P39688
Gene name |
Fyn |
Protein name |
Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn |
Names |
EC 2.7.10.2 , Proto-oncogene c-Fyn , p59-Fyn |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:14360 |
EC number |
2.7.10.2: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
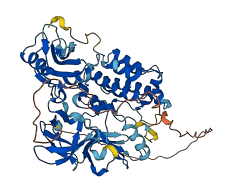
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
271-524 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
271-524 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
271-524 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Target domain |
271-524 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
407-431 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
271-524 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
407-431 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
271-524 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Hong E et al. (2004) "Solution structure and backbone dynamics of the non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinase-6 Src homology 2 domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 29700-8
- Ko S et al. (2009) "Structural basis of the auto-inhibition mechanism of nonreceptor tyrosine kinase PTK6", Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 384, 236-42
- Qiu H et al. (2002) "Regulation of the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Brk by autophosphorylation and by autoinhibition", The Journal of biological chemistry, 277, 34634-41
- Wang Q et al. (2010) "Multicolor monitoring of dysregulated protein kinases in chronic myelogenous leukemia", ACS chemical biology, 5, 887-95
- Sotirellis N et al. (1995) "Autophosphorylation induces autoactivation and a decrease in the Src homology 2 domain accessibility of the Lyn protein kinase", The Journal of biological chemistry, 270, 29773-80
- Williams NK et al. (2009) "Crystal structures of the Lyn protein tyrosine kinase domain in its Apo- and inhibitor-bound state", The Journal of biological chemistry, 284, 284-291
- Williams JC et al. (1997) "The 2.35 A crystal structure of the inactivated form of chicken Src: a dynamic molecule with multiple regulatory interactions", Journal of molecular biology, 274, 757-75
- Boggon TJ et al. (2004) "Structure and regulation of Src family kinases", Oncogene, 23, 7918-27
- Meng Y et al. (2014) "Locking the active conformation of c-Src kinase through the phosphorylation of the activation loop", Journal of molecular biology, 426, 423-35
- Register AC et al. (2014) "SH2-catalytic domain linker heterogeneity influences allosteric coupling across the SFK family", Biochemistry, 53, 6910-23
- Laham LE et al. (2000) "The activation loop in Lck regulates oncogenic potential by inhibiting basal kinase activity and restricting substrate specificity", Oncogene, 19, 3961-70
- Furlan G et al. (2014) "Phosphatase CD45 both positively and negatively regulates T cell receptor phosphorylation in reconstituted membrane protein clusters", The Journal of biological chemistry, 289, 28514-25
- Engen JR et al. (2008) "Structure and dynamic regulation of Src-family kinases", Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 65, 3058-73
- Alvarado JJ et al. (2010) "Crystal structure of the Src family kinase Hck SH3-SH2 linker regulatory region supports an SH3-dominant activation mechanism", The Journal of biological chemistry, 285, 35455-61
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for P39688
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3UF4 | X-ray | 198 A | A | 82-244 | PDB |
| AF-P39688-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
16 variants for P39688
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3400500089 | 4 | V>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3389097334 | 30 | Y>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389039432 | 60 | G>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3389097360 | 82 | T>S | No | EVA | |
| rs51545282 | 122 | A>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389069048 | 142 | D>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389100631 | 249 | G>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389096522 | 322 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3401178881 | 344 | Y>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3401051891 | 346 | S>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389106254 | 405 | K>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3401071827 | 457 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389081697 | 487 | C>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3389097964 | 508 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389105323 | 530 | Q>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389105347 | 534 | G>R | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P39688
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.2 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
19 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament | A filamentous structure formed of a two-stranded helical polymer of the protein actin and associated proteins. Actin filaments are a major component of the contractile apparatus of skeletal muscle and the microfilaments of the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. The filaments, comprising polymerized globular actin molecules, appear as flexible structures with a diameter of 5-9 nm. They are organized into a variety of linear bundles, two-dimensional networks, and three dimensional gels. In the cytoskeleton they are most highly concentrated in the cortex of the cell just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| cell body | The portion of a cell bearing surface projections such as axons, dendrites, cilia, or flagella that includes the nucleus, but excludes all cell projections. |
| cell periphery | The broad region around and including the plasma membrane of a cell, encompassing the cell cortex (inside the cell), the plasma membrane, and any external encapsulating structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The component of a plasma membrane consisting of gene products and protein complexes that are loosely bound to its cytoplasmic surface, but not integrated into the hydrophobic region. |
| glial cell projection | A prolongation or process extending from a glial cell. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| membrane raft | Any of the small (10-200 nm), heterogeneous, highly dynamic, sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that compartmentalize cellular processes. Small rafts can sometimes be stabilized to form larger platforms through protein-protein and protein-lipid interactions. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perikaryon | The portion of the cell soma (neuronal cell body) that excludes the nucleus. |
| perinuclear endoplasmic reticulum | The portion of endoplasmic reticulum, the intracellular network of tubules and cisternae, that occurs near the nucleus. The lumen of the perinuclear endoplasmic reticulum is contiguous with the nuclear envelope lumen (also called perinuclear space), the region between the inner and outer nuclear membranes. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| postsynaptic density, intracellular component | A network of proteins adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane forming an electron dense disc. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize neurotransmitter receptors in the adjacent membrane, such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse | A synapse between the Schaffer collateral axon of a CA3 pyramidal cell and a CA1 pyramidal cell. |
26 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| alpha-tubulin binding | Binding to the microtubule constituent protein alpha-tubulin. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| CD4 receptor binding | Binding to a CD4, a receptor found on the surface of T cells, monocytes and macrophages. |
| CD8 receptor binding | Binding to a CD8, a receptor found on the surface of thymocytes and cytotoxic and suppressor T-lymphocytes. |
