Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
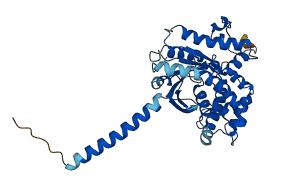
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P29797
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P29797-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P29797
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P29797 | |||||
No associated diseases with P29797
No regional properties for P29797
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for P29797 | |||
1 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| heterotrimeric G-protein complex | Any of a family of heterotrimeric GTP-binding and hydrolyzing proteins; they belong to a superfamily of GTPases that includes monomeric proteins such as EF-Tu and RAS. Heterotrimeric G-proteins consist of three subunits; the alpha subunit contains the guanine nucleotide binding site and possesses GTPase activity; the beta and gamma subunits are tightly associated and function as a beta-gamma heterodimer; extrinsic plasma membrane proteins (cytoplasmic face) that function as a complex to transduce signals from G protein-coupled receptors to an effector protein. |
12 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adenylate cyclase activator activity | Increases the activity of the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction: ATP = 3',5'-cyclic AMP + diphosphate. |
| beta-2 adrenergic receptor binding | Binding to a beta-2 adrenergic receptor. |
| corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 binding | Binding to a corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 (CRHR1). CRHR1 is the major subtype in the pituitary corticotroph, and mediates the stimulatory actions of corticotropin-releasing hormone on corticotropin hormone secretion. CRHR1 are also located in cortical areas of the brain, cerebellum and limbic system. |
| D1 dopamine receptor binding | Binding to a D1 dopamine receptor. |
| G protein-coupled receptor binding | Binding to a G protein-coupled receptor. |
| G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding | Binding to a complex of G-protein beta/gamma subunits. |
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
| insulin-like growth factor receptor binding | Binding to an insulin-like growth factor receptor. |
| ionotropic glutamate receptor binding | Binding to an ionotropic glutamate receptor. Ionotropic glutamate receptors bind glutamate and exert an effect through the regulation of ion channels. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| mu-type opioid receptor binding | Binding to a mu-type opioid receptor. |
7 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway | An adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway initiated by a ligand binding to an adrenergic receptor on the surface of the target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process. |
| adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway | An adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway initiated by dopamine binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process. |
| adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | A G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway in which the signal is transmitted via the activation of adenylyl cyclase activity and a subsequent increase in the intracellular concentration of cyclic AMP (cAMP). |
| adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | A G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway in which the signal is transmitted via the activation or inhibition of adenylyl cyclase activity and a subsequent change in the intracellular concentration of cyclic AMP (cAMP). |
| positive regulation of cAMP-mediated signaling | Any process which activates, maintains or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cAMP-mediated signaling. |
| positive regulation of GTPase activity | Any process that activates or increases the activity of a GTPase. |
| sensory perception of chemical stimulus | The series of events required for an organism to receive a sensory chemical stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. This is a neurological process. |
13 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P04896 | GNAS | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(s) subunit alpha isoforms short | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P63091 | GNAS | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(s) subunit alpha | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| P38405 | GNAL | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q2PKF4 | GNAQ | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| P93564 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Solanum tuberosum (Potato) | SS |
| P38406 | Gnal | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63803 | Gnas | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q0DJ33 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| P93163 | GPA2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-2 subunit | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | SS |
| P49084 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | SS |
| O80462 | XLG1 | Extra-large guanine nucleotide-binding protein 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P18064 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| P26981 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGCLGNSKTE | DQRNEEKAQR | EANKKIEKQL | QKDKQVYRAT | HRLLLLGAGE | SGKSTIVKQM |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| RILHVNGFNG | DEKATKVQDI | KNNLKEAIET | IVAAMSNLVP | PVELANPENQ | FRVDYILSVM |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| NVPDFDFPPE | FYEHAKALWE | DEGVRACYER | SNEYQLIDCA | QYFLDKIDVI | KQDDYVPSDQ |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| DLLRCRVLTS | GIFETKFQVD | KVNFHMFDVG | GQRDERRKWI | QCFNDVTAII | FVVASSSYNM |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| VIREDNQTNR | LQEALNLFKS | IWNNRWLRTI | SVILFLNKQD | LLAEKVLAGK | SKIELFVLDD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| RLFQERPFSF | IEDYFPEFAR | YTTPEDATPE | PGEDPRVTRA | KYFIRDEFLR | ISTASGDGRH |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | |||
| YCYPHFTCAV | DTENIRRVFN | DCRDIIQRMH | LRQYELL |