P35281
Gene name |
Rab10 |
Protein name |
Ras-related protein Rab-10 |
Names |
|
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
3.6.5.2: Acting on GTP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
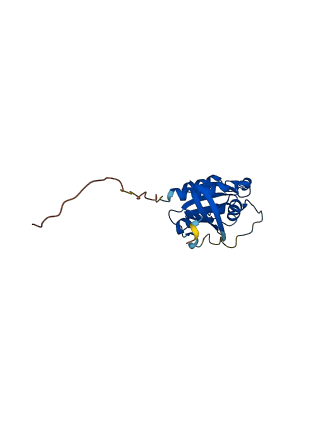
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P35281
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P35281-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P35281
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P35281 | |||||
No associated diseases with P35281
4 regional properties for P35281
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.5.2 | Acting on GTP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
17 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anchored component of synaptic vesicle membrane | The component of the synaptic vesicle membrane consisting of the gene products that are tethered to the membrane only by a covalently attached anchor, such as a lipid group that is embedded in the membrane. Gene products with peptide sequences that are embedded in the membrane are excluded from this grouping. |
| cilium | A specialized eukaryotic organelle that consists of a filiform extrusion of the cell surface and of some cytoplasmic parts. Each cilium is largely bounded by an extrusion of the cytoplasmic (plasma) membrane, and contains a regular longitudinal array of microtubules, anchored to a basal body. |
| endoplasmic reticulum membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| endoplasmic reticulum tubular network | A subcompartment of the endoplasmic reticulum consisting of tubules having membranes with high curvature in cross-section. |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| exocytic vesicle | A transport vesicle that mediates transport from an intracellular compartment to the plasma membrane, and fuses with the plasma membrane to release various cargo molecules, such as proteins or hormones, by exocytosis. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| insulin-responsive compartment | A small membrane-bounded vesicle that releases its contents by exocytosis in response to insulin stimulation; the contents are enriched in GLUT4, IRAP and VAMP2. |
| intracellular membrane-bounded organelle | Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| phagocytic vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a phagocytic vesicle. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| recycling endosome | An organelle consisting of a network of tubules that functions in targeting molecules, such as receptors transporters and lipids, to the plasma membrane. |
| recycling endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a recycling endosome. |
| synaptic vesicle | A secretory organelle, typically 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and secretes these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane. |
| trans-Golgi network | The network of interconnected tubular and cisternal structures located within the Golgi apparatus on the side distal to the endoplasmic reticulum, from which secretory vesicles emerge. The trans-Golgi network is important in the later stages of protein secretion where it is thought to play a key role in the sorting and targeting of secreted proteins to the correct destination. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| G protein activity | A molecular function regulator that cycles between active GTP-bound and inactive GDP-bound states. In its active state, binds to a variety of effector proteins to regulate cellular processes. Intrinsic GTPase activity returns the G protein to its GDP-bound state. The return to the GDP-bound state can be accelerated by the action of a GTPase-activating protein (GAP). |
| GDP binding | Binding to GDP, guanosine 5'-diphosphate. |
| GDP-dissociation inhibitor binding | Binding to a GDP-dissociation inhibitor protein. |
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
| myosin V binding | Binding to a class V myosin; myosin V is a dimeric molecule involved in intracellular transport. |
19 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| antigen processing and presentation | The process in which an antigen-presenting cell expresses antigen (peptide or lipid) on its cell surface in association with an MHC protein complex. |
| axonogenesis | De novo generation of a long process of a neuron, including the terminal branched region. Refers to the morphogenesis or creation of shape or form of the developing axon, which carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells. |
| cellular response to antibiotic | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an antibiotic stimulus. An antibiotic is a chemical substance produced by a microorganism which has the capacity to inhibit the growth of or to kill other microorganisms. |
| cellular response to insulin stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin stimulus. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in mammals, and by the homologous organs of other organisms. |
| endoplasmic reticulum tubular network organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) tubular network. The ER tubular network is the ER part that that has membranes with high curvature in cross-section. |
| endosomal transport | The directed movement of substances mediated by an endosome, a membrane-bounded organelle that carries materials enclosed in the lumen or located in the endosomal membrane. |
