P39524
Gene name |
DRS2 (SWA3, YAL026C, FUN38) |
Protein name |
Phospholipid-transporting ATPase DRS2 |
Names |
|
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YAL026C |
EC number |
7.6.2.1: Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate |
Protein Class |
PROBABLE PHOSPHOLIPID-TRANSPORTING ATPASE (PTHR24092) |
Descriptions
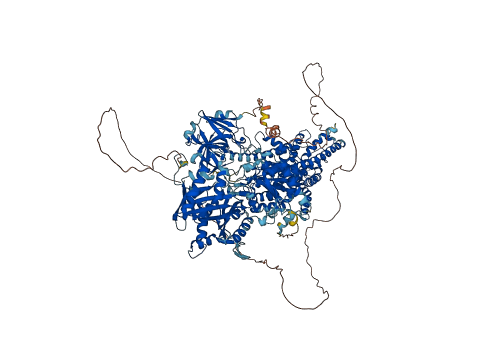
The heterodimeric eukaryotic Drs2p-Cdc50p complex is a lipid flippase that maintains cell membrane asymmetry by driving the transport of phospholipids directed to the cytoplasmic leaflet.
The enzyme complex exists in an autoinhibited form in the absence of an activator and is specifically activated by phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI4P). Drs2p belongs to a large family of Type IV P-type ATPases (P4 ATPases), having an actuator (A) domain, a nucleotide-binding (N) domain, a phosphorylation (P) domain, and a transmembrane domain (TMD) of 10 transmembrane helices (TMs). The N-terminal (N-tail) and C-terminal peptides (C-tail) of Drs2p inhibit the enzyme activity. The Drs2p C-tail inhibits the Drs2p activity by interacting extensively with the A, N, and P domains of Drs2p and occupying the ATP-binding pocket. Upon PI4P binding, the inhibitory C-tail of Drs2p is fully released from the extended horizontal groove in the regulatory A, N, and P domains of Drs2p and becomes disordered, and the putative substrate-translocating path becomes more open, especially in the cytosolic side. The N-terminal peptide of Drs2p is also known to be inhibitory, although its effect is much less severe than that of the C-tail. This N-tail engages in two hydrophobic interactions with the A domain.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
282-427 (A-domain); 526-989 (N-, P-domains) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
Structural analysis, Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment |
Target domain |
282-427 (A-domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Bai L et al. (2019) "Autoinhibition and activation mechanisms of the eukaryotic lipid flippase Drs2p-Cdc50p", Nature communications, 10, 4142
- Lyons JA et al. (2020) "P4-ATPases: how an old dog learnt new tricks - structure and mechanism of lipid flippases", Current opinion in structural biology, 63, 65-73
- Timcenko M et al. (2019) "Structure and autoregulation of a P4-ATPase lipid flippase", Nature, 571, 366-370
- Zhou X et al. (2013) "Auto-inhibition of Drs2p, a yeast phospholipid flippase, by its carboxyl-terminal tail", The Journal of biological chemistry, 288, 31807-15
- López-Marqués RL et al. (2020) "The transport mechanism of P4 ATPase lipid flippases", The Biochemical journal, 477, 3769-3790
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure
11 structures for P39524
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6PSX | EM | 330 A | A | 1-1355 | PDB |
| 6PSY | EM | 280 A | A | 1-1355 | PDB |
| 6ROH | EM | 280 A | A | 1-1355 | PDB |
| 6ROI | EM | 370 A | A | 1-1355 | PDB |
| 6ROJ | EM | 290 A | A | 1-1355 | PDB |
| 7OH4 | EM | 300 A | A | 1-1355 | PDB |
| 7OH5 | EM | 290 A | A | 1-1355 | PDB |
| 7OH6 | EM | 300 A | A | 1-1355 | PDB |
| 7OH7 | EM | 380 A | A | 1-1355 | PDB |
| 7PEM | EM | 310 A | A | 1-1355 | PDB |
| AF-P39524-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
19 variants for P39524
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s01-99611 | 30 | S>T | No | SGRP | |
| s01-99607 | 31 | H>L | No | SGRP | |
| s01-99575 | 42 | H>Y | No | SGRP | |
| s01-99472 | 76 | L>P | No | SGRP | |
| s01-99349 | 117 | N>S | No | SGRP | |
| s01-99149 | 184 | V>I | No | SGRP | |
| s01-99112 | 196 | F>S | No | SGRP | |
| s01-98903 | 266 | C>G | No | SGRP | |
| s01-98420 | 427 | L>M | No | SGRP | |
| s01-98122 | 526 | G>A | No | SGRP | |
| s01-97927 | 591 | T>M | No | SGRP | |
