P28028
Gene name |
Braf (B-raf) |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf |
Names |
EC 2.7.11.1 , Proto-oncogene B-Raf |
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:109880 |
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
TYROSINE-PROTEIN KINASE RECEPTOR (PTHR24416) |
Descriptions
NTRK1 is a high-affinity nerve growth factor receptor and its ligand is nerve growth factor (NGF), which is involved in the survival, differentiation, development, and maturation of the central and peripheral nervous systems, particularly the sensory and sympathetic neurons. Studies have shown that deletion of the second Ig-like domain of NTRK1 results in spontaneous activation, so the second Ig-like domain is an autoinhibitory domain required to prevent spontaneous activation by receptor dimerization.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
429-711 (Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, C-Raf, Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma, kinase) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
578-603 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
442-702 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
578-603 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
442-702 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Cutler RE Jr et al. (1998) "Autoregulation of the Raf-1 serine/threonine kinase", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95, 9214-9
- Tran NH et al. (2005) "B-Raf and Raf-1 are regulated by distinct autoregulatory mechanisms", The Journal of biological chemistry, 280, 16244-53
- Tran NH et al. (2003) "Phosphorylation of Raf-1 by p21-activated kinase 1 and Src regulates Raf-1 autoinhibition", The Journal of biological chemistry, 278, 11221-6
- Niault T et al. (2009) "From autoinhibition to inhibition in trans: the Raf-1 regulatory domain inhibits Rok-alpha kinase activity", The Journal of cell biology, 187, 335-42
- Zhang M et al. (2021) "B-Raf autoinhibition in the presence and absence of 14-3-3", Structure (London, England : 1993), 29, 768-777.e2
- Nussinov R et al. (2018) "Autoinhibition in Ras effectors Raf, PI3Kα, and RASSF5: a comprehensive review underscoring the challenges in pharmacological intervention", Biophysical reviews, 10, 1263-1282
- Hmitou I et al. (2007) "Differential regulation of B-raf isoforms by phosphorylation and autoinhibitory mechanisms", Molecular and cellular biology, 27, 31-43
- Hubbard SR (2004) "Oncogenic mutations in B-Raf: some losses yield gains", Cell, 116, 764-6
- Park E et al. (2019) "Architecture of autoinhibited and active BRAF-MEK1-14-3-3 complexes", Nature, 575, 545-550
- Cookis T et al. (2021) "Crystal Structure Reveals the Full Ras-Raf Interface and Advances Mechanistic Understanding of Raf Activation", Biomolecules, 11,
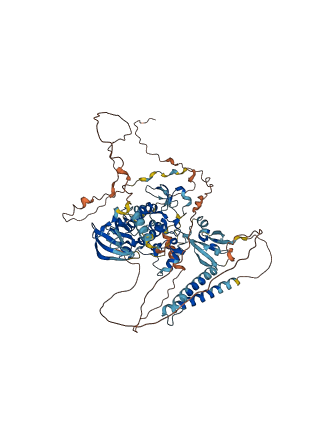
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for P28028
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-P28028-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for P28028
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for P28028 | |||||
2 associated diseases with P28028
[MIM: 256800]: Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (CIPA)
Characterized by a congenital insensitivity to pain, anhidrosis (absence of sweating), absence of reaction to noxious stimuli, self-mutilating behavior, and intellectual disability. This rare autosomal recessive disorder is also known as congenital sensory neuropathy with anhidrosis or hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type IV or familial dysautonomia type II. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10090906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10233776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10330344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10567924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10861667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10982191, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11159935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11310631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18077166, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22302274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27676246, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28177573, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28328124, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8696348}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Without disease ID
- Characterized by a congenital insensitivity to pain, anhidrosis (absence of sweating), absence of reaction to noxious stimuli, self-mutilating behavior, and intellectual disability. This rare autosomal recessive disorder is also known as congenital sensory neuropathy with anhidrosis or hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type IV or familial dysautonomia type II. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10090906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10233776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10330344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10567924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10861667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10982191, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11159935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11310631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18077166, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22302274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27676246, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28177573, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28328124, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8696348}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
6 regional properties for P28028
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 27 - 279 | IPR000719 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 146 - 158 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 33 - 56 | IPR017441 |
| domain | PRKAA1, UBA-like autoinhibitory domain | 296 - 360 | IPR028797 |
| domain | AMPK, C-terminal adenylate sensor domain | 406 - 480 | IPR032270 |
| domain | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase alpha 1 catalytic subunit, C-terminal | 404 - 557 | IPR039137 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR24416 | TYROSINE-PROTEIN KINASE RECEPTOR |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR24416:SF370 | HIGH AFFINITY NERVE GROWTH FACTOR RECEPTOR |
