P28867
Gene name |
Prkcd |
Protein name |
Protein kinase C delta type |
Names |
Tyrosine-protein kinase PRKCD, nPKC-delta |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:18753 |
EC number |
2.7.10.2: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
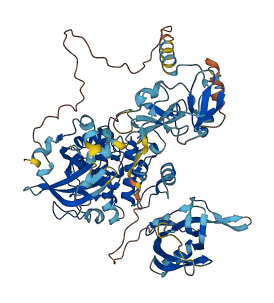
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

9 structures for P28867
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1PTQ | X-ray | 195 A | A | 231-280 | PDB |
| 1PTR | X-ray | 220 A | A | 231-280 | PDB |
| 3UEJ | X-ray | 130 A | A/B | 231-280 | PDB |
| 3UEY | X-ray | 130 A | A/B | 231-280 | PDB |
| 3UFF | X-ray | 130 A | A/B | 231-280 | PDB |
| 3UGD | X-ray | 145 A | A/B | 231-280 | PDB |
| 3UGI | X-ray | 136 A | A/B | 231-280 | PDB |
| 3UGL | X-ray | 136 A | A/B | 231-280 | PDB |
| AF-P28867-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
27 variants for P28867
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3413110924 | 4 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389306778 | 6 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3389306713 | 48 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389286126 | 61 | A>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3389322097 | 79 | D>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389298353 | 83 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389298305 | 131 | M>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389269919 | 182 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3389286129 | 360 | K>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3389269907 | 374 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs217321767 | 405 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389310584 | 461 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389312368 | 494 | K>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389309425 | 500 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389315051 | 502 | R>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389316146 | 521 | L>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3389309414 | 579 | K>T | No | EVA | |
| rs257116794 | 592 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389305275 | 620 | P>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389298290 | 622 | V>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389322083 | 627 | D>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389315057 | 639 | K>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389241147 | 642 | L>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3404913810 | 653 | M>K | No | EVA | |
| rs224386291 | 656 | E>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3389309454 | 661 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389312362 | 665 | N>K | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with P28867
5 regional properties for P28867
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | SCAN domain | 48 - 160 | IPR003309 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 251 - 278 | IPR013087-1 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 279 - 306 | IPR013087-2 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 307 - 334 | IPR013087-3 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 335 - 362 | IPR013087-4 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.2 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
12 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell-cell junction | A cell junction that forms a connection between two or more cells of an organism; excludes direct cytoplasmic intercellular bridges, such as ring canals in insects. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endolysosome | An transient hybrid organelle formed by fusion of a late endosome with a lysosome, and in which active degradation takes place. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nuclear matrix | The dense fibrillar network lying on the inner side of the nuclear membrane. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynaptic cytosol | The region of the cytosol consisting of all cytosol that is part of the postsynapse. |
14 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| calcium-dependent protein kinase C activity | Calcium-dependent catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. |
| calcium-independent protein kinase C activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. This reaction requires diacylglycerol but not calcium. |
| enzyme activator activity | Binds to and increases the activity of an enzyme. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| insulin receptor substrate binding | Binding to an insulin receptor substrate (IRS) protein, an adaptor protein that bind to the transphosphorylated insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors, are themselves phosphorylated and in turn recruit SH2 domain-containing signaling molecules to form a productive signaling complex. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + protein L-tyrosine = ADP + protein L-tyrosine phosphate by a non-membrane spanning protein. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein kinase C activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. This reaction requires diacylglycerol. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| TIR domain binding | Binding to a Toll-Interleukin receptor (TIR) domain of a protein. The TIR domain is an intracellular 200 residue domain that is found in the Toll protein, the interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R), and MyD88; it contains three highly-conserved regions, and mediates protein-protein interactions between the Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and signal-transduction components. |
48 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of protein kinase activity | Any process that initiates the activity of an inactive protein kinase. |
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| B cell proliferation | The expansion of a B cell population by cell division. Follows B cell activation. |
| cell chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). |
| cell cycle | The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division. |
| cellular response to angiotensin | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an angiotensin stimulus. Angiotensin is any of three physiologically active peptides (angiotensin II, III, or IV) processed from angiotensinogen. |
| cellular response to hydrogen peroxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulus. |
| cellular response to hydroperoxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydroperoxide stimulus. Hydroperoxides are monosubstitution products of hydrogen peroxide, HOOH. |
| cellular response to oxidative stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of oxidative stress, a state often resulting from exposure to high levels of reactive oxygen species, e.g. superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals. |
| cellular response to UV | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ultraviolet radiation (UV light) stimulus. Ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength in the range of 10 to 380 nanometers. |
| cellular senescence | A cell aging process stimulated in response to cellular stress, whereby normal cells lose the ability to divide through irreversible cell cycle arrest. |
| collagen metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals. Collagen is highly enriched in glycine (some regions are 33% glycine) and proline, occurring predominantly as 3-hydroxyproline (about 20%). |
| D-aspartate import across plasma membrane | The directed import of D-aspartate from the extracellular region across the plasma membrane and into the cytosol. |
| defense response to bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| immunoglobulin mediated immune response | An immune response mediated by immunoglobulins, whether cell-bound or in solution. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| negative regulation of actin filament polymerization | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of actin polymerization. |
| negative regulation of filopodium assembly | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly of a filopodium, a thin, stiff protrusion extended by the leading edge of a motile cell such as a crawling fibroblast or amoeba, or an axonal growth cone. |