| s01-97892 | 603 | R>G | No | SGRP | |
| s01-97847 | 618 | E>K | No | SGRP | |
| s01-96674 | 1009 | S>T | No | SGRP | |
| s01-96599 | 1034 | A>S | No | SGRP | |
| s01-95884 | 1272 | Q>P | No | SGRP | |
| s01-95749 | 1317 | G>V | No | SGRP | |
| s01-95728 | 1324 | E>G | No | SGRP | |
| s01-95689 | 1337 | G>D | No | SGRP |
No associated diseases with P39524
4 regional properties for P39524
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 7.6.2.1 | Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR24092 | PROBABLE PHOSPHOLIPID-TRANSPORTING ATPASE |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR24092:SF214 | PHOSPHOLIPID-TRANSPORTING ATPASE |
| PANTHER Protein Class |
primary active transporter
transporter |
|
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Cdc50p-Drs2p complex | A protein complex that functions as a phospholipid-translocating P-Type ATPase. In budding yeast, this complex consists of Cdc50p and Drs2p proteins, and is involved in the trafficking of transport vesicles between the late Golgi and the early endosome. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an endosome. |
| phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex | A protein complex that functions as a phospholipid-translocating P-Type ATPase. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| trans-Golgi network | The network of interconnected tubular and cisternal structures located within the Golgi apparatus on the side distal to the endoplasmic reticulum, from which secretory vesicles emerge. The trans-Golgi network is important in the later stages of protein secretion where it is thought to play a key role in the sorting and targeting of secreted proteins to the correct destination. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity | Catalysis of the movement of lipids from one membrane leaflet to the other, driven by ATP hydrolysis. This includes flippases and floppases. |
| magnesium ion binding | Binding to a magnesium (Mg) ion. |
| phosphatidylcholine flippase activity | Catalysis of the movement of phosphatidylcholine from the exoplasmic to the cytosolic leaftlet of a membrane, using energy from the hydrolysis of ATP. |
| phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity | Catalysis of the movement of phosphatidylethanolamine from the exoplasmic to the cytosolic leaftlet of a membrane, using energy from the hydrolysis of ATP. |
| phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding | Binding to phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate, a derivative of phosphatidylinositol in which the inositol ring is phosphorylated at the 4' position. |
| phosphatidylserine flippase activity | Catalysis of the movement of phosphatidylserine from the exoplasmic to the cytosolic leaftlet of a membrane, using energy from the hydrolysis of ATP. |
| phosphatidylserine floppase activity | Catalysis of the movement of phosphatidylserine from the cytosolic to the exoplasmic leaftlet of a membrane, using energy from the hydrolysis of ATP. |
5 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| endocytic recycling | The directed movement of membrane-bounded vesicles from endosomes back to the plasma membrane, a trafficking pathway that promotes the recycling of internalized transmembrane proteins. |
| endocytosis | A vesicle-mediated transport process in which cells take up external materials or membrane constituents by the invagination of a part of the plasma membrane to form a new membrane-bounded vesicle. |
| intracellular protein transport | The directed movement of proteins in a cell, including the movement of proteins between specific compartments or structures within a cell, such as organelles of a eukaryotic cell. |
| phospholipid translocation | The movement of a phospholipid molecule from one leaflet of a membrane bilayer to the opposite leaflet. |
