P28693
Gene name |
EPHB2 (CEK5) |
Protein name |
Ephrin type-B receptor 2 |
Names |
EPH-like kinase 5, EK5, cEK5 |
Species |
Gallus gallus (Chicken) |
KEGG Pathway |
gga:396513 |
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
(Annotation based on sequence homology with P29323)
Ephrin type-B receptor 2 is a membrane-associated protein that mediates axon guidance, cell migration and morphogenesis. The Eph receptor tyrosine kinase family is regulated by autophosphorylation within the juxtamembrane region and the kinase activation segment. The structure, supported by mutagenesis data, reveals that the juxtamembrane segment adopts a helical conformation that distorts the small lobe of the kinase domain, and blocks the activation segment from attaining an activated conformation. Phosphorylation of the conserved juxtamembrane tyrosines would relieve this autoinhibition by disturbing the association of the juxtamembrane segment with the kinase domain, while liberating phosphotyrosine sites for binding SH2 domains of target proteins.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
781-809 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
639-902 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
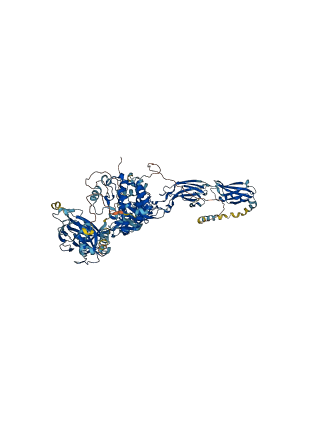
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for P28693
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1SGG | NMR | - | A | 924-998 | PDB |
| AF-P28693-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P28693
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P28693 | |||||
No associated diseases with P28693
14 regional properties for P28693
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 639 - 902 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Ephrin receptor ligand binding domain | 21 - 203 | IPR001090 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 640 - 898 | IPR001245 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class V, conserved site | 179 - 199 | IPR001426-1 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class V, conserved site | 242 - 262 | IPR001426-2 |
| domain | Sterile alpha motif domain | 928 - 995 | IPR001660 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 325 - 435 | IPR003961-1 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 436 - 531 | IPR003961-2 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 760 - 772 | IPR008266 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase ephrin type A/B receptor-like | 265 - 303 | IPR011641 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 645 - 671 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 639 - 898 | IPR020635 |
| domain | Ephrin receptor, transmembrane domain | 545 - 635 | IPR027936 |
| domain | Ephrin type-B receptor 2, ligand binding domain | 20 - 197 | IPR034238 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | Combining with a signal and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate. |
| transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity | Combining with a transmembrane ephrin to initiate a change in cell activity. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| angiogenesis | Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels. |
| axon guidance | The chemotaxis process that directs the migration of an axon growth cone to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| axonal fasciculation | The collection of axons into a bundle of rods, known as a fascicle. |
| central nervous system projection neuron axonogenesis | Generation of a long process of a CNS neuron, that carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells in a different central nervous system region. |
| dendritic spine development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendritic spine over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A dendritic spine is a protrusion from a dendrite and a specialized subcellular compartment involved in synaptic transmission. |
| dendritic spine morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of a dendritic spine are generated and organized. A dendritic spine is a protrusion from a dendrite and a specialized subcellular compartment involved in synaptic transmission. |
| ephrin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by ephrin binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| positive regulation of synapse assembly | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the frequency, rate or extent of synapse assembly, the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a synapse. |
| spinothalamic tract morphogenesis | Generation of a long process of a CNS neuron, that carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body in the spinal cord towards target cells in the thalamus. This axonal process is a member of those that make up the spinothalamic tract, one of the major routes of nociceptive signaling. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
52 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q07494 | EPHB1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| O42422 | EPHA7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P29318 | EPHA3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07496 | EPHA4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07497 | EPHB5 | Ephrin type-B receptor 5 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P54755 | EPHA5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07498 | EPHB3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P0C0K6 | EPHB6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | SS |
