P31434
Gene name |
yicI (b3656, JW3631) |
Protein name |
Alpha-xylosidase |
Names |
|
Species |
Escherichia coli (strain K12) |
KEGG Pathway |
eco:b3656 |
EC number |
3.2.1.177: Glycosidases, ie enzymes hydrolyzing O- and S-glycosyl compounds |
Protein Class |
|
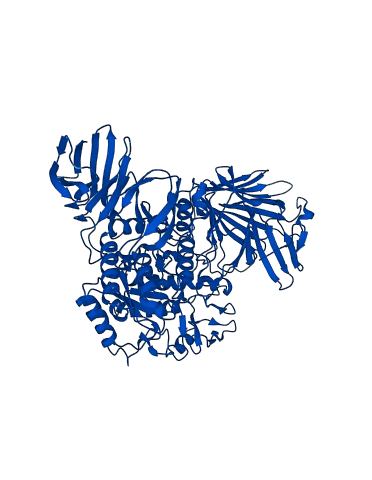
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

6 structures for P31434
No variants for P31434
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P31434 | |||||
No associated diseases with P31434
1 regional properties for P31434
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Glycoside hydrolase family 31, N-terminal domain | 159 - 218 | IPR025887 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.2.1.177 | Glycosidases, ie enzymes hydrolyzing O- and S-glycosyl compounds |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
No GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| No GO annotations for cellular component |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| alpha-D-xyloside xylohydrolase | Catalysis of the hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing alpha-D-xylose residues with release of alpha-D-xylose. |
| carbohydrate binding | Binding to a carbohydrate, which includes monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides as well as substances derived from monosaccharides by reduction of the carbonyl group (alditols), by oxidation of one or more hydroxy groups to afford the corresponding aldehydes, ketones, or carboxylic acids, or by replacement of one or more hydroxy group(s) by a hydrogen atom. Cyclitols are generally not regarded as carbohydrates. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| xyloglucan 1,6-alpha-xylosidase activity | Catalysis of the hydrolysis of xyloglucan side chains so as to remove unsubstituted D-xylose residues attached to the glucose located at the non-reducing terminus. |
1 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| carbohydrate metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MKISDGNWLI | QPGLNLIHPL | QVFEVEQQDN | EMVVYAAPRD | VRERTWQLDT | PLFTLRFFSP |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QEGIVGVRIE | HFQGALNNGP | HYPLNILQDV | KVTIENTERY | AEFKSGNLSA | RVSKGEFWSL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DFLRNGERIT | GSQVKNNGYV | QDTNNQRNYM | FERLDLGVGE | TVYGLGERFT | ALVRNGQTVE |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TWNRDGGTST | EQAYKNIPFY | MTNRGYGVLV | NHPQCVSFEV | GSEKVSKVQF | SVESEYLEYF |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| VIDGPTPKAV | LDRYTRFTGR | PALPPAWSFG | LWLTTSFTTN | YDEATVNSFI | DGMAERNLPL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| HVFHFDCFWM | KAFQWCDFEW | DPLTFPDPEG | MIRRLKAKGL | KICVWINPYI | GQKSPVFKEL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| QEKGYLLKRP | DGSLWQWDKW | QPGLAIYDFT | NPDACKWYAD | KLKGLVAMGV | DCFKTDFGER |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| IPTDVQWFDG | SDPQKMHNHY | AYIYNELVWN | VLKDTVGEEE | AVLFARSASV | GAQKFPVHWG |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| GDCYANYESM | AESLRGGLSI | GLSGFGFWSH | DIGGFENTAP | AHVYKRWCAF | GLLSSHSRLH |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| GSKSYRVPWA | YDDESCDVVR | FFTQLKCRMM | PYLYREAARA | NARGTPMMRA | MMMEFPDDPA |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| CDYLDRQYML | GDNVMVAPVF | TEAGDVQFYL | PEGRWTHLWH | NDELDGSRWH | KQQHGFLSLP |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| VYVRDNTLLA | LGNNDQRPDY | VWHEGTAFHL | FNLQDGHEAV | CEVPAADGSV | IFTLKAARTG |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | |
| NTITVTGAGE | AKNWTLCLRN | VVKVNGLQDG | SQAESEQGLV | VKPQGNALTI | TL |