| post-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | The directed movement of substances from the Golgi to other parts of the cell, including organelles and the plasma membrane, mediated by small transport vesicles. |
5 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P40527 | NEO1 | Probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase NEO1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| P32660 | DNF1 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase DNF1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q9Y2Q0 | ATP8A1 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase IA | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P70704 | Atp8a1 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase IA | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9U280 | tat-1 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase tat-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MNDDRETPPK | RKPGEDDTLF | DIDFLDDTTS | HSGSRSKVTN | SHANANYIPP | SHVLPEETID |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LDADDDNIEN | DVHENLFMSN | NHDDQTSWNA | NRFDSDAYQP | QSLRAVKPPG | LFARFGNGLK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| NAFTFKRKKG | PESFEMNHYN | AVTNNELDDN | YLDSRNKFNI | KILFNRYILR | KNVGDAEGNG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| EPRVIHINDS | LANSSFGYSD | NHISTTKYNF | ATFLPKFLFQ | EFSKYANLFF | LCTSAIQQVP |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| HVSPTNRYTT | IGTLLVVLIV | SAMKECIEDI | KRANSDKELN | NSTAEIFSEA | HDDFVEKRWI |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DIRVGDIIRV | KSEEPIPADT | IILSSSEPEG | LCYIETANLD | GETNLKIKQS | RVETAKFIDV |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KTLKNMNGKV | VSEQPNSSLY | TYEGTMTLND | RQIPLSPDQM | ILRGATLRNT | AWIFGLVIFT |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| GHETKLLRNA | TATPIKRTAV | EKIINRQIIA | LFTVLIVLIL | ISSIGNVIMS | TADAKHLSYL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| YLEGTNKAGL | FFKDFLTFWI | LFSNLVPISL | FVTVELIKYY | QAFMIGSDLD | LYYEKTDTPT |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| VVRTSSLVEE | LGQIEYIFSD | KTGTLTRNIM | EFKSCSIAGH | CYIDKIPEDK | TATVEDGIEV |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| GYRKFDDLKK | KLNDPSDEDS | PIINDFLTLL | ATCHTVIPEF | QSDGSIKYQA | ASPDEGALVQ |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| GGADLGYKFI | IRKPNSVTVL | LEETGEEKEY | QLLNICEFNS | TRKRMSAIFR | FPDGSIKLFC |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| KGADTVILER | LDDEANQYVE | ATMRHLEDYA | SEGLRTLCLA | MRDISEGEYE | EWNSIYNEAA |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| TTLDNRAEKL | DEAANLIEKN | LILIGATAIE | DKLQDGVPET | IHTLQEAGIK | IWVLTGDRQE |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| TAINIGMSCR | LLSEDMNLLI | INEETRDDTE | RNLLEKINAL | NEHQLSTHDM | NTLALVIDGK |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| SLGFALEPEL | EDYLLTVAKL | CKAVICCRVS | PLQKALVVKM | VKRKSSSLLL | AIGDGANDVS |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| MIQAAHVGVG | ISGMEGMQAA | RSADIAVGQF | KFLKKLLLVH | GSWSYQRISV | AILYSFYKNT |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| ALYMTQFWYV | FANAFSGQSI | MESWTMSFYN | LFFTVWPPFV | IGVFDQFVSS | RLLERYPQLY |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| KLGQKGQFFS | VYIFWGWIIN | GFFHSAIVFI | GTILIYRYGF | ALNMHGELAD | HWSWGVTVYT |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| TSVIIVLGKA | ALVTNQWTKF | TLIAIPGSLL | FWLIFFPIYA | SIFPHANISR | EYYGVVKHTY |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | 1260 |
| GSGVFWLTLI | VLPIFALVRD | FLWKYYKRMY | EPETYHVIQE | MQKYNISDSR | PHVQQFQNAI |
| 1270 | 1280 | 1290 | 1300 | 1310 | 1320 |
| RKVRQVQRMK | KQRGFAFSQA | EEGGQEKIVR | MYDTTQKRGK | YGELQDASAN | PFNDNNGLGS |
| 1330 | 1340 | 1350 | |||
| NDFESAEPFI | ENPFADGNQN | SNRFSSSRDD | ISFDI |