P36506
Gene name |
Map2k2 (Mek2, Mkk2, Prkmk2) |
Protein name |
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 |
Names |
SCFR, Proto-oncogene c-Kit, Tyrosine-protein kinase Kit, MAP kinase kinase 2, MAPKK 2, ERK activator kinase 2, MAPK/ERK kinase 2, MEK 2 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:58960 |
EC number |
2.7.12.2: Dual-specificity kinases (those acting on Ser/Thr and Tyr residues) |
Protein Class |
|
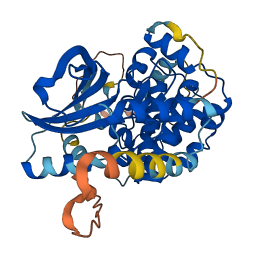
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
72-369 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
211-232 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
72-369 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Min X et al. (2009) "The structure of the MAP2K MEK6 reveals an autoinhibitory dimer", Structure (London, England : 1993), 17, 96-104
- Ohren JF et al. (2004) "Structures of human MAP kinase kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2 describe novel noncompetitive kinase inhibition", Nature structural & molecular biology, 11, 1192-7
- Fischmann TO et al. (2009) "Crystal structures of MEK1 binary and ternary complexes with nucleotides and inhibitors", Biochemistry, 48, 2661-74
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P36506
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P36506-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P36506
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P36506 | |||||
No associated diseases with P36506
8 regional properties for P36506
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | SH2 domain | 280 - 376 | IPR000980 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 2 - 61 | IPR001452-1 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 106 - 165 | IPR001452-2 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 190 - 252 | IPR001452-3 |
| domain | Nck1, SH3 domain 1 | 3 - 61 | IPR035562 |
| domain | Nck1, SH3 domain 2 | 108 - 162 | IPR035564 |
| domain | Nck1, SH3 domain 3 | 193 - 249 | IPR035565 |
| domain | Nck1, SH2 domain | 280 - 376 | IPR035882 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.12.2 | Dual-specificity kinases (those acting on Ser/Thr and Tyr residues) |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
14 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell cortex | The region of a cell that lies just beneath the plasma membrane and often, but not always, contains a network of actin filaments and associated proteins. |
| cell-cell junction | A cell junction that forms a connection between two or more cells of an organism; excludes direct cytoplasmic intercellular bridges, such as ring canals in insects. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The leaflet the plasma membrane that faces the cytoplasm and any proteins embedded or anchored in it or attached to its surface. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| focal adhesion | A cell-substrate junction that anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix and that forms a point of termination of actin filaments. In insects focal adhesion has also been referred to as hemi-adherens junction (HAJ). |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| late endosome | A prelysosomal endocytic organelle differentiated from early endosomes by lower lumenal pH and different protein composition. Late endosomes are more spherical than early endosomes and are mostly juxtanuclear, being concentrated near the microtubule organizing center. |
| microtubule | Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
12 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| MAP kinase kinase activity | Catalysis of the concomitant phosphorylation of threonine (T) and tyrosine (Y) residues in a Thr-Glu-Tyr (TEY) thiolester sequence in a MAP kinase (MAPK) substrate. |
| MAP-kinase scaffold activity | The binding activity of a molecule that functions as a physical support for the assembly of a multiprotein mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) complex. Binds multiple kinases of the MAPKKK cascade, and also upstream signaling proteins, permitting those molecules to function in a coordinated way. Bringing together multiple enzymes and their substrates enables the signal to be transduced quickly and efficiently. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| molecular adaptor activity | The binding activity of a molecule that brings together two or more molecules through a selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric interaction, permitting those molecules to function in a coordinated way. |
| PDZ domain binding | Binding to a PDZ domain of a protein, a domain found in diverse signaling proteins. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity | Binds to and increases the activity of a protein serine/threonine kinase. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| scaffold protein binding | Binding to a scaffold protein. Scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signaling pathways. Although not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signaling pathway, tethering them into complexes. |
21 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| epithelial cell proliferation involved in lung morphogenesis | The multiplication or reproduction of epithelial cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population that contributes to the shaping of the lung. |
| ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least ERK1 or ERK2 (MAPKs), a MEK (a MAPKK) and a MAP3K. The cascade may involve 4 different kinases, as it can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| face development | The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a face from an initial condition to its mature state. The face is the ventral division of the head. |
| heart development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. |
| lung morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the lung are generated and organized. |
| MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tiers: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| peptidyl-serine autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own serine amino acid residues, or a serine residue on an identical protein. |
| positive regulation of axonogenesis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis. |
| positive regulation of cell motility | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell motility. |
| positive regulation of production of miRNAs involved in gene silencing by miRNA | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of maturation of miRNAs. |
| positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of protein serine/threonine kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of axon regeneration | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of axon regeneration. |
| regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of early endosome to late endosome transport. |
| regulation of Golgi inheritance | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of Golgi inheritance. Golgi inheritance is the partitioning of Golgi apparatus between daughter cells at cell division. |
| regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the stress-activated MAPK cascade. |
| thymus development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the thymus over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The thymus is a symmetric bi-lobed organ involved primarily in the differentiation of immature to mature T cells, with unique vascular, nervous, epithelial, and lymphoid cell components. |
| thyroid gland development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the thyroid gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The thyroid gland is an endoderm-derived gland that produces thyroid hormone. |
| trachea formation | The process pertaining to the initial formation of a trachea from unspecified parts. The process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the trachea is recognizable. The trachea is the portion of the airway that attaches to the bronchi as it branches. |
20 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P32491 | MKK2 | MAP kinase kinase MKK2/SSP33 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| P32490 | MKK1 | MAP kinase kinase MKK1/SSP32 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q90891 | MAP2K2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q9XT09 | MAP2K1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | PR |
| Q1HG70 | MAP2K2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| Q24324 | Dsor1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase dSOR1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q13163 | MAP2K5 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q02750 | MAP2K1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P36507 | MAP2K2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9WVS7 | Map2k5 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P31938 | Map2k1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q63932 | Map2k2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q4KSH7 | Map2k7 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q62862 | Map2k5 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q01986 | Map2k1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q5QN75 | MKK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q10664 | mek-2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase mek-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9FJV0 | MKK6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9S7U9 | MKK2 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q94A06 | MKK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MLARRKPVLP | ALTINPTIAE | GPSPTSEGAS | EAHLVDLQKK | LEELDLDEQQ | RKRLEAFLTQ |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| KAKVGELKDD | DFERISELGA | GNGGVVTKAR | HRPSGLIMAR | KLIHLEIKPA | VRNQIIRELQ |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VLHECNSPYI | VGFYGAFYSD | GEISICMEHM | DGGSLDQVLK | EAKRIPEDIL | GKVSIAVLRG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LAYLREKHQI | MHRDVKPSNI | LVNSRGEIKL | CDFGVSGQLI | DSMANSFVGT | RSYMSPERLQ |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| GTHYSVQSDI | WSMGLSLVEL | AIGRYPIPPP | DAKELEASFG | RPVVDGADGE | PHSVSPRPRP |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| PGRPISGHGM | DSRPAMAIFE | LLDYIVNEPP | PKLPSGVFSS | DFQEFVNKCL | IKNPAERADL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | |||
| KLLTNHAFIK | RSEGEDVDFA | GWLCRTLRLK | QPSTPTRTAV |