P34730
Gene name |
BMH2 (YDR099W, YD8557.08) |
Protein name |
Protein BMH2 |
Names |
|
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YDR099W |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
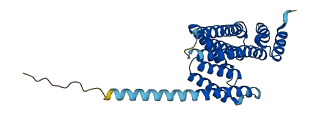
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P34730
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P34730-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P34730
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P34730 | |||||
No associated diseases with P34730
3 regional properties for P34730
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| conserved_site | 14-3-3 protein, conserved site | 43 - 53 | IPR023409-1 |
| conserved_site | 14-3-3 protein, conserved site | 216 - 235 | IPR023409-2 |
| domain | 14-3-3 domain | 5 - 247 | IPR023410 |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA replication origin binding | Binding to a DNA replication origin, a unique DNA sequence of a replicon at which DNA replication is initiated and proceeds bidirectionally or unidirectionally. |
| phosphoserine residue binding | Binding to a phosphorylated serine residue within a protein. |
14 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ascospore formation | The process in which cells that are products of meiosis acquire the specialized features of ascospores. Ascospores are generally found in clusters of four or eight spores within a single mother cell, the ascus, and are characteristic of the ascomycete fungi (phylum Ascomycota). |
| DNA damage checkpoint signaling | A signal transduction process that contributes to a DNA damage checkpoint. |
| DNA replication initiation | The process in which DNA-dependent DNA replication is started; this begins with the ATP dependent loading of an initiator complex onto the DNA, this is followed by DNA melting and helicase activity. In bacteria, the gene products that enable the helicase activity are loaded after the initial melting and in archaea and eukaryotes, the gene products that enable the helicase activity are inactive when they are loaded and subsequently activate. |
| fungal-type cell wall chitin biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cell wall chitin, a linear polysaccharide consisting of P-1,4-linked N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues, found in the walls of fungal cells. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of ubiquitin protein ligase activity. |
| pre-replicative complex assembly involved in nuclear cell cycle DNA replication | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form the nuclear pre-replicative complex, a protein-DNA complex that forms at the eukaryotic DNA replication origin and is required for replication initiation. |
| protein localization | Any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| pseudohyphal growth | The process in which cells grow as a chain of physically attached, elongated cells in response to an environmental stimulus or stimuli. |
| Ras protein signal transduction | The series of molecular signals within the cell that are mediated by a member of the Ras superfamily of proteins switching to a GTP-bound active state. |
| regulation of glycogen metabolic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving glycogen. |
| regulation of mitotic cell cycle | Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progress through the mitotic cell cycle. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
| signal transduction involved in filamentous growth | Relaying of environmental signals promoting filamentous growth. |
4 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P29311 | BMH1 | Protein BMH1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q9S9Z8 | GRF11 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 omicron | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9C5W6 | GRF12 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 iota | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P93212 | TFT7 | 14-3-3 protein 7 | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSQTREDSVY | LAKLAEQAER | YEEMVENMKA | VASSGQELSV | EERNLLSVAY | KNVIGARRAS |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| WRIVSSIEQK | EESKEKSEHQ | VELIRSYRSK | IETELTKISD | DILSVLDSHL | IPSATTGESK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VFYYKMKGDY | HRYLAEFSSG | DAREKATNSS | LEAYKTASEI | ATTELPPTHP | IRLGLALNFS |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| VFYYEIQNSP | DKACHLAKQA | FDDAIAELDT | LSEESYKDST | LIMQLLRDNL | TLWTSDISES |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | |||
| GQEDQQQQQQ | QQQQQQQQQQ | QAPAEQTQGE | PTK |