P35465
Gene name |
Pak1 |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 |
Names |
Alpha-PAK, Protein kinase MUK2, p21-activated kinase 1, PAK-1, p68-PAK |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:29431 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
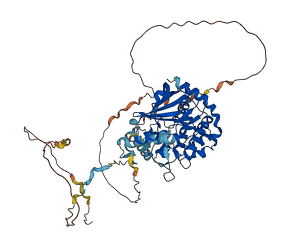
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
269-520 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
405-428 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
269-520 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Lei M et al. (2000) "Structure of PAK1 in an autoinhibited conformation reveals a multistage activation switch", Cell, 102, 387-97
- Totaro A et al. (2007) "Identification of an intramolecular interaction important for the regulation of GIT1 functions", Molecular biology of the cell, 18, 5124-38
- Bautista L et al. (2020) "p21-Activated Kinases in Thyroid Cancer", Endocrinology, 161,
- Chong C et al. (2001) "The mechanism of PAK activation. Autophosphorylation events in both regulatory and kinase domains control activity", The Journal of biological chemistry, 276, 17347-53
- Wang J et al. (2011) "Structural insights into the autoactivation mechanism of p21-activated protein kinase", Structure (London, England : 1993), 19, 1752-61
- Ha BH et al. (2012) "Type II p21-activated kinases (PAKs) are regulated by an autoinhibitory pseudosubstrate", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109, 16107-12
- Rousseau V et al. (2003) "A new constitutively active brain PAK3 isoform displays modified specificities toward Rac and Cdc42 GTPases", The Journal of biological chemistry, 278, 3912-20
- Ching YP et al. (2003) "Identification of an autoinhibitory domain of p21-activated protein kinase 5", The Journal of biological chemistry, 278, 33621-4
- Dan C et al. (2002) "PAK5, a new brain-specific kinase, promotes neurite outgrowth in N1E-115 cells", Molecular and cellular biology, 22, 567-77
- Kaur R et al. (2005) "Activation of p21-activated kinase 6 by MAP kinase kinase 6 and p38 MAP kinase", The Journal of biological chemistry, 280, 3323-30
- Gao J et al. (2013) "Substrate and inhibitor specificity of the type II p21-activated kinase, PAK6", PloS one, 8, e77818
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for P35465
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1E0A | NMR | - | B | 75-118 | PDB |
| AF-P35465-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P35465
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P35465 | |||||
No associated diseases with P35465
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
25 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament | A filamentous structure formed of a two-stranded helical polymer of the protein actin and associated proteins. Actin filaments are a major component of the contractile apparatus of skeletal muscle and the microfilaments of the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. The filaments, comprising polymerized globular actin molecules, appear as flexible structures with a diameter of 5-9 nm. They are organized into a variety of linear bundles, two-dimensional networks, and three dimensional gels. In the cytoskeleton they are most highly concentrated in the cortex of the cell just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| cell-cell junction | A cell junction that forms a connection between two or more cells of an organism; excludes direct cytoplasmic intercellular bridges, such as ring canals in insects. |
| chromosome | A structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| focal adhesion | A cell-substrate junction that anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix and that forms a point of termination of actin filaments. In insects focal adhesion has also been referred to as hemi-adherens junction (HAJ). |
| GABA-ergic synapse | A synapse that uses GABA as a neurotransmitter. These synapses are typically inhibitory. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| growth cone | The migrating motile tip of a growing neuron projection, where actin accumulates, and the actin cytoskeleton is the most dynamic. |
| intercalated disc | A complex cell-cell junction at which myofibrils terminate in cardiomyocytes; mediates mechanical and electrochemical integration between individual cardiomyocytes. The intercalated disc contains regions of tight mechanical attachment (fasciae adherentes and desmosomes) and electrical coupling (gap junctions) between adjacent cells. |
| lamellipodium | A thin sheetlike process extended by the leading edge of a migrating cell or extending cell process; contains a dense meshwork of actin filaments. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| microtubule organizing center | An intracellular structure that can catalyze gamma-tubulin-dependent microtubule nucleation and that can anchor microtubules by interacting with their minus ends, plus ends or sides. |
| nuclear membrane | Either of the lipid bilayers that surround the nucleus and form the nuclear envelope; excludes the intermembrane space. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| presynapse | The part of a synapse that is part of the presynaptic cell. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
| ruffle | Projection at the leading edge of a crawling cell; the protrusions are supported by a microfilament meshwork. |
| ruffle membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a ruffle. |
| Z disc | Platelike region of a muscle sarcomere to which the plus ends of actin filaments are attached. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| collagen binding | Binding to collagen, a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals. Collagen is highly enriched in glycine (some regions are 33% glycine) and proline, occurring predominantly as 3-hydroxyproline (about 20%). |
| gamma-tubulin binding | Binding to the microtubule constituent protein gamma-tubulin. |
| MAP kinase kinase kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation and activation of a MAP kinase kinase; each MAP kinase kinase can be phosphorylated by any of several MAP kinase kinase kinases. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
53 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton reorganization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in dynamic structural changes to the arrangement of constituent parts of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| amygdala development | The progression of the amygdala over time from its initial formation until its mature state. The amygdala is an almond-shaped set of neurons in the medial temporal lobe of the brain that play a key role in processing emotions such as fear and pleasure. |
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube | The process in which the anatomical structures of branches in an epithelial tube are generated and organized. A tube is a long hollow cylinder. |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| cellular response to DNA damage stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism. |
| cellular response to insulin stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin stimulus. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in mammals, and by the homologous organs of other organisms. |
| cellular response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| cerebellum development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cerebellum over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The cerebellum is the portion of the brain in the back of the head between the cerebrum and the pons. In mice, the cerebellum controls balance for walking and standing, modulates the force and range of movement and is involved in the learning of motor skills. |
| chromatin remodeling | A dynamic process of chromatin reorganization resulting in changes to chromatin structure. These changes allow DNA metabolic processes such as transcriptional regulation, DNA recombination, DNA repair, and DNA replication. |
| dendrite development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendrite over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| dendritic spine development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendritic spine over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A dendritic spine is a protrusion from a dendrite and a specialized subcellular compartment involved in synaptic transmission. |