| disordered domain specific binding | Binding to a disordered domain of a protein. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| ephrin receptor binding | Binding to an ephrin receptor. |
| G protein-coupled receptor binding | Binding to a G protein-coupled receptor. |
| growth factor receptor binding | Binding to a growth factor receptor. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| peptide hormone receptor binding | Binding to a receptor for a peptide hormone. |
| phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding | Binding to a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the addition of a phosphate group to an inositol lipid at the 3' position of the inositol ring. |
| phospholipase activator activity | Binds to and increases the activity of a phospholipase, an enzyme that catalyzes of the hydrolysis of a glycerophospholipid. |
| phospholipase binding | Binding to a phospholipase. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| scaffold protein binding | Binding to a scaffold protein. Scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signaling pathways. Although not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signaling pathway, tethering them into complexes. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| T cell receptor binding | Binding to a T cell receptor, the antigen-recognizing receptor on the surface of T cells. |
| tau protein binding | Binding to tau protein. tau is a microtubule-associated protein, implicated in Alzheimer's disease, Down Syndrome and ALS. |
| transmembrane transporter binding | Binding to a transmembrane transporter, a protein or protein complex that enables the transfer of a substance, usually a specific substance or a group of related substances, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| tubulin binding | Binding to monomeric or multimeric forms of tubulin, including microtubules. |
| type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding | Binding to a type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor. |
46 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activated T cell proliferation | The expansion of a T cell population following activation by an antigenic stimulus. |
| adaptive immune response | An immune response mediated by cells expressing specific receptors for antigens produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for an enhanced secondary response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). |
| cell differentiation | The cellular developmental process in which a relatively unspecialized cell, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cell, acquires specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize a specific cell. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cell surface receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by activation of a receptor on the surface of a cell. The pathway begins with binding of an extracellular ligand to a cell surface receptor, or for receptors that signal in the absence of a ligand, by ligand-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. The pathway ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| cellular response to amyloid-beta | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a amyloid-beta stimulus. |
| cellular response to glycine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glycine stimulus. |
| cellular response to hydrogen peroxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulus. |
| cellular response to L-glutamate | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a L-glutamate(1-) stimulus. |
| cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a platelet-derived growth factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a transforming growth factor beta stimulus. |
| dendrite morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of a dendrite are generated and organized. |
| detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain | The series of events involved in the perception of pain in which a mechanical stimulus is received and converted into a molecular signal. |
| forebrain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions). |
| gene expression | The process in which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript and its processing, translation and maturation for protein-coding genes. |
| heart process | A circulatory system process carried out by the heart. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| modulation of chemical synaptic transmission | Any process that modulates the frequency or amplitude of synaptic transmission, the process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse. Amplitude, in this case, refers to the change in postsynaptic membrane potential due to a single instance of synaptic transmission. |
| myelination | The process in which myelin sheaths are formed and maintained around neurons. Oligodendrocytes in the brain and spinal cord and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system wrap axons with compact layers of their plasma membrane. Adjacent myelin segments are separated by a non-myelinated stretch of axon called a node of Ranvier. |
| negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of dendritic spine maintenance. |
| negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide biosynthetic process | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of hydrogen peroxide biosynthesis. The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a potentially harmful byproduct of aerobic cellular respiration which can cause damage to DNA. |
| negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process in neurons. |
| negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of protein catabolic process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein catabolic process. |
| negative regulation of protein ubiquitination | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the addition of ubiquitin groups to a protein. |
| neuron migration | The characteristic movement of an immature neuron from germinal zones to specific positions where they will reside as they mature. |
| neuron projection development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase B signaling, a series of reactions mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B. |
| positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to nucleus. |
| positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the process of directing proteins towards a membrane, usually using signals contained within the protein. |
| positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the introduction of a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue of a STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) protein. |
| protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by the destruction of the native, active configuration, with or without the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. |
| protein ubiquitination | The process in which one or more ubiquitin groups are added to a protein. |
| regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of calcium ion import across plasma membrane. |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of glutamate receptor signaling pathway. |
| regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| response to amyloid-beta | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a amyloid-beta stimulus. |
| response to ethanol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ethanol stimulus. |
| response to singlet oxygen | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a singlet oxygen stimulus. Singlet oxygen is a dioxygen (O2) molecule in which two 2p electrons have similar spin. Singlet oxygen is more highly reactive than the form in which these electrons are of opposite spin, and it is produced in mutant chloroplasts lacking carotenoids and by leukocytes during metabolic burst. |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a T cell. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