| PANTHER Protein Class | transmembrane signal receptor | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell body | The portion of a cell bearing surface projections such as axons, dendrites, cilia, or flagella that includes the nucleus, but excludes all cell projections. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| presynapse | The part of a synapse that is part of the presynaptic cell. |
12 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| calcium ion binding | Binding to a calcium ion (Ca2+). |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| MAP kinase kinase activity | Catalysis of the concomitant phosphorylation of threonine (T) and tyrosine (Y) residues in a Thr-Glu-Tyr (TEY) thiolester sequence in a MAP kinase (MAPK) substrate. |
| MAP kinase kinase kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation and activation of a MAP kinase kinase; each MAP kinase kinase can be phosphorylated by any of several MAP kinase kinase kinases. |
| mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding | Binding to a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, a protein that can phosphorylate a MAP kinase. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| scaffold protein binding | Binding to a scaffold protein. Scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signaling pathways. Although not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signaling pathway, tethering them into complexes. |
| small GTPase binding | Binding to a small monomeric GTPase. |
46 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| alpha-beta T cell differentiation | The process in which a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of an alpha-beta T cell. An alpha-beta T cell is a T cell that expresses an alpha-beta T cell receptor complex. |
| CD4-positive or CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment | The process in which an immature T cell commits to CD4-positive T cell lineage or the CD8-positive lineage of alpha-beta T cells. |
| CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized T cell acquires specialized features of a mature CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell. |
| cell differentiation | The cellular developmental process in which a relatively unspecialized cell, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cell, acquires specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize a specific cell. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cellular response to calcium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a calcium ion stimulus. |
| cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus | A process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a nerve growth factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organism exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| endothelial cell apoptotic process | Any apoptotic process in an endothelial cell. An endothelial cell comprises the outermost layer or lining of anatomical structures and can be squamous or cuboidal. |
| epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a ligand to the tyrosine kinase receptor EGFR (ERBB1) on the surface of a cell. The pathway ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least ERK1 or ERK2 (MAPKs), a MEK (a MAPKK) and a MAP3K. The cascade may involve 4 different kinases, as it can also contain an additional tier |
| establishment of protein localization to membrane | The directed movement of a protein to a specific location in a membrane. |
| face development | The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a face from an initial condition to its mature state. The face is the ventral division of the head. |
| head morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the head are generated and organized. The head is the anterior-most division of the body. |
| long-term synaptic potentiation | A process that modulates synaptic plasticity such that synapses are changed resulting in the increase in the rate, or frequency of synaptic transmission at the synapse. |
| MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tiers |
| myeloid progenitor cell differentiation | The process in which a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a myeloid progenitor cell. Myeloid progenitor cells include progenitor cells for any of the myeloid lineages. |
| negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of endothelial cell apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of fibroblast migration | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of fibroblast cell migration. Fibroblast cell migration is accomplished by extension and retraction of a pseudopodium. |
| negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process in neurons. |
| negative regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. |
| positive regulation of axon regeneration | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of axon regeneration. |
| positive regulation of axonogenesis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of glucose transmembrane transport | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of glucose transport across a membrane. Glucose transport is the directed movement of the hexose monosaccharide glucose into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine. |
| positive regulation of stress fiber assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly of a stress fiber, a bundle of microfilaments and other proteins found in fibroblasts. |
| positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading. |
| positive T cell selection | The process of sparing immature T cells which react with self-MHC protein complexes with low affinity levels from apoptotic death. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| Ras protein signal transduction | The series of molecular signals within the cell that are mediated by a member of the Ras superfamily of proteins switching to a GTP-bound active state. |
| regulation of axon regeneration | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of axon regeneration. |
| regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| regulation of T cell differentiation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of T cell differentiation. |
| response to cAMP | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate) stimulus. |
