinc finger and SCAN domain containing protein 4C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q3URS2 | Zscan4f | Zinc finger and SCAN domain containing protein 4F | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60980 | Klf3 | Krueppel-like factor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9ERU3 | Znf22 | Zinc finger protein 22 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8K3J5 | Znf131 | Zinc finger protein 131 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9Z2K3 | Znf394 | Zinc finger protein 394 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q642B9 | Znf18 | Zinc finger protein 18 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| B0K011 | Osr1 | Protein odd-skipped-related 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| D3ZUU2 | Gzf1 | GDNF-inducible zinc finger protein 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| B1WBU4 | Zbtb8a | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 8A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q7TNK3 | Znf24 | Zinc finger protein 24 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O35819 | Klf6 | Krueppel-like factor 6 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9R1D1 | Ctcf | Transcriptional repressor CTCF | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P43301 | Egr3 | Early growth response protein 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P08154 | Egr1 | Early growth response protein 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| A0JPL0 | Znf382 | Zinc finger protein 382 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q4KLI1 | Zkscan1 | Zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| A1L1J6 | Znf652 | Zinc finger protein 652 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9SHD0 | ZAT4 | Zinc finger protein ZAT4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q0P4X6 | zbtb44 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 44 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| A4II20 | egr1 | Early growth response protein 1 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| Q6P882 | zbtb8a.2 | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 8A.2 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| Q567C6 | znf367 | Zinc finger protein 367 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| A7Y7X5 | znf711 | Zinc finger protein 711 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MASPADSCIQ | FTRHASDVLL | NLNRLRSRDI | LTDVVIVVSR | EQFRAHKTVL | MACSGLFYSI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| FTDQLKCNLS | VINLDPEISP | EGFCILLDFM | YTSRLNLREG | NIMAVMTTAM | YLQMEHVVDT |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| CRKFIKASEA | EMAPALKPPR | EEFLNSRMLM | PHDIMAYRGR | EVVENNMPLR | NTPGCESRAF |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| APPLYSGLST | PPASYPMYSH | LPLSTFLFSD | EELRDAPRMP | VANPFPKERA | LPCDSARQVP |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NEYSRPAMEV | SPSLCHSNIY | SPKEAVPEEA | RSDIHYSVPE | GPKPAVPSAR | NAPYFPCDKA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| SKEEERPSSE | DEIALHFEPP | NAPLNRKGLV | SPQSPQKSDC | QPNSPTESCS | SKNACILQAS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| GSPPAKSPTD | PKACNWKKYK | FIVLNSLNQN | AKPEGSEQAE | LGRLSPRAYP | APPACQPPME |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| PANLDLQSPT | KLSASGEDST | IPQASRLNNL | VNRSLAGSPR | SSSESHSPLY | MHPPKCTSCG |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| SQSPQHTEMC | LHTAGPTFPE | EMGETQSEYS | DSSCENGTFF | CNECDCRFSE | EASLKRHTLQ |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| THSDKPYKCD | RCQASFRYKG | NLASHKTVHT | GEKPYRCNIC | GAQFNRPANL | KTHTRIHSGE |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| KPYKCETCGA | RFVQVAHLRA | HVLIHTGEKP | YPCEICGTRF | RHLQTLKSHL | RIHTGEKPYH |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | ||
| CEKCNLHFRH | KSQLRLHLRQ | KHGAITNTKV | QYRVSAADLP | PELPKAC |