90 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q0VBZ0 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q3ZC95 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | EV SS |
| A0JNB0 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P42683 | LCK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P41239 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P00523 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | EV |
| Q02977 | YRK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Yrk | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8JH64 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P09324 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q75R65 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q05876 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q24592 | hop | Tyrosine-protein kinase hopscotch | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P08630 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Btk | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9V9J3 | Src42A | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src42A | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P00528 | Src64B | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src64B | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P41240 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P51451 | BLK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P06239 | LCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lck | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P23458 | JAK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P51813 | BMX | Cytoplasmic tyrosine-protein kinase BMX | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P12931 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09769 | FGR | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42680 | TEC | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O60674 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P42679 | MATK | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P52333 | JAK3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q08881 | ITK | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07948 | LYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29597 | TYK2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13882 | PTK6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P08631 | HCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07947 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42685 | FRK | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q06187 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P06241 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9R117 | Tyk2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62137 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62120 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P52332 | Jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P48025 | Syk | Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P43404 | Zap70 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ZAP-70 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q64434 | Ptk6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P14234 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P25911 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P05480 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P06240 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16277 | Blk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P08103 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q04736 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q922K9 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03526 | Itk | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35991 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P24604 | Tec | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P41242 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P41241 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q9QVP9 | Ptk2b | Protein-tyrosine kinase 2-beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P34152 | Ptk2 | Focal adhesion kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q99ML2 | Tnk1 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TNK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O54967 | Tnk2 | Activated CDC42 kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70451 | Fer | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fer | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q6J9G1 | Styk1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P00520 | Abl1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q62270 | Srms | Tyrosine-protein kinase Srms | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q4JIM5 | Abl2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O19064 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| A1Y2K1 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q62662 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q07014 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P50545 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WUD9 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q01621 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6P6U0 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62689 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63272 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P32577 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P41243 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1LM93 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62844 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G5ECJ6 | csk-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase csk-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| O45539 | src-2 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| G5EE56 | src-1 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| F4JTP5 | STY46 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY46 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O22558 | STY8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q2MHE4 | HT1 | Serine/threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase HT1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWL6 | STY17 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY17 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| A1A5H8 | yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase yes | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O12990 | jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q1JPZ3 | src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q6EWH2 | fyna | Tyrosine-protein kinase fyna | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| F1RDG9 | fynb | Tyrosine-protein kinase fynb | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGCVQCKDKE | AAKLTEERDG | SLNQSSGYRY | GTDPTPQHYP | SFGVTSIPNY | NNFHAAGGQG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LTVFGGVNSS | SHTGTLRTRG | GTGVTLFVAL | YDYEARTEDD | LSFHKGEKFQ | ILNSSEGDWW |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| EARSLTTGET | GYIPSNYVAP | VDSIQAEEWY | FGKLGRKDAE | RQLLSFGNPR | GTFLIRESET |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TKGAYSLSIR | DWDDMKGDHV | KHYKIRKLDN | GGYYITTRAQ | FETLQQLVQH | YSERAAGLCC |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| RLVVPCHKGM | PRLTDLSVKT | KDVWEIPRES | LQLIKRLGNG | QFGEVWMGTW | NGNTKVAIKT |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LKPGTMSPES | FLEEAQIMKK | LKHDKLVQLY | AVVSEEPIYI | VTEYMSKGSL | LDFLKDGEGR |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| ALKLPNLVDM | AAQVAAGMAY | IERMNYIHRD | LRSANILVGN | GLICKIADFG | LARLIEDNEY |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| TARQGAKFPI | KWTAPEAALY | GRFTIKSDVW | SFGILLTELV | TKGRVPYPGM | NNREVLEQVE |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | |
| RGYRMPCPQD | CPISLHELMI | HCWKKDPEER | PTFEYLQGFL | EDYFTATEPQ | YQPGENL |