| response to peptide hormone | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a peptide hormone stimulus. A peptide hormone is any of a class of peptides that are secreted into the blood stream and have endocrine functions in living animals. |
| somatic stem cell population maintenance | Any process by which an organism retains a population of somatic stem cells, undifferentiated cells in the embryo or adult which can undergo unlimited division and give rise to cell types of the body other than those of the germ-line. |
| stress fiber assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a stress fiber. A stress fiber is a contractile actin filament bundle that consists of short actin filaments with alternating polarity. |
| substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading | The morphogenetic process that results in flattening of a cell as a consequence of its adhesion to a substrate. |
| synaptic vesicle exocytosis | Fusion of intracellular membrane-bounded vesicles with the pre-synaptic membrane of the neuronal cell resulting in release of neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. |
| T cell differentiation in thymus | The process in which a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a T cell via a differentiation pathway dependent upon transit through the thymus. |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a T cell. |
| thymus development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the thymus over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The thymus is a symmetric bi-lobed organ involved primarily in the differentiation of immature to mature T cells, with unique vascular, nervous, epithelial, and lymphoid cell components. |
| thyroid gland development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the thyroid gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The thyroid gland is an endoderm-derived gland that produces thyroid hormone. |
| trehalose metabolism in response to stress | The chemical reactions and pathways involving trehalose that occur as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. |
| visual learning | Any process in an organism in which a change in behavior of an individual occurs in response to repeated exposure to a visual cue. |
27 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A7E3S4 | RAF1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P05625 | RAF1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q04982 | BRAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P11346 | Raf | Raf homolog serine/threonine-protein kinase Raf | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P04049 | RAF1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P10398 | ARAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P15056 | BRAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P58801 | Ripk2 | Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q66L42 | Map3k10 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 10 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3U1V8 | Map3k9 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 9 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8VDG6 | Map3k21 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 21 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q80XI6 | Map3k11 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 11 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O55222 | Ilk | Integrin-linked protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9ESL4 | Map3k20 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 20 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q99N57 | Raf1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P04627 | Araf | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9D2Y4 | Mlkl | Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O19004 | ARAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| P11345 | Raf1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P14056 | Araf | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q07292 | lin-45 | Raf homolog serine/threonine-protein kinase | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| F4JTP5 | STY46 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY46 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O22558 | STY8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q05609 | CTR1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase CTR1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q2MHE4 | HT1 | Serine/threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase HT1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWL6 | STY17 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY17 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FPR3 | EDR1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase EDR1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MLRGGRRGQL | GWHSWAAGPG | SLLAWLILAS | AGAAPCPDAC | CPHGSSGLRC | TRDGALDSLH |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| HLPGAENLTE | LYIENQQHLQ | HLELRDLRGL | GELRNLTIVK | SGLRFVAPDA | FHFTPRLSRL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| NLSFNALESL | SWKTVQGLSL | QELVLSGNPL | HCSCALRWLQ | RWEEEGLGGV | PEQKLQCHGQ |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GPLAHMPNAS | CGVPTLKVQV | PNASVDVGDD | VLLRCQVEGR | GLEQAGWILT | ELEQSATVMK |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SGGLPSLGLT | LANVTSDLNR | KNVTCWAEND | VGRAEVSVQV | NVSFPASVQL | HTAVEMHHWC |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| IPFSVDGQPA | PSLRWLFNGS | VLNETSFIFT | EFLEPAANET | VRHGCLRLNQ | PTHVNNGNYT |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| LLAANPFGQA | SASIMAAFMD | NPFEFNPEDP | IPVSFSPVDT | NSTSGDPVEK | KDETPFGVSV |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| AVGLAVFACL | FLSTLLLVLN | KCGRRNKFGI | NRPAVLAPED | GLAMSLHFMT | LGGSSLSPTE |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| GKGSGLQGHI | IENPQYFSDA | CVHHIKRRDI | VLKWELGEGA | FGKVFLAECH | NLLPEQDKML |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| VAVKALKEAS | ESARQDFQRE | AELLTMLQHQ | HIVRFFGVCT | EGRPLLMVFE | YMRHGDLNRF |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| LRSHGPDAKL | LAGGEDVAPG | PLGLGQLLAV | ASQVAAGMVY | LAGLHFVHRD | LATRNCLVGQ |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| GLVVKIGDFG | MSRDIYSTDY | YRVGGRTMLP | IRWMPPESIL | YRKFTTESDV | WSFGVVLWEI |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| FTYGKQPWYQ | LSNTEAIDCI | TQGRELERPR | ACPPEVYAIM | RGCWQREPQQ | RHSIKDVHAR |
| 790 | |||||
| LQALAQAPPV | YLDVLG |