| P29322 | EPHA8 | Ephrin type-A receptor 8 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P21709 | EPHA1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54764 | EPHA4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54753 | EPHB3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29320 | EPHA3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P54760 | EPHB4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29317 | EPHA2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q15375 | EPHA7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q5JZY3 | EPHA10 | Ephrin type-A receptor 10 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9UF33 | EPHA6 | Ephrin type-A receptor 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54762 | EPHB1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54756 | EPHA5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O15197 | EPHB6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29323 | EPHB2 | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P54754 | Ephb3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03145 | Epha2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q03137 | Epha4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61772 | Epha7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O09127 | Epha8 | Ephrin type-A receptor 8 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8CBF3 | Ephb1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8BYG9 | Epha10 | Ephrin type-A receptor 10 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60629 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P29319 | Epha3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62413 | Epha6 | Ephrin type-A receptor 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60750 | Epha1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54761 | Ephb4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O08644 | Ephb6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P54763 | Ephb2 | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54757 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P54759 | Epha7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09759 | Ephb1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P0C0K7 | Ephb6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08680 | Epha3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O61460 | vab-1 | Ephrin receptor 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q0WNY5 | WAKL18 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 18 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q7X8C5 | WAKL2 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8VYA3 | WAKL10 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 10 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9C9L5 | WAKL9 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 9 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LMN7 | WAK5 | Wall-associated receptor kinase 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9M092 | WAKL17 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 17 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9S9M2 | WAKL4 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O13147 | ephb3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O73878 | ephb4b | Ephrin type-B receptor 4b | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O13146 | epha3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGPLWFCCLP | LALLPLLAAV | EETLMDSTTA | TAELGWMVHP | PSGWEEVSGY | DENMNTIRTY |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QVCNVFESSQ | NNWLRTKYIR | RRGAHRIHVE | MKFSVRDCSS | IPNVPGSCKE | TFNLYYYESD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| FDSATKTFPN | WMENPWMKVD | TIAADESFSQ | VDLGGRVMKI | NTEVRSFGPV | SKNGFYLAFQ |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| DYGGCMSLIA | VRVFYRKCPR | VIQNGAVFQE | TLSGAESTSL | VAARGTCISN | AEEVDVPIKL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| YCNGDGEWLV | PIGRCMCRPG | YESVENGTVC | RGCPSGTFKA | SQGDEGCVHC | PINSRTTSEG |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| ATNCVCRNGY | YRADADPVDM | PCTTIPSAPQ | AVISSVNETS | LMLEWTPPRD | SGGREDLVYN |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| IICKSCGSGR | GACTRCGDNV | QFAPRQLGLT | EPRIYISDLL | AHTQYTFEIQ | AVNGVTDQSP |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| FSPQFASVNI | TTNQAAPSAV | SIMHQVSRTV | DSITLSWSQP | DQPNGVILDY | ELQYYEKNLS |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| ELNSTAVKSP | TNTVTVQNLK | AGTIYVFQVR | ARTVAGYGRY | SGKMYFQTMT | EAEYQTSVQE |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| KLPLIIGSSA | AGLVFLIAVV | VIIIVCNRRR | GFERADSEYT | DKLQHYTSGH | STYRGPPPGL |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| GVRLFVMTPG | MKIYIDPFTY | EDPNEAVREF | AKEIDISCVK | IEQVIGAGEF | GEVCSGHLKL |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| PGKREIFVAI | KTLKSGYTEK | QRRDFLSEAS | IMGQFDHPNV | IHLEGVVTKS | SPVMIITEFM |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| ENGSLDSFLR | QNDGQFTVIQ | LVGMLRGIAA | GMKYLADMNY | VHRDLAARNI | LVNSNLVCKV |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| SDFGLSRFLE | DDTSDPTYTS | ALGGKIPIRW | TAPEAIQYRK | FTSASDVWSY | GIVMWEVMSY |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| GERPYWDMTN | QDVINAIEQD | YRLPPPMDCP | NALHQLMLDC | WQKDRNHRPK | FGQIVNTLDK |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| MIRNPNSLKA | MAPLSSGVNL | PLLDRTIPDY | TSFNTVDEWL | DAIKMSQYKE | SFASAGFTTF |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | ||
| DIVSQMTVED | ILRVGVTLAG | HQKKILNSIQ | VMRAQMNQIQ | SVEV |