P29397
Gene name |
nusG (TM_0453) |
Protein name |
Transcription termination/antitermination protein NusG |
Names |
|
Species |
Thermotoga maritima (strain ATCC 43589 / DSM 3109 / JCM 10099 / NBRC 100826 / MSB8) |
KEGG Pathway |
tma:TM0453 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
RHO-INTERACTING TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION FACTOR NUSG (PTHR30265) |
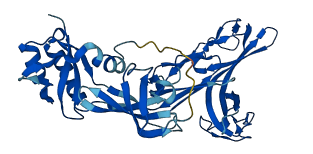
Descriptions
NusG from Thermotoga maritima exhibits a unique autoinhibition mechanism where its N-terminal domain (NTD) and C-terminal domain (CTD) interact tightly, masking the binding sites for interaction partners such as Rho, NusE, and RNA polymerase (RNAP). This interaction stabilizes the CTD but inhibits NusG's function in transcription regulation by preventing its interaction with other transcription factors and RNAP.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-284 (N-terminal domain for interaction with RNAP) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Mutagenesis experiment, Structural analysis |
Target domain |
296-351 (C-terminal domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Mutagenesis experiment, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Drögemüller J et al. (2017) "Thermotoga maritima NusG: domain interaction mediates autoinhibition and thermostability", Nucleic acids research, 45, 446-460
- Drögemüller J et al. (2013) "An autoinhibited state in the structure of Thermotoga maritima NusG", Structure (London, England : 1993), 21, 365-75
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

4 structures for P29397
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2LQ8 | NMR | - | PDB | ||
| 2XHA | X-ray | 191 A | A/B | 41-233 | PDB |
| 2XHC | X-ray | 245 A | A | 1-352 | PDB |
| AF-P29397-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P29397
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P29397 | |||||
No associated diseases with P29397
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR30265 | RHO-INTERACTING TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION FACTOR NUSG |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR30265:SF2 | TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION_ANTITERMINATION PROTEIN NUSG |
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
1 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
No GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| No GO annotations for molecular function |
4 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA-templated transcription termination | The completion of transcription |
| regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription elongation, the extension of an RNA molecule after transcription initiation and promoter clearance by the addition of ribonucleotides catalyzed by a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. |
| transcription antitermination | A positive regulation of gene expression mechanism that allows RNA polymerase to continue transcription beyond a termination site, thus allowing expression of downstream genes under specific conditions. |
| transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling | A chromatin remodeling process that reestablishes the chromatin structure following the passage of RNA polymerase II during transcription elongation, thus preventing cryptic transcription initiation. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MKKKWYIVLT | MSGYEEKVKE | NIEKKVEATG | IKNLVGRIVI | PEEVVLDATS | PSERLILSPK |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| AKLHVNNGKD | VNKGDLIAEE | PPIYARRSGV | IVDVKNVRKI | VVETIDRKYT | KTYYIPESAG |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| IEPGLRVGTK | VKQGLPLSKN | EEYICELDGK | IVEIERMKKV | VVQTPDGEQD | VYYIPLDVFD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| RDRIKKGKEV | KQGEMLAEAR | KFFAKVSGRV | EVVDYSTRKE | IRIYKTKRRK | LFPGYVFVEM |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| IMNDEAYNFV | RSVPYVMGFV | SSGGQPVPVK | DREMRPILRL | AGLEEYEEKK | KPVKVELGFK |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | |
| VGDMVKIISG | PFEDFAGVIK | EIDPERQELK | VNVTIFGRET | PVVLHVSEVE | KIE |