P39940
Gene name |
RSP5 (MDP1, NPI1, YER125W, SYGP-ORF41) |
Protein name |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RSP5 |
Names |
HECT-type E3 ubiquitin transferase RSP5, Reverses SPT-phenotype protein 5 |
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YER125W |
EC number |
2.3.2.26: Aminoacyltransferases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
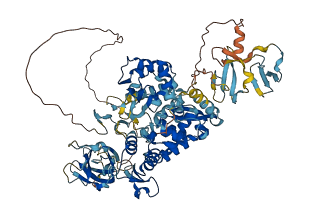
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

4 structures for P39940
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3OLM | X-ray | 250 A | A | 384-809 | PDB |
| 4LCD | X-ray | 310 A | A/B | 383-809 | PDB |
| 5HPL | X-ray | 231 A | A/B | 430-809 | PDB |
| AF-P39940-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
2 variants for P39940
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s05-410456 | 91 | V>A | No | SGRP | |
| s05-410804 | 207 | S>N | No | SGRP |
No associated diseases with P39940
4 regional properties for P39940
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.3.2.26 | Aminoacyltransferases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
11 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cortical patch | An endocytic patch that consists of an actin-containing structure found at the plasma membrane in cells; formed of networks of branched actin filaments that lie just beneath the plasma membrane and assemble, move, and disassemble rapidly. An example of this is the actin cortical patch found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
| cellular bud tip | The end of a cellular bud distal to the site of attachment to the mother cell. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an endosome. |
| extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The component of a plasma membrane consisting of gene products and protein complexes that are loosely bound to its cytoplasmic surface, but not integrated into the hydrophobic region. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| RSP5-BUL ubiquitin ligase complex | A ubiquitin ligase complex consisting of RSP5 and BUL components. It polyubiquinates plasma membrane transporters and permeases, required for their endocytosis and subsequent degradation in the vacuole. BUL1 or BUL2, respectively, bind to the target protein, enabling ubiquitylation by Rsp5. Phosphorylation of BUL proteins results in binding to 14-3-3 proteins, protecting the permeases from down-regulation. |
| ubiquitin ligase complex | A protein complex that includes a ubiquitin-protein ligase and enables ubiquitin protein ligase activity. The complex also contains other proteins that may confer substrate specificity on the complex. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| phosphatidylinositol binding | Binding to an inositol-containing glycerophospholipid, i.e. phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) and its phosphorylated derivatives. |
| ubiquitin binding | Binding to ubiquitin, a protein that when covalently bound to other cellular proteins marks them for proteolytic degradation. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of ubiquitin to a substrate protein via the reaction X-ubiquitin + S -> X + S-ubiquitin, where X is either an E2 or E3 enzyme, the X-ubiquitin linkage is a thioester bond, and the S-ubiquitin linkage is an amide bond: an isopeptide bond between the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin and the epsilon-amino group of lysine residues in the substrate or, in the linear extension of ubiquitin chains, a peptide bond the between the C-terminal glycine and N-terminal methionine of ubiquitin residues. |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of ubiquitin from one protein to another via the reaction X-Ub + Y --> Y-Ub + X, where both X-Ub and Y-Ub are covalent linkages. |
36 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to UV | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ultraviolet radiation (UV light) stimulus. Ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength in the range of 10 to 380 nanometers. |
| chromatin organization | The assembly or remodeling of chromatin composed of DNA complexed with histones, other associated proteins, and sometimes RNA. |
| late endosome to vacuole transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway | The directed movement of substances from endosomes to vacuoles by a pathway in which molecules are sorted into multivesicular bodies, which then fuse with the vacuole. |
| mitochondria-associated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of proteins transported from mitochondria and targeted to cytoplasmic proteasomes for degradation as a response to oxidative stress conditions. |
| mitochondrion organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a mitochondrion; includes mitochondrial morphogenesis and distribution, and replication of the mitochondrial genome as well as synthesis of new mitochondrial components. |
| poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus | The directed movement of poly(A)+ mRNA out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm. |
| positive regulation of endocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of endocytosis. |
| positive regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of fatty acids. |
| positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, and mediated by the proteasome. |
| positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of receptor mediated endocytosis, the uptake of external materials by cells, utilizing receptors to ensure specificity of transport. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of ubiquitin-dependent endocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of ubiquitin-dependent endocytosis. |
| proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, and mediated by the proteasome. |
| protein autoubiquitination | The ubiquitination by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues, or residues on an identical protein. Ubiquitination occurs on the lysine residue by formation of an isopeptide crosslink. |
| protein monoubiquitination | Addition of a single ubiquitin group to a protein. |
| protein polyubiquitination | Addition of multiple ubiquitin groups to a protein, forming a ubiquitin chain. |
| protein ubiquitination | The process in which one or more ubiquitin groups are added to a protein. |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of dolichol biosynthetic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of dolichol biosynthesis. Dolichol biosynthesis consists of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of dolichols, any 2,3-dihydropolyprenol derived from four or more linked isoprene units. |