| establishment of cell polarity | The specification and formation of anisotropic intracellular organization or cell growth patterns. |
| exocytosis | A process of secretion by a cell that results in the release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle. Exocytosis can occur either by full fusion, when the vesicle collapses into the plasma membrane, or by a kiss-and-run mechanism that involves the formation of a transient contact, a pore, between a granule (for exemple of chromaffin cells) and the plasma membrane. The latter process most of the time leads to only partial secretion of the granule content. Exocytosis begins with steps that prepare vesicles for fusion with the membrane (tethering and docking) and ends when molecules are secreted from the cell. |
| gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion, neurotransmission | The regulated release of gamma-aminobutyric acid by a cell, in which the gamma-aminobutyric acid acts as a neurotransmitter. |
| glutamate secretion, neurotransmission | The controlled release of glutamate by a cell, in which the glutamate acts as a neurotransmitter. |
| hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to a hepatocyte growth factor receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| negative regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of the growth of a cardiac muscle cell, where growth contributes to the progression of the cell over time from its initial formation to its mature state. |
| negative regulation of cell proliferation involved in contact inhibition | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation in response to cell density. |
| neuromuscular junction development | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a neuromuscular junction. |
| neuron projection morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of a neuron projection are generated and organized. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites. |
| observational learning | Learning that occurs through observing the behavior of others. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| positive regulation of axon extension | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of axon extension. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of fibroblast migration | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of fibroblast cell migration. Fibroblast cell migration is accomplished by extension and retraction of a pseudopodium. |
| positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of insulin receptor signaling. |
| positive regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the activity of an intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of JUN kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of JUN kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of microtubule nucleation | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of microtubule nucleation. Microtubule nucleation is the 'de novo' formation of a microtubule, in which tubulin heterodimers form metastable oligomeric aggregates, some of which go on to support formation of a complete microtubule. Microtubule nucleation usually occurs from a specific site within a cell. |
| positive regulation of microtubule polymerization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of microtubule polymerization. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the process of directing proteins towards a membrane, usually using signals contained within the protein. |
| positive regulation of stress fiber assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly of a stress fiber, a bundle of microfilaments and other proteins found in fibroblasts. |
| positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration. |
| positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| receptor clustering | The receptor metabolic process that results in grouping of a set of receptors at a cellular location, often to amplify the sensitivity of a signaling response. |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of axonogenesis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis, the generation of an axon, the long process of a neuron. |
| regulation of gene expression | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of long-term synaptic potentiation. |
| regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAP kinase (MAPK) cascade. |
| response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
| response to organic substance | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic substance stimulus. |
| small GTPase mediated signal transduction | The series of molecular signals in which a small monomeric GTPase relays a signal. |
| trans-synaptic signaling by endocannabinoid, modulating synaptic transmission | Cell-cell signaling between presynapse and postsynapse, via the release and reception of endocannabinoid ligands, that modulates the synaptic transmission properties of the synapse. |
| transmission of nerve impulse | The neurological system process in which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by a combination of action potential propagation and synaptic transmission. |
| wound healing | The series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury. |
22 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q12469 | SKM1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SKM1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q08E52 | PAK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q7YQL4 | PAK3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | SS |
| Q9VXE5 | mbt | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK mbt | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q9P286 | PAK5 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9NQU5 | PAK6 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O96013 | PAK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O75914 | PAK3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q13177 | PAK2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13153 | PAK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8C015 | Pak5 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3ULB5 | Pak6 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61036 | Pak3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8CIN4 | Pak2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O88643 | Pak1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q64303 | Pak2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| D4A280 | Pak5 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 5 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62829 | Pak3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O54748 | Stk3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G5EFU0 | pak-2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase pak-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q17850 | pak-1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase pak-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| G5EGQ3 | max-2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase max-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSNNGLDVQD | KPPAPPMRNT | STMIGAGSKD | PGTLNHGSKP | LPPNPEEKKK | KDRFYRSILA |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GDKTNKKKEK | ERPEISLPSD | FEHTIHVGFD | AVTGEFTGMP | EQWARLLQTS | NITKSEQKKN |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PQAVLDVLEF | YNSKKTSNSQ | KYMSFTDKSA | EDYNSSNTLN | VKTVSETPAV | PPVSEDEDDD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| DDATPPPVIA | PRPEHTKSVY | TRSVIEPLPV | TPTRDVATSP | ISPTENNTTP | PDALTRNTEK |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| QKKKPKMSDE | EILEKLRSIV | SVGDPKKKYT | RFEKIGQGAS | GTVYTAMDVA | TGQEVAIKQM |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| NLQQQPKKEL | IINEILVMRE | NKNPNIVNYL | DSYLVGDELW | VVMEYLAGGS | LTDVVTETCM |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| DEGQIAAVCR | ECLQALEFLH | SNQVIHRDIK | SDNILLGMDG | SVKLTDFGFC | AQITPEQSKR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| STMVGTPYWM | APEVVTRKAY | GPKVDIWSLG | IMAIEMIEGE | PPYLNENPLR | ALYLIATNGT |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| PELQNPEKLS | AIFRDFLNRC | LEMDVEKRGS | AKELLQHQFL | KIAKPLSSLT | PLIAAAKEAT |
| KNNH |