P29295
Gene name |
HRR25 (YPL204W) |
Protein name |
Casein kinase I homolog HRR25 |
Names |
|
Species |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) |
KEGG Pathway |
sce:YPL204W |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
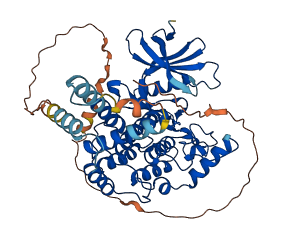
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

4 structures for P29295
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4XHL | X-ray | 301 A | A | 1-394 | PDB |
| 5CYZ | X-ray | 184 A | A | 1-394 | PDB |
| 5CZO | X-ray | 289 A | A/B | 1-394 | PDB |
| AF-P29295-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
2 variants for P29295
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s16-165212 | 313 | L>S | No | SGRP | |
| s16-165394 | 374 | A>T | No | SGRP |
No associated diseases with P29295
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
14 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular bud neck | The constriction between the mother cell and daughter cell (bud) in an organism that reproduces by budding. |
| cellular bud tip | The end of a cellular bud distal to the site of attachment to the mother cell. |
| chromosome, centromeric region | The region of a chromosome that includes the centromeric DNA and associated proteins. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| monopolin complex | A protein complex required for clamping microtubule binding sites, ensuring orientation of sister kinetochores to the same pole (mono-orientation) during meiosis I. In the yeast S. cerevisiae this complex consists of Csm1p, Lrs4p, Hrr25p and Mam1p; in S. pombe Psc1 and Mde4 have been identified as subunits. |
| nucleolus | A small, dense body one or more of which are present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is rich in RNA and protein, is not bounded by a limiting membrane, and is not seen during mitosis. Its prime function is the transcription of the nucleolar DNA into 45S ribosomal-precursor RNA, the processing of this RNA into 5.8S, 18S, and 28S components of ribosomal RNA, and the association of these components with 5S RNA and proteins synthesized outside the nucleolus. This association results in the formation of ribonucleoprotein precursors; these pass into the cytoplasm and mature into the 40S and 60S subunits of the ribosome. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| phagophore assembly site | Punctate structures proximal to the endoplasmic reticulum which are the sites where the Atg machinery assembles upon autophagy induction. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| preribosome, small subunit precursor | A preribosomal complex consisting of 20S pre-rRNA, ribosomal proteins including late-associating small subunit proteins, and associated proteins; a precursor of the eukaryotic cytoplasmic small ribosomal subunit. |
| spindle pole body | The microtubule organizing center in fungi; functionally homologous to the animal cell centrosome. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
16 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| autophagy of peroxisome | The process in which peroxisomes are delivered to a type of vacuole and degraded in response to changing nutrient conditions. |
| DNA repair | The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway. |
| endocytosis | A vesicle-mediated transport process in which cells take up external materials or membrane constituents by the invagination of a small region of the plasma membrane to form a new membrane-bounded vesicle. |
| meiotic chromosome segregation | The process in which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized into specific structures and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets during M phase of the meiotic cell cycle. |
| monopolar spindle attachment to meiosis I kinetochore | The process in which spindle microtubules become physically associated with the proteins making up the kinetochore complex during meiosis I. During meiosis I sister kinetochores are lying next to each other facing the same spindle pole and monopolar attachment of the chromatid to the spindle occurs. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| positive regulation of clathrin-dependent endocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. |
| regulation of autophagosome assembly | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of autophagosome assembly. |
| regulation of ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport, the directed movement of substances from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi, mediated by COP II vesicles. Small COP II coated vesicles form from the ER and then fuse directly with the cis-Golgi. Larger structures are transported along microtubules to the cis-Golgi. |
| regulation of protein localization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| regulation of protein localization by the Cvt pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization by the Cvt pathway. |
| regulation of vesicle fusion with Golgi apparatus | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of vesicle fusion with Golgi apparatus. |
| ribosomal large subunit biogenesis | A cellular process that results in the biosynthesis of constituent macromolecules, assembly, and arrangement of constituent parts of a large ribosomal subunit; includes transport to the sites of protein synthesis. |
| ribosomal small subunit biogenesis | A cellular process that results in the biosynthesis of constituent macromolecules, assembly, and arrangement of constituent parts of a small ribosomal subunit; includes transport to the sites of protein synthesis. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
| tRNA wobble uridine modification | The process in which a uridine in position 34 of a tRNA is post-transcriptionally modified. |
13 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P35508 | CSNK1D | Casein kinase I isoform delta | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q5ZLL1 | CSNK1E | Casein kinase I isoform epsilon | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q86Y07 | VRK2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase VRK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P48730 | CSNK1D | Casein kinase I isoform delta | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P49674 | CSNK1E | Casein kinase I isoform epsilon | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8BN21 | Vrk2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase VRK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9DC28 | Csnk1d | Casein kinase I isoform delta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9JMK2 | Csnk1e | Casein kinase I isoform epsilon | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q06486 | Csnk1d | Casein kinase I isoform delta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q6P647 | csnk1d | Casein kinase I isoform delta | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| Q7ZUS1 | vrk1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase VRK1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q6P3K7 | csnk1db | Casein kinase I isoform delta-B | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q7T2E3 | csnk1da | Casein kinase I isoform delta-A | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MDLRVGRKFR | IGRKIGSGSF | GDIYHGTNLI | SGEEVAIKLE | SIRSRHPQLD | YESRVYRYLS |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GGVGIPFIRW | FGREGEYNAM | VIDLLGPSLE | DLFNYCHRRF | SFKTVIMLAL | QMFCRIQYIH |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| GRSFIHRDIK | PDNFLMGVGR | RGSTVHVIDF | GLSKKYRDFN | THRHIPYREN | KSLTGTARYA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SVNTHLGIEQ | SRRDDLESLG | YVLIYFCKGS | LPWQGLKATT | KKQKYDRIME | KKLNVSVETL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| CSGLPLEFQE | YMAYCKNLKF | DEKPDYLFLA | RLFKDLSIKL | EYHNDHLFDW | TMLRYTKAMV |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| EKQRDLLIEK | GDLNANSNAA | SASNSTDNKS | ETFNKIKLLA | MKKFPTHFHY | YKNEDKHNPS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| PEEIKQQTIL | NNNAASSLPE | ELLNALDKGM | ENLRQQQPQQ | QVQSSQPQPQ | PQQLQQQPNG |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| QRPNYYPEPL | LQQQQRDSQE | QQQQVPMATT | RATQYPPQIN | SNNFNTNQAS | VPPQMRSNPQ |
| 490 | |||||
| QPPQDKPAGQ | SIWL |