P35821
Gene name |
Ptpn1 |
Protein name |
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 1 |
Names |
Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B, PTP-1B, Protein-tyrosine phosphatase HA2, PTP-HA2 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:19246 |
EC number |
3.1.3.48: Phosphoric monoester hydrolases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
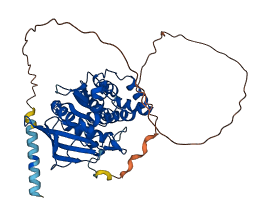
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P35821
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P35821-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
19 variants for P35821
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3392543348 | 16 | W>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3392515381 | 35 | A>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388615898 | 40 | N>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3388606807 | 70 | S>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3388612677 | 73 | K>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388615844 | 87 | P>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388616051 | 103 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388612780 | 178 | T>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3388610353 | 204 | L>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388616538 | 240 | D>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388606789 | 260 | L>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388610356 | 334 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388617306 | 352 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs218774121 | 365 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388617329 | 371 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388612712 | 375 | G>C | No | EVA | |
| rs251631195 | 383 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388616558 | 387 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388607144 | 418 | L>V | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P35821
4 regional properties for P35821
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Tyrosine-specific protein phosphatase, PTPase domain | 3 - 279 | IPR000242 |
| domain | Tyrosine-specific protein phosphatases domain | 189 - 268 | IPR000387 |
| domain | Protein-tyrosine phosphatase, catalytic | 170 - 276 | IPR003595 |
| active_site | Protein-tyrosine phosphatase, active site | 213 - 223 | IPR016130 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.1.3.48 | Phosphoric monoester hydrolases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
11 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane | The side (leaflet) of the plasma membrane that faces the cytoplasm. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| mitochondrial crista | Any of the inward folds of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Their number, extent, and shape differ in mitochondria from different tissues and organisms. They appear to be devices for increasing the surface area of the mitochondrial inner membrane, where the enzymes of electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation are found. Their shape can vary with the respiratory state of the mitochondria. |
| mitochondrial matrix | The gel-like material, with considerable fine structure, that lies in the matrix space, or lumen, of a mitochondrion. It contains the enzymes of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and, in some organisms, the enzymes concerned with fatty acid oxidation. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
| sorting endosome | A multivesicular body surrounded by and connected with multiple tubular compartments with associated vesicles. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| ephrin receptor binding | Binding to an ephrin receptor. |
| insulin receptor binding | Binding to an insulin receptor. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine phosphatase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine phosphate + H2O = non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine + phosphate. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein phosphatase 2A binding | Binding to protein phosphatase 2A. |
| protein tyrosine phosphatase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: protein tyrosine phosphate + H2O = protein tyrosine + phosphate. |
| receptor tyrosine kinase binding | Binding to a receptor that possesses protein tyrosine kinase activity. |
| zinc ion binding | Binding to a zinc ion (Zn). |
22 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton reorganization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in dynamic structural changes to the arrangement of constituent parts of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of the presence of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) or other ER-related stress; results in changes in the regulation of transcription and translation. |
| insulin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of the insulin receptor binding to insulin. |
| IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response | The series of molecular signals mediated by the endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor IRE1 (Inositol-requiring transmembrane kinase/endonuclease). Begins with activation of IRE1 in response to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. One target of activated IRE1 is the transcription factor HAC1 in yeast, or XBP1 in mammals; IRE1 cleaves an intron of a mRNA coding for HAC1/XBP1 to generate an activated HAC1/XBP1 transcription factor, which controls the up regulation of UPR-related genes. At least in mammals, IRE1 can also signal through additional intracellular pathways including JNK and NF-kappaB. |
| negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| negative regulation of MAP kinase activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity. |
| negative regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the PERK-mediated unfolded protein response. |
| negative regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway activity. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation | The removal of phosphoric residues from peptidyl-O-phospho-tyrosine to form peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation involved in inactivation of protein kinase activity | Any peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation that is involved in inactivation of protein kinase activity. |
| platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a ligand to a beta-type platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFbeta) on the surface of a signal-receiving cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| positive regulation of JUN kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of JUN kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of protein tyrosine kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of receptor catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of receptor catabolic process. |
| protein dephosphorylation | The process of removing one or more phosphoric residues from a protein. |
| regulation of endocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of endocytosis. |
| regulation of hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway. |
| regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of insulin receptor signaling. |
| regulation of intracellular protein transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of proteins within cells. |
| regulation of signal transduction | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction. |
| response to endoplasmic reticulum stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stress acting at the endoplasmic reticulum. ER stress usually results from the accumulation of unfolded or misfolded proteins in the ER lumen. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P17706 | PTPN2 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P18031 | PTPN1 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q06180 | Ptpn2 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| A1L1L3 | Ptpn20 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 20 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P35233 | Ptpn2 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P20417 | Ptpn1 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MEMEKEFEEI | DKAGNWAAIY | QDIRHEASDF | PCKVAKLPKN | KNRNRYRDVS | PFDHSRIKLH |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QEDNDYINAS | LIKMEEAQRS | YILTQGPLPN | TCGHFWEMVW | EQKSRGVVML | NRIMEKGSLK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| CAQYWPQQEE | KEMVFDDTGL | KLTLISEDVK | SYYTVRQLEL | ENLTTKETRE | ILHFHYTTWP |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| DFGVPESPAS | FLNFLFKVRE | SGSLSLEHGP | IVVHCSAGIG | RSGTFCLADT | CLLLMDKRKD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| PSSVDIKKVL | LEMRRFRMGL | IQTADQLRFS | YLAVIEGAKF | IMGDSSVQDQ | WKELSREDLD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LPPEHVPPPP | RPPKRTLEPH | NGKCKELFSS | HQWVSEETCG | DEDSLAREEG | RAQSSAMHSV |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| SSMSPDTEVR | RRMVGGGLQS | AQASVPTEEE | LSSTEEEHKA | HWPSHWKPFL | VNVCMATLLA |
| 430 | |||||
| TGAYLCYRVC | FH |