| regulation of ergosterol biosynthetic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of ergosterol. |
| regulation of initiation of mating projection growth | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of the start of mating projection formation by unicellular fungi. |
| regulation of mRNA export from nucleus | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. |
| regulation of multivesicular body size | Any process that modulates the volume of a multivesicular body, a type of late endosome in which regions of the limiting endosomal membrane invaginate to form internal vesicles. |
| regulation of nitrogen utilization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nitrogen utilization. |
| regulation of phosphate metabolic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates. |
| regulation of protein localization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| regulation of ribosomal large subunit export from nucleus | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of ribosomal large subunit export from nucleus. |
| regulation of rRNA processing | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of rRNA processing. |
| regulation of tRNA export from nucleus | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of tRNA export from nucleus. |
| regulation of tRNA processing | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of tRNA processing. |
| regulation of ubiquinone biosynthetic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of ubiquinone biosynthesis. Ubiquinone biosynthesis consists of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of ubiquinone, a lipid-soluble electron-transporting coenzyme. |
| response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| ribophagy | The selective autophagy process in which cells degrade mature ribosomes under conditions of starvation. |
| ubiquitin-dependent endocytosis | Endocytosis of a protein that requires the substrate to be modified by ubiquitination. Several plasma membrane proteins, including cell surface permeases and some receptors, are targeted for internalization by endocytosis, and are thereafter delivered to the vacuole or lysosome, where they are degraded. |
| ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of a ubiquitin group, or multiple ubiquitin groups, to the protein. |
| ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide covalently tagged with ubiquitin, via the multivesicular body (MVB) sorting pathway; ubiquitin-tagged proteins are sorted into MVBs, and delivered to a lysosome/vacuole for degradation. |
19 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9Y0H4 | Su(dx) | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Su | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9V853 | Smurf | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Smurf1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9H0M0 | WWP1 | NEDD4-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase WWP1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q96J02 | ITCH | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Itchy homolog | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O00308 | WWP2 | NEDD4-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase WWP2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q96PU5 | NEDD4L | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4-like | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P46934 | NEDD4 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9HCE7 | SMURF1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9HAU4 | SMURF2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8BZZ3 | Wwp1 | NEDD4-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase WWP1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8C863 | Itch | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Itchy | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q9DBH0 | Wwp2 | NEDD4-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase WWP2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P46935 | Nedd4 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9CUN6 | Smurf1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| A2A5Z6 | Smurf2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8CFI0 | Nedd4l | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4-like | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62940 | Nedd4 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9N2Z7 | wwp-1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase wwp-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| A9JRZ0 | smurf2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MPSSISVKLV | AAESLYKRDV | FRSPDPFAVL | TIDGYQTKST | SAAKKTLNPY | WNETFKFDDI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NENSILTIQV | FDQKKFKKKD | QGFLGVVNVR | VGDVLGHLDE | DTATSSGRPR | EETITRDLKK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| SNDGMAVSGR | LIVVLSKLPS | SSPHSQAPSG | HTASSSTNTS | STTRTNGHST | SSTRNHSTSH |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| PSRGTAQAVE | STLQSGTTAA | TNTATTSHRS | TNSTSSATRQ | YSSFEDQYGR | LPPGWERRTD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NFGRTYYVDH | NTRTTTWKRP | TLDQTEAERG | NQLNANTELE | RRQHRGRTLP | GGSSDNSSVT |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| VQVGGGSNIP | PVNGAAAAAF | AATGGTTSGL | GELPSGWEQR | FTPEGRAYFV | DHNTRTTTWV |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| DPRRQQYIRT | YGPTNTTIQQ | QPVSQLGPLP | SGWEMRLTNT | ARVYFVDHNT | KTTTWDDPRL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| PSSLDQNVPQ | YKRDFRRKVI | YFRSQPALRI | LPGQCHIKVR | RKNIFEDAYQ | EIMRQTPEDL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| KKRLMIKFDG | EEGLDYGGVS | REFFFLLSHE | MFNPFYCLFE | YSAYDNYTIQ | INPNSGINPE |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| HLNYFKFIGR | VVGLGVFHRR | FLDAFFVGAL | YKMMLRKKVV | LQDMEGVDAE | VYNSLNWMLE |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| NSIDGVLDLT | FSADDERFGE | VVTVDLKPDG | RNIEVTDGNK | KEYVELYTQW | RIVDRVQEQF |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| KAFMDGFNEL | IPEDLVTVFD | ERELELLIGG | IAEIDIEDWK | KHTDYRGYQE | SDEVIQWFWK |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| CVSEWDNEQR | ARLLQFTTGT | SRIPVNGFKD | LQGSDGPRRF | TIEKAGEVQQ | LPKSHTCFNR |
| 790 | 800 | ||||
| VDLPQYVDYD | SMKQKLTLAV | EETIGFGQE |