| establishment of neuroblast polarity | The specification and formation of the apicobasal polarity of a neuroblast cell, a progenitor of the central nervous system. |
| establishment of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum membrane | The directed movement of a protein to a specific location in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. |
| establishment of protein localization to membrane | The directed movement of a protein to a specific location in a membrane. |
| Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport | The directed movement of proteins from the Golgi to the plasma membrane in transport vesicles that move from the trans-Golgi network to the plasma membrane. |
| Golgi to plasma membrane transport | The directed movement of substances from the Golgi to the plasma membrane in transport vesicles that move from the trans-Golgi network to the plasma membrane, where they fuse and release their contents by exocytosis. |
| polarized epithelial cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a polarized epithelial cell. The polarized epithelial cell can be any of the cells within an epithelium where the epithelial sheet is oriented with respect to the planar axis. |
| protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane | Any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, basolateral regions of the plasma membrane. |
| protein localization to plasma membrane | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location in the plasma membrane. |
| protein secretion | The controlled release of proteins from a cell. |
| regulated exocytosis | A process of exocytosis in which soluble proteins and other substances are initially stored in secretory vesicles for later release. It is found mainly in cells that are specialized for secreting products such as hormones, neurotransmitters, or digestive enzymes rapidly on demand. |
| regulation of exocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of exocytosis. |
| vesicle docking involved in exocytosis | The initial attachment of a vesicle membrane to a target membrane, mediated by proteins protruding from the membrane of the vesicle and the target membrane, that contributes to exocytosis. |
| vesicle-mediated transport | A cellular transport process in which transported substances are moved in membrane-bounded vesicles; transported substances are enclosed in the vesicle lumen or located in the vesicle membrane. The process begins with a step that directs a substance to the forming vesicle, and includes vesicle budding and coating. Vesicles are then targeted to, and fuse with, an acceptor membrane. |
26 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q2HJI8 | RAB8B | Ras-related protein Rab-8B | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| A4FV54 | RAB8A | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q1RMR4 | RAB15 | Ras-related protein Rab-15 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q5F470 | RAB8A | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P0C0E4 | RAB40AL | Ras-related protein Rab-40A-like | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P61006 | RAB8A | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q92930 | RAB8B | Ras-related protein Rab-8B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6IQ22 | RAB12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8WXH6 | RAB40A | Ras-related protein Rab-40A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96S21 | RAB40C | Ras-related protein Rab-40C | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q12829 | RAB40B | Ras-related protein Rab-40B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P55258 | Rab8a | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8K386 | Rab15 | Ras-related protein Rab-15 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P61028 | Rab8b | Ras-related protein Rab-8B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35283 | Rab12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9DD03 | Rab13 | Ras-related protein Rab-13 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8CB87 | Rab44 | Ras-related protein Rab-44 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VHP8 | Rab40b | Ras-related protein Rab-40B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VHQ4 | Rab40c | Ras-related protein Rab-40C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35280 | Rab8a | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P35284 | Rab12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P35289 | Rab15 | Ras-related protein Rab-15 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P70550 | Rab8b | Ras-related protein Rab-8B | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O24466 | RABE1A | Ras-related protein RABE1a | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LZD4 | RABE1D | Ras-related protein RABE1d | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SF91 | RABE1E | Ras-related protein RABE1e | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAKKTYDLLF | KLLLIGDSGV | GKTCVLFRFS | DDAFNTTFIS | TIEIDFKIKT | VELQGKKIKL |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QIWDTAGQER | FHTITTSYYR | GAMGIMLVYD | ITNGKSFENI | SKWLRNIDQH | ANEDVERMLL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| RNKCDMDHKR | VVPKGKGEQI | AREHRIRFFE | TSAKANINIE | KAFLTLPEDI | LRKTPVKEPN |
| 190 | |||||
| SENVDISSGG | GVTGWKSKCC |