| negative regulation of glial cell apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of glial cell apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of insulin receptor signaling. |
| negative regulation of MAP kinase activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity. |
| negative regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| negative regulation of platelet aggregation | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of platelet aggregation. Platelet aggregation is the adhesion of one platelet to one or more other platelets via adhesion molecules. |
| neutrophil activation | The change in morphology and behavior of a neutrophil resulting from exposure to a cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-threonine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-threonine. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of ceramide biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of ceramide biosynthetic process. |
| positive regulation of endodeoxyribonuclease activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of endodeoxyribonuclease activity, the hydrolysis of ester linkages within deoxyribonucleic acid by creating internal breaks. |
| positive regulation of glucose import | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the import of the hexose monosaccharide glucose into a cell or organelle. |
| positive regulation of glucosylceramide catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of glucosylceramide catabolic process. |
| positive regulation of MAP kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPK cascade. |
| positive regulation of phospholipid scramblase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of phospholipid scramblase activity. |
| positive regulation of protein dephosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of removal of phosphate groups from a protein. |
| positive regulation of protein import into nucleus | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of movement of proteins from the cytoplasm into the nucleus. |
| positive regulation of response to DNA damage stimulus | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of response to DNA damage stimulus. |
| positive regulation of sphingomyelin catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of sphingomyelin catabolic process. |
| positive regulation of superoxide anion generation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of enzymatic generation of superoxide by a cell. |
| post-translational protein modification | The process of covalently altering one or more amino acids in a protein after the protein has been completely translated and released from the ribosome. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of ceramide biosynthetic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a ceramide biosynthetic process. |
| regulation of phosphorylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into a molecule. |
| response to oxidative stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of oxidative stress, a state often resulting from exposure to high levels of reactive oxygen species, e.g. superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals. |
| termination of signal transduction | The signaling process in which signal transduction is brought to an end rather than being reversibly modulated. |
38 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P24583 | PKC1 | Protein kinase C-like 1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | SS |
| A1A4I4 | PKN1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| A1Z7T0 | Pkn | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P83099 | Pkcdelta | Putative protein kinase C delta type homolog | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q04759 | PRKCQ | Protein kinase C theta type | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6P5Z2 | PKN3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q96LW2 | RSKR | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase-related protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q02156 | PRKCE | Protein kinase C epsilon type | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P24723 | PRKCH | Protein kinase C eta type | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q16512 | PKN1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q16513 | PKN2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q05655 | PRKCD | Protein kinase C delta type | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9Z2A0 | Pdpk1 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q02956 | Prkcz | Protein kinase C zeta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62074 | Prkci | Protein kinase C iota type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70268 | Pkn1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8K045 | Pkn3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8BWW9 | Pkn2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P23298 | Prkch | Protein kinase C eta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P16054 | Prkce | Protein kinase C epsilon type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q02111 | Prkcq | Protein kinase C theta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P20444 | Prkca | Protein kinase C alpha type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P63318 | Prkcg | Protein kinase C gamma type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P68404 | Prkcb | Protein kinase C beta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60823 | Akt2 | RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P31750 | Akt1 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9WUA6 | Akt3 | RAC-gamma serine/threonine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9ERE3 | Sgk3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Sgk3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8QZV4 | Stk32c | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 32C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91VJ4 | Stk38 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 38 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q7TSE6 | Stk38l | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 38-like | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q63433 | Pkn1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q64617 | Prkch | Protein kinase C eta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P09216 | Prkce | Protein kinase C epsilon type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O08874 | Pkn2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09215 | Prkcd | Protein kinase C delta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P34722 | tpa-1 | Protein kinase C-like 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| A7MBL8 | pkn2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAPFLRISFN | SYELGSLQVE | DEASQPFCAV | KMKEALSTER | GKTLVQKKPT | MYPEWKTTFD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| AHIYEGRVIQ | IVLMRAAEDP | VSEVTVGVSV | LAERCKKNNG | KAEFWLDLQP | QAKVLMCVQY |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| FLEDGDCKQS | MRSEEEAKFP | TMNRRGAIKQ | AKIHYIKNHE | FIATFFGQPT | FCSVCKEFVW |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GLNKQGYKCR | QCNAAIHKKC | IDKIIGRCTG | TATNSRDTIF | QKERFNIDMP | HRFKVYNYMS |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| PTFCDHCGSL | LWGLVKQGLK | CEDCGMNVHH | KCREKVANLC | GINQKLLAEA | LNQVTQRSSR |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| KLDTTESVGI | YQGFEKKPEV | SGSDILDNNG | TYGKIWEGST | RCTLENFTFQ | KVLGKGSFGK |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VLLAELKGKD | KYFAIKCLKK | DVVLIDDDVE | CTMVEKRVLA | LAWESPFLTH | LICTFQTKDH |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LFFVMEFLNG | GDLMFHIQDK | GRFELYRATF | YAAEIICGLQ | FLHSKGIIYR | DLKLDNVMLD |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| RDGHIKIADF | GMCKENIFGE | GRASTFCGTP | DYIAPEILQG | LKYSFSVDWW | SFGVLLYEML |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| IGQSPFHGDD | EDELFESIRV | DTPHYPRWIT | KESKDIMEKL | FERDPDKRLG | VTGNIRIHPF |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| FKTINWSLLE | KRKVEPPFKP | KVKSPSDYSN | FDPEFLNEKP | QLSFSDKNLI | DSMDQEAFHG |
| 670 | |||||
| FSFVNPKFEQ | FLDI |